The China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) announced at the 74th International Aeronautical Congress in Baku, Azerbaijan on October 4th that the operational lifespan of the Chinese space station will exceed 15 years.
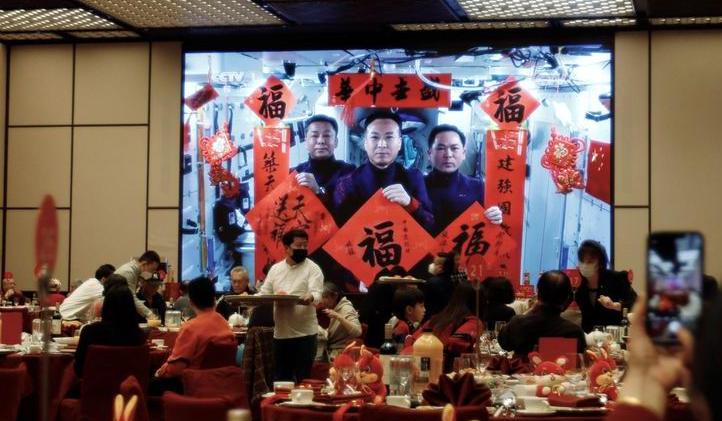

Image of Chinese astronauts during the holiday. Photo: Reuters
China's domestically built space station, known as Tiangong, has been fully operational since late 2022, accommodating up to three astronauts at an orbital altitude of up to 450 km.
Weighing in at 180 tons after expanding into six modules, Tiangong is still only 40% the mass of the ISS, which can accommodate seven astronauts. But the ISS, which has been operating in orbit for more than two decades and is expected to be decommissioned after 2030, is the same time China has declared its aspiration to become "a space power."
Chinese state media said "some countries" have requested to send their astronauts to the Tiangong station.
The Celestial Palace has become a symbol of China's growing power and confidence in its space endeavors, and a new challenge to the United States in this field.
Russia, a member of the ISS, also has similar space diplomacy plans. Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, said last year it was planning to build its own space station comprising six modules capable of housing up to four astronauts.
Trung Kien (according to Reuters)
Source




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)



















































Comment (0)