Reduce spending on antibiotics
Antibiotic costs at Cho Ray Hospital have continuously decreased over the past 10 years, from VND 213 billion in 2013 to VND 15.7 billion in 2024. The ratio of antibiotic costs to total treatment costs will decrease to 13% in 2024.
The above information was announced by a representative of Cho Ray Hospital at a workshop to evaluate the implementation of the National Strategy on Antimicrobial Resistance Prevention and Control for the 2023-2025 period, organized by the Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization (WHO) on the afternoon of November 24.

At Cho Ray Hospital, the rate of antibiotic use has decreased and treatment quality is guaranteed.
PHOTO: LIEN CHAU
At the workshop, providing information on solutions for the rational use of antibiotics, a representative of Cho Ray Hospital said that treatment departments have signed a commitment to prevent and combat antibiotic resistance; the hospital has software to look up antibiotic use instructions; maintain control and determine the amount of antibiotics used in the entire hospital; determine the ratio of antibiotic costs used to the total number of drugs, and analyze non-compliant medical records.
Cases of non-compliance (dosage, time, route of administration) with antibiotics are analyzed in detail to provide interventions and adjustments. During the years 2015 - 2024, 22,720 medical records at Cho Ray Hospital were surveyed.
At the same time, the hospital deployed a team of clinical pharmacists to support doctors in the ward, advise on antibiotic use; monitor before prescribing in clinical departments; analyze and warn departments with a sudden increase in the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
With comprehensive solutions, by 2024, the compliance rate for using antibiotics for treatment according to hospital guidelines will reach 97.3% (compared to 63% in 2015); the compliance rate for using prophylactic antibiotics according to hospital guidelines will reach 98.2%, compared to 14% in 2015.
Quality of treatment is guaranteed, with good treatment results (freedom from infection and reduction of infection) in 2024 being 88.5%.
Antibiotic resistance is increasingly complex
Highlighting the need for bold action to tackle antimicrobial resistance, World Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Awareness Week from 18-24 November this year has the theme Act Now: Protect the present, secure the future.
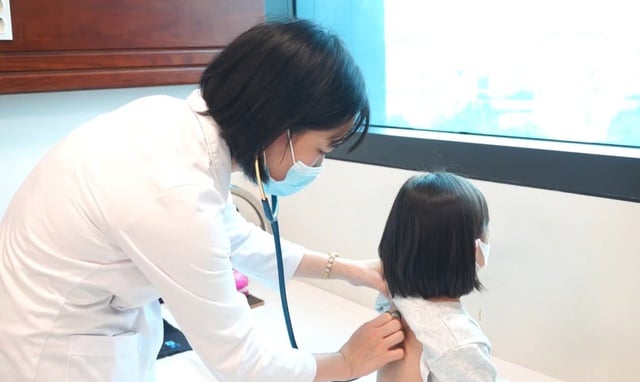
Correct diagnosis of the causative agent helps prescribe safe and appropriate antibiotics.
PHOTO: PHAM THAO
WHO warns that adding antibiotics to animal feed, antibiotics leaking into the environment, into water, into food, using antibiotics without a doctor's prescription..., we are helping bacteria develop defense mechanisms (drug resistance). Therefore, only use antibiotics when necessary and properly, according to a doctor's prescription.
According to data from the National Children's Hospital, respiratory diseases accounted for the highest rate of hospitalizations from 2020 to 2024 and are on the rise. The main bacteria causing pneumonia in children in the North are Haemophilus Influenzae, pneumococcus and Moraxella catarrhalis. Most of these strains have a high resistance rate to commonly prescribed antibiotics.
Therefore, in addition to compliance with antibiotic management and use, it is necessary to promote accurate diagnosis of the cause of the disease, help prescribe the right and sufficient antibiotics, and reduce antibiotic prescriptions in cases of viral infections.
According to the Vietnam Otorhinolaryngology Association, data shows that pneumococcal strains causing respiratory diseases are significantly reducing their sensitivity to second-generation cephalosporin and macrolide antibiotics. This is a warning sign of increasingly complex drug resistance, requiring close coordination between microbiological testing and appropriate antibiotic selection in treatment.
Dr. Ha Anh Duc, Director of the Department of Medical Examination and Treatment Management (Ministry of Health ), said that the antibiotic-resistant bacteria surveillance system currently has the participation of 59 hospitals in provinces and cities and will be expanded to assess drug-resistant bacteria, thereby making intervention measures more effective.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/khang-khang-sinh-ngay-cang-phuc-tap-185251124193037555.htm



![[Photo] VinUni students' emotions are sublimated with "Homeland in the Heart: The Concert Film"](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F26%2F1764174931822_10-3878-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Photo] Close-up of heavy damage at the school located on the banks of the Ban Thach River](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F26%2F1764152130492_ndo_bl_img-8188-8805-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



































































![[Photo] Opening of the 28th Session of the Hanoi People's Council](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/26/1764155991133_image.jpeg)






























Comment (0)