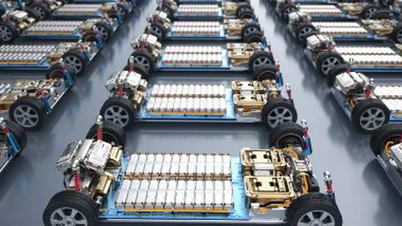
Nissan said its prototype all-solid-state battery cell (ASSB) has achieved the performance targets required for commercialization, including twice the energy density per volume and the ability to accept higher charging power, reducing charging time by a third compared to current lithium-ion batteries. The company aims to mass produce it in fiscal 2028.
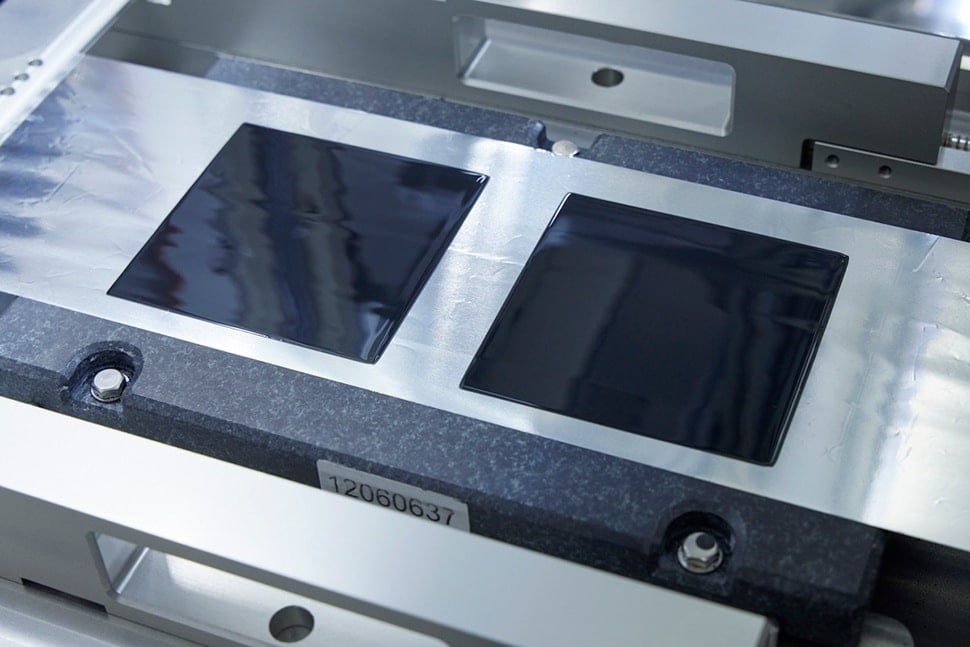

Nissan's ASSB: A performance step forward and what it means for EVs
Compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, Nissan’s ASSB has twice the energy density in the same volume. This allows electric vehicles to travel further without increasing the size of the battery pack. Thanks to the higher charging power, charging times are estimated to be reduced by one-third, promising to improve the user experience and reduce waiting times at charging stations.
Nissan is launching the ASSB prototype from 2022 and maintaining the commercialization roadmap in fiscal 2028. The cells achieving the performance target is an important milestone to move to large-scale production.
Why are solid-state batteries advantageous?
ASSB uses a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid solution, eliminating many unwanted side reactions and maintaining stability at high temperatures. This architecture expands the material selection space for the cathode/anode, making it easier for engineers to optimize overall performance, including energy density, safety, and durability.
Dry electrodes and the role of LiCAP Technologies
To achieve the efficiency improvement, Nissan is collaborating with LiCAP Technologies (USA) on electrode technology. The focus is on the “dry electrode” process, which eliminates the drying step in production – an energy-consuming and costly step. This approach has the potential to reduce costs and emissions, but requires precise process control.
LiCAP provides a fibrous binder to the cathode, allowing ions to move more efficiently without covering the active material surface. This results in a high-quality electrode – a key factor in achieving superior performance in solid-state batteries.
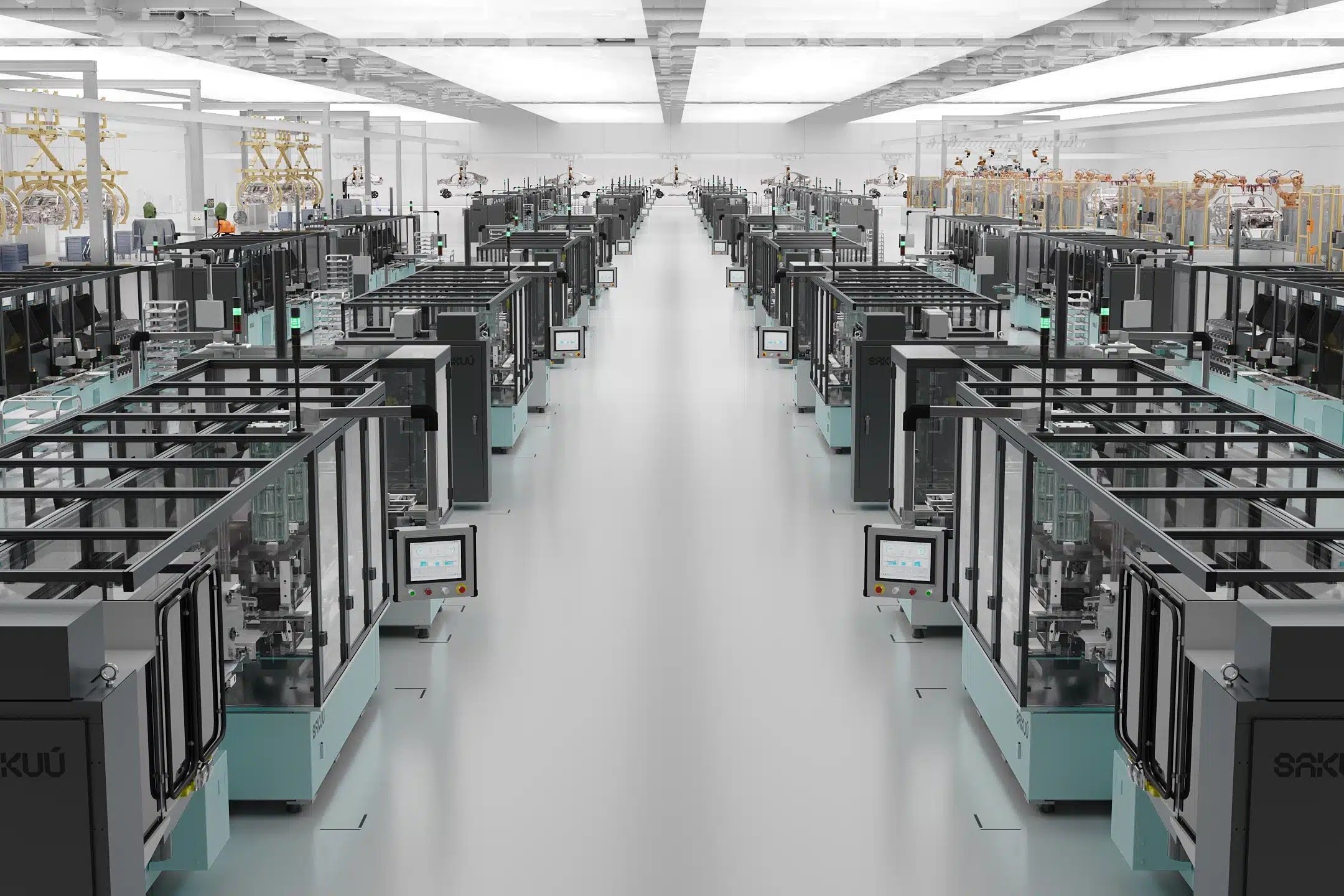

From cell to finished battery: the roadmap to mass production
LiCAP has no experience operating a large-scale production line, while Nissan said it has been operating a pilot line since January this year to perfect mass production technology. The next goal is to move from single-cell production to full battery manufacturing, ensuring repeatability in quality and performance to meet the requirements of the automotive industry.
In addition to shortening charging times and increasing operating range, Nissan aims to cut costs to $75/kWh – about 30% lower than the global average by 2024. If achieved, ASSB could make long-range EVs with short charging times more competitively priced.
Supply chain dynamics and technological competition
Japanese automakers are increasing investments to reduce their dependence on battery supplies from China, which holds about 70% of the global market share. According to the announced roadmap: Toyota cooperates with Idemitsu Kosan and plans to mass produce solid-state batteries as early as fiscal 2027; Honda invests 43 billion Yen (281 million USD) to build one of the largest ASSB lines, aiming for commercialization by the end of the decade.
Outside Japan, the race is fierce: in the US, QuantumScape (in partnership with Volkswagen) plans to start mass production in 2026 with an annual capacity of 5 GWh; in China, SAIC Motor plans to start solid-state batteries as early as next year.

Potential impact on EV products
The high energy density of ASSB allows manufacturers to reduce the size, or keep the same size to significantly increase the travel range. The high-power charging capability optimizes the charging time, opening up the opportunity to design simpler fast charging systems in vehicles. With a target cost of 75 USD/kWh, ASSB can also improve the price structure of mainstream EV models.
However, to realize the technology on an industrial scale, it needs to overcome several manufacturing challenges: uniformity of the dry electrode in large format, the solid electrode–electrolyte interface, and cycling durability. The pilot line that Nissan has been operating since January is a necessary preparation to solve the scale problem.
Summary table of key goals and progress
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Cell status | Achieve performance targets required for commercialization |
| Energy density | Twice the capacity in the same volume (compared to lithium-ion batteries) |
| Charging time | About a third of lithium-ion batteries |
| Production process | Dry electrode; technology collaboration with LiCAP Technologies |
| Cost target | 75 USD/kWh |
| Production roadmap | Fiscal year 2028; pilot line operation from January |
Conclusion: A stepping stone to the next generation of fast-charging, long-range EVs
With the validation of the ASSB cells meeting their performance targets, Nissan is one step closer to commercialization in fiscal 2028. The combination of a solid electrolyte and dry electrode process – along with the contribution of materials from LiCAP – enables the company to simultaneously achieve three important goals: long range, fast charging and competitive cost. With global competition intensifying, the ability to transition from prototype cells to mass-produced batteries will be key to how quickly ASSB-equipped EVs can hit the market.
Source: https://baonghean.vn/nissan-assb-2028-pin-the-ran-tang-gap-doi-tam-sac-nhanh-10309656.html





![[Photo] Fall Fair 2025 - An attractive experience](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/30/1761791564603_1761738410688-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Standing member of the Secretariat Tran Cam Tu visits and encourages people in the flooded areas of Da Nang](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/30/1761808671991_bt4-jpg.webp)































![[Photo] New-era Party members in the "Green Industrial Park"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/30/1761789456888_1-dsc-5556-jpg.webp)












































































Comment (0)