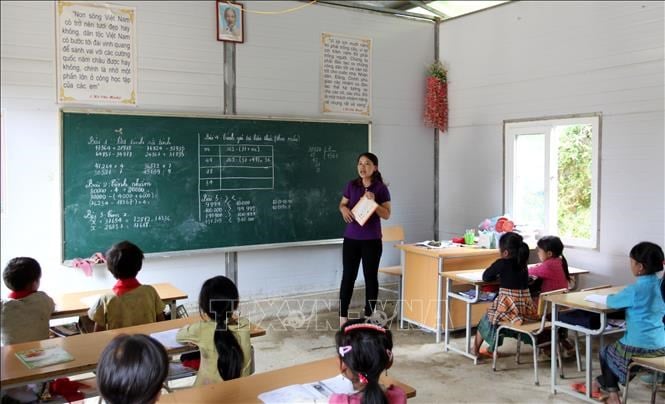
 |
| A class of 4th graders at Hong Ngai branch (Y Ty Primary School), Hong Ngai commune (Bat Xat). Photo: Quoc Khanh/VNA |
This is the first specialized law that fully regulates the legal status, rights, obligations and policies for teachers and is an important milestone affirming the major policy of the Party and State in honoring, caring for, protecting and developing teachers, the key force in theeducation cause.
Previously, on June 14, the National Assembly Standing Committee reported on the acceptance, explanation and revision of the draft law to submit to the National Assembly for approval. The report on the acceptance, explanation and revision of the draft Law on Teachers of the National Assembly Standing Committee said that the majority of opinions expressed highly appreciated the efforts and seriousness of the drafting agency and the reviewing agency in researching, explaining and absorbing most of the comments and basically agreed on the revised content of the draft. After acceptance and revision, the draft law consists of 9 chapters and 42 articles, 4 articles less than the draft submitted to the National Assembly at the discussion session on the morning of May 6.
The Law consists of 9 chapters and 42 articles, effective from January 1, 2026 with the following highlights:
Affirming position, protecting honor and reputation of teaching profession
The Law on Teachers establishes a full legal status for teachers in both public and non-public educational institutions.
For the first time, non-public teachers are recognized as a specialized practitioner with professional standards, similar rights and obligations, not just contract workers as before. The law clearly stipulates the right to respect, protection of honor and dignity, and a strict mechanism for handling acts of insulting teachers, including prohibiting individuals and organizations from spreading information accusing teachers without an official conclusion from the competent authority. This is an important highlight to protect teachers from unreasonable social pressure and maintain a safe and civilized pedagogical environment.
Teachers' salaries are ranked highest in the administrative career salary scale system.
The Law on Teachers stipulates that “Teachers’ salaries are ranked highest in the administrative career salary scale system” and assigns the Government to specify salary policies for teachers in detail. This is an important basis for the Government to have regulations related to teachers’ salaries to ensure the policy of “ranking highest”.
In the Draft Decree regulating salary policies, allowances, support and attraction regimes for teachers in the draft Law on Teachers, the Ministry of Education and Training plans to advise the Government to rearrange the salary tables of a number of teacher positions (such as preschool teachers, general education teachers, university preparatory teachers, vocational education teachers of grade IV, etc.) to ensure consistency in the salary tables applied to professional positions of teachers and civil servants and other sectors and fields; at the same time, ensuring the living standards of teachers, helping teachers feel secure in their work and contribute to the cause of education.
In addition, according to the provisions of the Law, teachers are also entitled to additional special allowances, responsibilities, incentives, subsidies for disadvantaged areas, subsidies for inclusive education, seniority, mobility, etc., contributing to increasing comprehensive income.
Policy to protect, support and attract high quality human resources
The Law on Teachers expands and consolidates the support policy system, emphasizing: Support for public housing or rent for teachers in extremely difficult areas; periodic health benefits, training, and professional development for all teachers, regardless of public or non-public; priority in recruitment, transfer, and reception for teachers working in remote, border, and island areas; attracting highly qualified people with good vocational skills to participate in teaching, especially in strategic areas such as science, technology, digital transformation, and vocational education.
Preschool teachers who wish to retire early can retire up to 5 years without a reduction in pension (if they have paid social insurance for 15 years). Meanwhile, professors, associate professors, doctors or teachers working in specialized fields can retire at an older age to retain talent.
Standardize and develop staff, improve education quality
The law merges two systems of standards (professional titles and professional standards) into one system of titles linked to professional competency standards, applied uniformly to both public and non-public sectors. This aims to create a common quality level for the entire workforce; ensure fairness in access to quality education for students; and increase transparency and accessibility in the assessment, selection and training of teachers.
The law also stipulates that teacher recruitment must be linked to pedagogical practice, ensuring quality input, appropriate to each grade and training level.
Professional ethics and mechanisms to protect teachers' reputation
For the first time, teachers' ethics were codified with specific rules of conduct in relations with students, colleagues, students' families and society.
The Law defines the responsibility to set an example as an inseparable part of the professional activities of teachers, demonstrated through exemplary conduct, integrity, and dedication in teaching and social behavior. Notably, the Law stipulates a mechanism to protect teachers from acts of infringement on honor, dignity, and reputation, especially prohibiting the dissemination of false information on social networks without an official conclusion. These acts will be handled according to the provisions of the law. In addition to the right to protection, teachers also have the responsibility to maintain professional ethics.
Strict handling of violations contributes to enhancing the status of teachers, while maintaining pedagogical standards in the educational environment.
Delegate initiative to the education sector
The Law on Teachers gives the education sector the initiative in recruiting and using teachers. In particular, it unifies the authority to give the education sector the initiative in recruiting teachers, and decentralizes the recruitment authority to the heads of public universities and vocational training institutions to be autonomous in recruiting teachers.
The Law grants the Minister of Education and Training authority to regulate the authority to recruit teachers in preschool, general education, and continuing education institutions. Granting authority to the education sector in recruiting and using teachers is an important adjustment step to remove "bottlenecks" in policies for teachers, especially solving the problem of surplus and shortage of staff; proactively coordinating and planning short-term, medium-term, and long-term staff development plans in the future.
The Law also stipulates that the Ministry of Education and Training is the agency in charge of coordinating with ministries, ministerial-level agencies, and provincial People's Committees to develop strategies, projects, and development plans, and the total number of teachers under its management authority to submit to competent authorities for decision; Coordinate with ministries, ministerial-level agencies, and provincial People's Committees to propose to competent authorities to approve the number of teachers in public educational institutions.
Immediately after being approved by the National Assembly, the Ministry of Education and Training urgently developed 2 Decrees and nearly 20 Circulars guiding the implementation to be issued simultaneously with the Law taking effect on January 1, 2026. This system of documents will specify the policies of the law, ensuring consistency, feasibility and effectiveness when put into practice.
News and People Newspaper
Source: https://baodanang.vn/xa-hoi/202506/quoc-hoi-thong-qua-luat-nha-giao-va-nhung-diem-noi-bat-4009683/

































































































Comment (0)