These differences can help individuals make informed decisions about which activities best suit their needs and interests.
1. Walking
1.1 Walking is suitable for people of all ages
Walking, a low-impact activity, is accessible to people of all ages and fitness levels. It is a gentle cardiovascular exercise that can be maintained for longer periods of time than jogging.
Walking is ideal for people recovering from injuries or those with joint problems, as it helps reduce stress on joints. Regular walking can help lower blood pressure, reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and improve circulation… all of which contribute to a healthier heart.
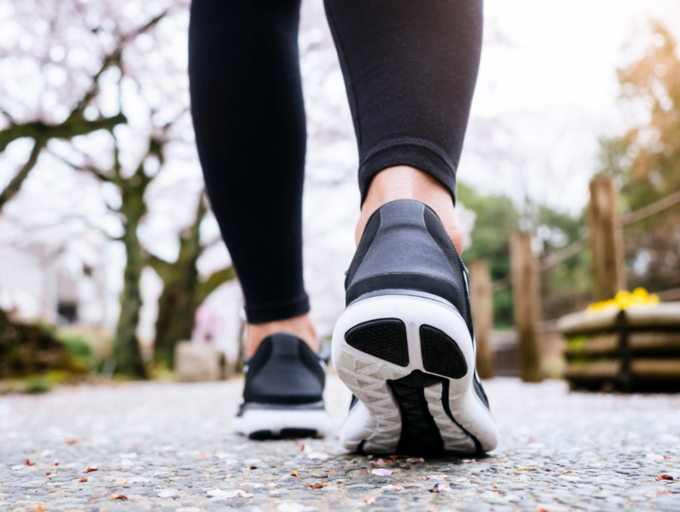

Walking regularly helps keep your heart healthy.
1.2. Walking helps lose weight, controlling the main risk factor causing heart disease
One of the main benefits of walking for cardiovascular health is its ability to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease. By engaging in regular walking sessions, you can help strengthen your heart muscle, improve blood flow and improve the efficiency of your cardiovascular system.
In addition, walking also promotes weight management and helps control risk factors such as obesity and diabetes, which are closely linked to heart disease.
1.3 Walking improves mental health
Walking has been shown to have positive effects on mental health, reducing stress and anxiety levels.
Stress can negatively impact heart health by raising blood pressure and increasing the risk of heart disease, so incorporating regular walking into a person's routine can contribute to improved overall heart health.
2. Jogging
2.1 Running is a high intensity activity compared to walking
Running is a higher intensity exercise that raises the heart rate faster and burns more calories per minute than walking. It is a more vigorous cardiovascular exercise and can help individuals achieve their fitness goals more effectively.
Running stimulates greater improvements in aerobic capacity, enhancing the heart's ability to pump blood and deliver oxygen to the muscles.
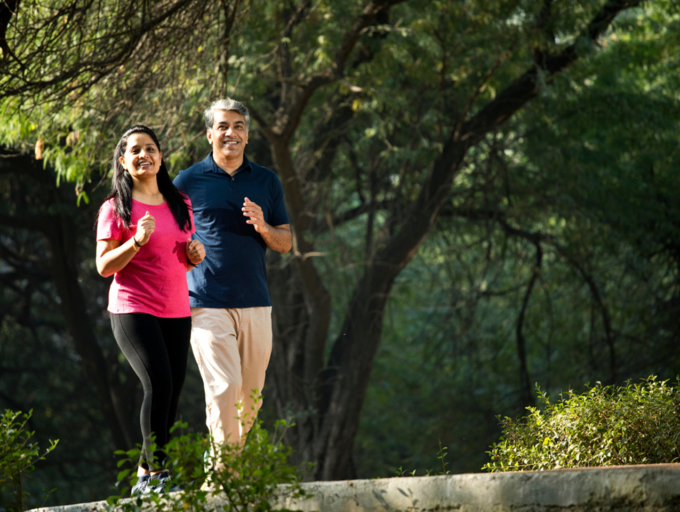

Running burns more calories than walking, reducing the risk of heart disease associated with obesity.
2.2 High-intensity running reduces the risk of heart disease
Regular running is linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke, lowers blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels and increases the heart's pumping efficiency.
The intensity of running also promotes the release of endorphins, which can elevate mood and reduce stress levels, further benefiting heart health.
2.3 Running burns more calories than walking
Running has been shown to have a significant impact on weight management, making it an effective strategy for reducing the risk of obesity-related heart disease. Running burns more calories than walking and can help people achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reduce stress on the heart and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
2.4 People with pre-existing joint problems should limit jogging.
While running offers many cardiovascular health benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with joint problems or pre-existing medical conditions.
The higher impact nature of running can place stress on the joints and musculoskeletal system, increasing the risk of injury. Therefore, individuals should gradually increase running intensity and incorporate appropriate warm-up and cool-down routines to minimize the risk of injury.
Source




























![[Photo] Panorama of the Opening Ceremony of the National Press Festival 2025](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/20/6b835ee92c2c4df587af73cb2d1f4f5f)
























![[Maritime News] Wan Hai Lines invests $150 million to buy 48,000 containers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/20/c945a62aff624b4bb5c25e67e9bcc1cb)














































Comment (0)