Traditional medicine is the crystallization of thousands of years of wisdom and experience of the nation, making an important contribution to the work of caring for, protecting and improving people's health.
1. Some legal documents related to traditional medicine registration and circulation
According to information from the Department of Traditional Medicine Management, Ministry of Health, some legal documents related to the registration of traditional medicine circulation are as follows:
1.1 The Law on Pharmacy amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Pharmacy No. 105/2016/QH13 was passed by the National Assembly on November 21, 2024, which stipulates many policies related to the registration of drugs and pharmaceutical ingredients:
- Priority policy in registration of circulation of traditional medicine:
+ For drugs purchased from the state budget and other legal sources of revenue of public health facilities, the provisions of the law on bidding and incentives in drug purchases for medicinal herbs and traditional medicines produced from domestic medicinal herbs that meet Good Practices for cultivation and collection of medicinal herbs shall apply.
+ Herbal medicines and traditional medicines produced on the basis of accepted national, ministerial or provincial science and technology tasks ; medicines on the List of national products approved by the Prime Minister.
+ Priority is given to the order, procedures, and time for granting registration certificates for circulation of drugs and pharmaceutical ingredients for drugs produced from medicinal materials that meet Good Practices for Cultivation and Harvesting of Medicinal Materials; drugs and pharmaceutical ingredients produced on the basis of accepted national science and technology tasks; drugs serving national defense and security requirements, overcoming consequences of incidents, natural disasters, catastrophes, and disease prevention and control.
+ Apply incentive and support mechanisms from the National Technology Innovation Fund, the National Science and Technology Development Fund, the National High-Tech Venture Investment Fund and other funds to support scientific and technological activities in research, development, clinical trials, technology transfer, production and commercialization of traditional medicines in modern dosage forms, and herbal medicines produced on the basis of national and ministerial-level scientific and technological tasks.

Priority is given to the order, procedures, and time for granting registration certificates for drugs and pharmaceutical ingredients for drugs produced from medicinal materials that meet Good Practices for Cultivation and Harvesting of Medicinal Materials.
+ Combine state budget investment with mobilizing other resources for the development of the pharmaceutical and traditional medicine production industry, and medicines produced from domestic medicinal materials; cultivation and production of medicinal materials; discovery, conservation and application of science and technology in research and development of precious, rare and endemic medicinal gene sources.
+ Support and facilitate the discovery, clinical trials, registration for circulation, protection of intellectual property rights related to and inheritance of traditional medicines and herbal medicines produced on the basis of accepted national, ministerial or provincial science and technology tasks; search for, exploit and use new medicinal herbs; export cultivated medicinal herbs; transplant medicinal herbs; exploit natural medicinal herbs reasonably; research, survey and investigate medicinal species suitable for cultivation locally; develop medicinal herb cultivation areas; modernize production and have trade promotion policies to export medicinal herbs and traditional medicines.
+ Have a policy to protect confidentiality in the preparation, processing and clinical trial data of traditional medicines; provide reasonable treatment for those who donate valuable traditional medicines to the State; create conditions for granting practice certificates to those who own traditional medicines recognized by the Ministry of Health.
+ Have policies to improve the quality of pharmaceutical human resources , support training activities for high-quality human resources in research, development, technology transfer, production, testing of medicinal herbs and traditional medicines.

There should be a policy to protect confidentiality in the preparation, processing and clinical trial data of traditional medicines.
- 'Semi-automatic' renewal policy:
"Semi-automatic" renewal policy for traditional medicines, after submitting the application in accordance with regulations, the facility can continue to use it until it is renewed or when the receiving agency issues a written notice of non-renewal or notice of temporary suspension of the use of the circulation registration certificate due to the discovery of traditional medicines, traditional medicinal ingredients, and medicinal herbs that pose a risk of being unsafe for users or are suspected of forging legal documents.
- Simplify the renewal profile components:
Reduce the dossier components from 06 components to 03 components for foreign drugs and 02 components for domestic drugs.
1.2 The Ministry of Health also issued Circular No. 29/2025/TT-BYT dated July 1, 2025 regulating the registration of circulation of traditional medicines, traditional medicinal ingredients, and medicinal herbs (replacing Circular No. 21/2018/TT-BYT, Circular No. 39/2021/TT-BYT, Circular No. 54/2024/TT-BYT) and amended a number of contents to facilitate the registration of circulation of traditional medicines.
In which, traditional medicines exempted from clinical trials are divided into 3 groups:
(1) Traditional medicine in the books of Hai Thuong Lan Ong and Tue Tinh published by prestigious domestic and foreign publishers as prescribed in the Decision approving the list of scientific journals that are scored by the State Council of Professors for the fields of pharmacy and medicine.
As we know, Vietnam has two great physicians, Hai Thuong Lan Ong and Tue Tinh, who are considered the two founders of Vietnamese traditional medicine. In particular, Hai Thuong Lan Ong was honored by UNESCO as a world cultural celebrity. This is the world's affirmation of his contribution to Vietnamese and world traditional medicine. Hai Thuong Lan Ong and Tue Tinh left behind many valuable prescriptions, notably the books: Hai Thuong Y Tong Tam Linh by Hai Thuong Lan Ong and Nam Duoc Than Hieu by Tue Tinh.
( 2) The prescription is included in the Vietnamese pharmacopoeia or the pharmacopoeia of one of the countries of China, Japan, or Korea. These are countries with a long-standing traditional medicine and many similarities in the theory of Vietnamese traditional medicine. Using this treasure trove of researched prescriptions helps contribute to the work of caring for and protecting people's health.
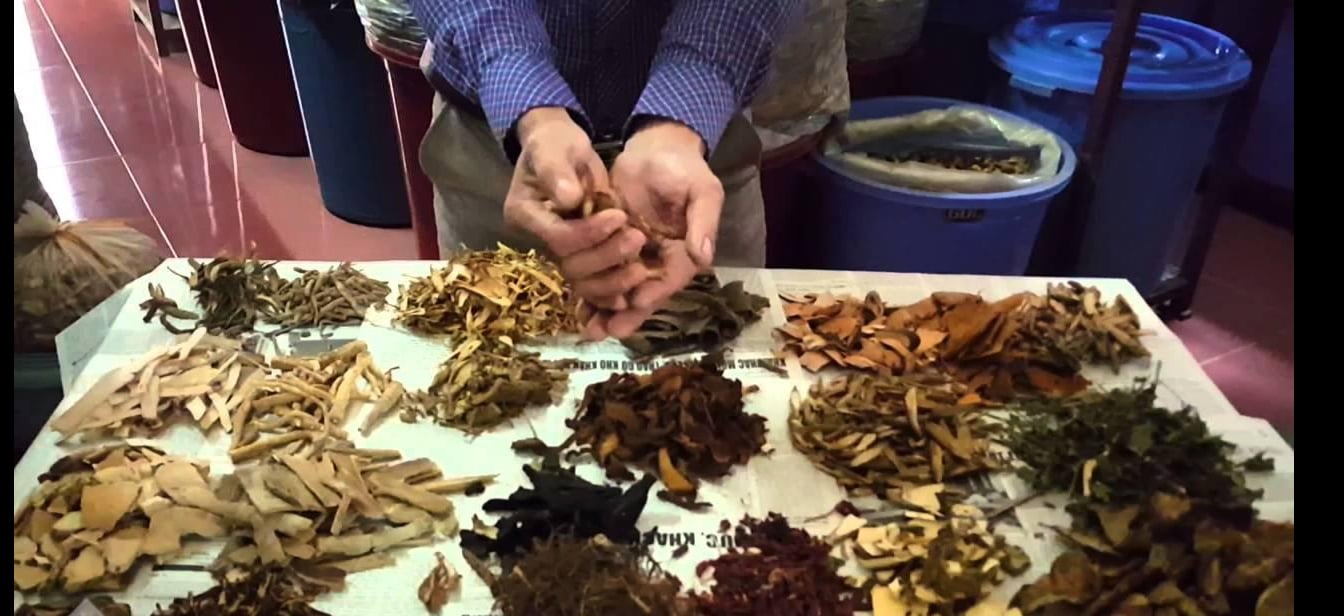

Promoting the advantages of traditional medicine to contribute to caring for and protecting people's health.
( 3) Traditional medicine that has been granted a traditional medicine certificate according to the provisions of law is assessed for acute and subchronic toxicity. To promote traditional experience, many traditional medicine have been recognized and put into production to promote the unique characteristics of traditional medicine in folk medicine. There are many very effective medicines in clinical practice, contributing significantly to the work of caring for and protecting people's health.
However, currently the number of monographs on traditional medicine in the Vietnamese Pharmacopoeia is still small; the traditional medicine testing system has not received proper investment and attention; and locally there are no specialized staff to monitor traditional medicine work.
In addition, there are no specific guidelines for clinical trials of traditional medicines. Some folk remedies have been passed down for a long time and are believed to be effective, but their safety and clinical effectiveness have not been fully evaluated, leading to difficulties in completing registration dossiers.
2. Need a separate mechanism for traditional medicine
According to information from the Department of Traditional Medicine Management, Ministry of Health, regulations and guidelines on traditional medicine are still scattered in the Law on Pharmacy and circulars, instructions and general regulations. This makes it difficult and confusing for people, individuals, organizations and traditional medicine enterprises in the process of implementing tasks related to the Law and regulations and guidelines under the Law.
To promote the quintessence of Vietnamese Traditional Medicine, it is necessary to build a specific legal framework for traditional medicine, promptly promulgate a specialized Law on Traditional Medicine with specific policies and regulations in accordance with the direction of Resolution No. 72-NQ/TW dated September 9, 2025 of the Politburo on a number of breakthrough solutions to strengthen the protection, care and improvement of people's health.
Completing regulations on registration and circulation of traditional medicines is not only a state management task, but also a strategic step to preserve and promote the quintessence of Vietnamese traditional medicine.
A flexible, scientific, and specific management mechanism will help traditional medicine develop sustainably, reach out to the world, and contribute to affirming the position of traditional medicine in modern, integrated medicine while still imbued with national identity.
See more popular articles:
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/hoan-thien-quy-dinh-ve-dang-ky-luu-hanh-thuoc-co-truyen-169251110114110061.htm







![[Photo] Deep sea sand deposits, ancient wooden ship An Bang faces the risk of being buried again](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/13/1763033175715_ndo_br_thuyen-1-jpg.webp)




























































![[Photo] Panorama of the 2nd Vietnam-Cambodia Border Defense Friendship Exchange](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/13/1763033233033_image.jpeg)
























![Dong Nai OCOP transition: [Article 3] Linking tourism with OCOP product consumption](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/10/1762739199309_1324-2740-7_n-162543_981.jpeg)







Comment (0)