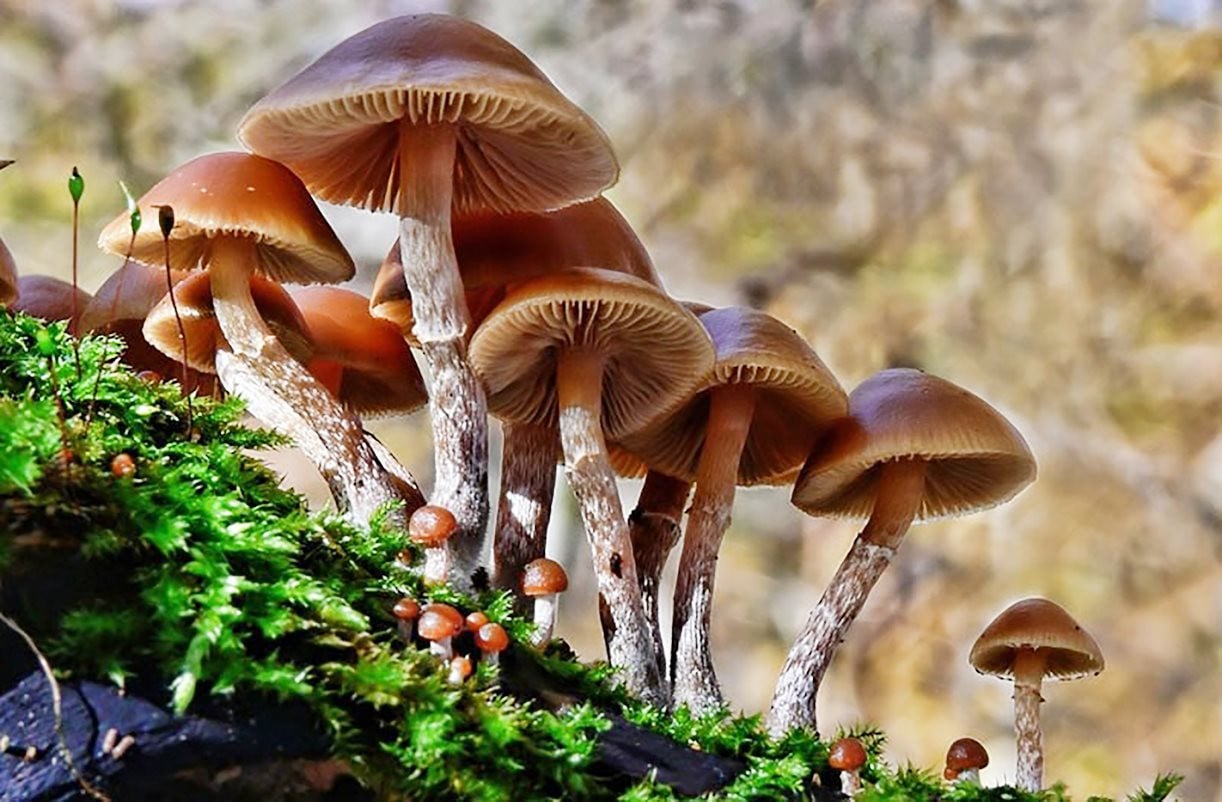

A series of emergency cases due to wild mushrooms
In just the past 4 months, localities have recorded many cases of mushroom poisoning, mostly due to people picking wild mushrooms for use. In mid-June 2023, in Tay Ninh province, there were 9 cases of food poisoning suspected to be due to eating poisonous wild mushrooms, including one death. Previously, on May 29, up to 15 people from 8 families in Son Dien commune, Di Linh district ( Lam Dong ) were poisoned and had to be hospitalized due to eating a type of poisonous mushroom picked in the forest. After eating for 30 minutes, the patients all had symptoms of chest tightness, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions. They were diagnosed with digestive disorders, suspected of being poisoned by toxins from wild mushrooms.
Similarly, at the end of February, the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital received and treated 2 patients diagnosed with wild mushroom poisoning. These were 2 patients in a family in Hoa Binh province, including 8 people who ate mushrooms together and 6 people were poisoned. It is known that the family picked wild mushrooms to cook, after eating about 12 hours, 6 people showed signs of vomiting, stomachache, dizziness, and diarrhea many times, continuously.
The family took the victims to the emergency room at Mai Chau District Hospital (Hoa Binh) and then the patients were transferred to Hoa Binh Provincial General Hospital. After that, 2 severe cases were transferred to the Poison Control Center. According to doctors at Bach Mai Hospital, 2 patients were transferred in a state of abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, severe dehydration, metabolic acidosis, and severe hepatitis. More seriously, one patient suffered from severe hypovolemic shock, signs of acidosis, liver damage, and severe kidney failure, with additional damage to the intestines, pancreas, and heart, severe blood clotting disorders, liver failure, kidney failure, and acute heart failure. The patient was treated intensively, detoxified, treated for shock, put on a ventilator, continuous blood filtration, and plasma exchange... However, this patient later died.
It is difficult to distinguish between poisonous and non-poisonous mushrooms.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Trung Nguyen, Director of the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital, said that people should absolutely not pick wild mushrooms to eat, including white mushrooms that look like normal mushrooms because even scientists can still confuse poisonous mushrooms with non-poisonous mushrooms. Note that people should not try eating mushrooms, even if they have eaten similar mushrooms many times before and have not been affected.
According to Dr. Nguyen Trung Nguyen, in the process of treating patients with mushroom poisoning, doctors have seen many cases of mushroom poisoning due to picking mushrooms to eat based on word of mouth experience, even though it is not clear whether the mushrooms are poisonous or not.
Many people think that poisonous mushrooms are usually brightly colored. However, in reality, the most poisonous and deadly mushrooms look white, look benign, like normal mushrooms and are delicious to eat. People in remote rural and mountainous areas often say that if they see mushrooms that have been eaten by insects, they can still be eaten by humans. However, this is completely wrong because in reality, all poisonous mushrooms are eaten by ants, snails, and insects.
Medical experts warn that poisonous mushrooms are often wild mushrooms. The most poisonous and deadly mushrooms are the most attractive looking and delicious to eat. When poisoned, there are no immediate symptoms, so detection is often late, the illness is severe, and many people die.
The most important measure to prevent mushroom poisoning is not to pick wild mushrooms to eat. People traveling should also avoid dishes made from strange mushrooms. After eating mushrooms, if there are signs of poisoning, if the patient is still conscious, give the patient water to drink and induce vomiting, then urgently take the patient to the nearest medical facility. If activated charcoal is available, the patient should immediately take a dose of 1 gram/kg of body weight (about 40 - 50 grams for adults); pay attention to bringing those who ate the mushrooms, even if they have no symptoms, to the medical facility; bring samples of remaining mushrooms or processed mushrooms to the medical facility so that doctors can identify the type of mushroom (these mushrooms need to be kept carefully to bring to the final hospitals, where there are conditions to help identify poisonous mushrooms).
The worrying thing is that with the most poisonous mushrooms, the symptoms of poisoning appear slowly - 6 hours or more after eating, when the poison has gone deep into the intestines and into the blood, so first aid measures are unlikely to have the necessary effect. In this case, the patient initially vomits and has diarrhea, so it is very important to quickly drink enough ORS, broth, boiled vegetable water, fruit juice or mineral water. The patient needs to urgently go to the nearest medical facility, then quickly transfer to a medical facility with conditions for emergency resuscitation and full detoxification.
Source









































































































Comment (0)