
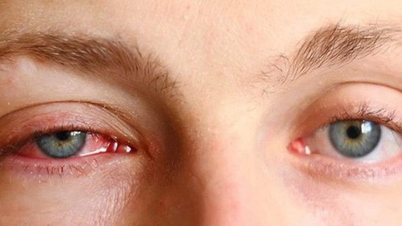
The World Health Organization (WHO) on July 22 called for urgent action to prevent the resurgence of the Chikungunya virus, as new outbreaks involving several African island nations in the Indian Ocean spread.
The WHO says an estimated 5.6 billion people in 119 countries are now at risk of infection with the virus, which can cause high fever, joint pain and long-term disability. The 2004-2005 pandemic of the virus affected nearly half a million people, mainly in small island states, before spreading worldwide .
The Chikungunya virus outbreak began earlier this year with major outbreaks on African islands in the Indian Ocean that have been affected by the disease, such as La Reunion and Mayotte, France, and Mauritius.
The virus has since spread to other countries in Africa such as Madagascar, Somalia and Kenya, as well as signs of spreading to India and Southeast Asia.
European countries have also seen a worrying situation as infections from outside the continent have increased rapidly.
According to WHO, in France alone, since May 1, 800 imported cases of Chikungunya have been detected, with 12 cases of infection recorded in some regions in southern France.
Chikungunya virus disease currently has no specific treatment, is spread mainly by aedes mosquitoes, including the “Aedes” group that is infected with dengue and zika viruses, and can cause rapid outbreaks on a large scale.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/who-canh-bao-nguy-co-lay-lan-cao-cua-virus-chikungunya-post895628.html


![[Photo] Dan Mountain Ginseng, a precious gift from nature to Kinh Bac land](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F11%2F30%2F1764493588163_ndo_br_anh-longform-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

















![[Video] “Weekend Music” Project: New cultural meeting place by Hoan Kiem Lake](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/30/1764513986851_nhac-jazzz-2-2934-jpg.webp)








































































Comment (0)