The abdomen is one of the body parts that is prone to storing fat. In addition to the aesthetic aspect, the accumulation of fat in the abdomen (belly fat) is also harmful to health. Of course, we are not talking about the layer of fat that lies just under the skin, but about the visceral fat that is stored under the abdominal muscles.

Belly fat causes many health problems.
1. Causes of belly fat
- Decreased muscle strength: Belly fat develops due to a decrease in the muscles in the abdominal wall. As we age, the muscle mass and strength of these muscles decrease (sarcopenia).
- Unhealthy lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, combined with increased calorie intake, promotes an increase in visceral fat.
- Hormonal changes: Decreased estrogen in women and decreased testosterone in men can promote fat storage in the abdomen. Weight gain during menopause is controversial, but many studies have shown that it does not happen naturally and is often related to decreased muscle activity during this period. Men tend to gain weight in the abdomen because they are less active and less mobile, and their calorie intake is not appropriate compared to their energy expenditure .
- Slow metabolism: As we age, our bodies burn fewer calories and fat tends to accumulate around the belly.
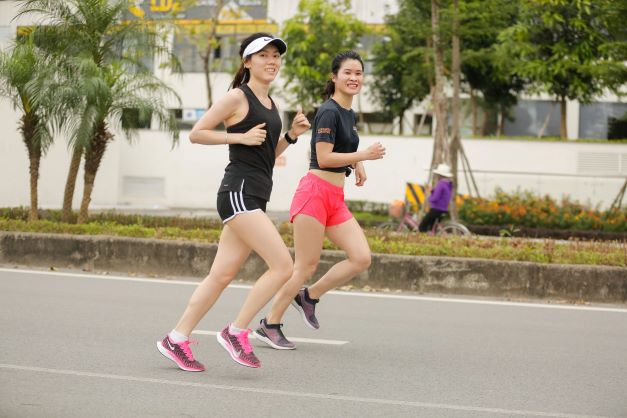

Regular physical activity helps prevent belly fat.
2. Consequences of belly fat
Belly fat greatly affects health, increases the risk of disease and weakens bones and joints. Specifically:
- Lipid metabolism disorders : People with belly fat often have problems with lipid metabolism (the process by which the body uses and metabolizes fat). This can lead to high blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke.
- Diabetes: Abdominal obesity is closely related to the development of type 2 diabetes. Fat accumulation in the abdominal area causes insulin resistance, increases blood sugar levels and leads to diabetes.
- Impact on bones and joints: Excess fat in the abdominal area creates great pressure on bones and joints, leading to degeneration and reduced quality of life due to pain and reduced mobility.
- Cardiovascular disease: Abdominal obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as vascular degeneration, myocardial infarction and stroke.
- Kidney failure: Some studies have shown that people with abdominal obesity have a higher risk of kidney problems, including kidney failure.
- Cancer: Belly fat is also linked to an increased risk of cancer, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer and several other types of cancer.
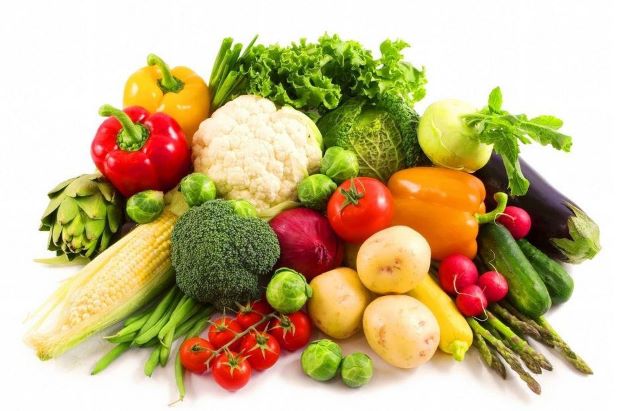

Fruits and vegetables rich in fiber prevent belly fat accumulation.
3. How to overcome belly fat
To limit the accumulation of belly fat due to age or even reduce belly fat (when it has formed), you should:
- Maintain regular physical activity: Swim, cycle, or run to increase endurance, combined with muscle-strengthening exercises to maintain good muscle mass. Belly fat will decrease significantly if you regularly do aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, or swimming.
Regular exercise can completely prevent belly fat from returning after weight loss. Exercise also helps reduce inflammation, lower blood sugar levels, and improve other metabolic activities related to excess belly fat in the body.
- Balanced, varied diet: Adopt a varied and balanced diet, rich in protein, fiber and essential fatty acids; choose fresh foods and cook for yourself.
+ Avoid foods high in sugar, salt and fat. Foods high in sugar are very harmful to your health. Consuming too much of these foods can lead to uncontrolled weight gain.
Researchers have revealed that adding too much sugar will affect the body's metabolism. In addition, excess sugar is mainly fructose, which will increase the risk of accumulating bad fat around the liver and abdomen.
When you consume too much sugar, your liver becomes overloaded with excess fructose and is forced to convert it into fat. This process can have negative effects on your overall health, including increased liver fat, belly fat, insulin resistance, and other metabolic problems.
+ Load up on protein especially effective in reducing belly fat. Scientists say that people who eat more protein have less belly fat.
+ A low-carb diet helps reduce excess fat in the abdomen and around other organs. Refined carbs like candy, sugar, and white bread should be avoided.
+ Add fiber-rich foods: A study has shown that adding 14g of fiber per day will help reduce 10% of calories and about 2kg of weight within 4 months. If you eat 10g of fiber per day, it will reduce 3.7% of excess fat in the abdominal cavity. This is proof that soluble fiber is very useful in reducing harmful belly fat. You can add more fiber through foods such as fruits, green vegetables, beans, cereals, and oats.
- Maintain sleep quality: Melatonin production tends to decline with age. The deep, slow-wave sleep that helps the body recover also declines. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that you maintain quality sleep to regulate the hormones involved in appetite control, thereby maintaining weight and limiting the formation of belly fat.
Source

























































































![[OCOP REVIEW] Tu Duyen Syrup - The essence of herbs from the mountains and forests of Nhu Thanh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/5/58ca32fce4ec44039e444fbfae7e75ec)





Comment (0)