1. The importance of diet for people with fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease damages the liver, making it unable to remove toxins from the blood and produce bile for digestion. When the liver cannot perform these tasks effectively, it is at risk of developing other problems.
There are certain foods that should be included in the fatty liver diet and others that should be avoided. The main goal of a fatty liver diet is to eliminate fat deposits in the abdominal area to help slow the progression of fat in the liver.
Diet plays an essential role in weight loss, and specific nutrients are a focus for people with fatty liver disease. Reducing simple carbohydrates and saturated fats can reverse or prevent the progression of the disease.
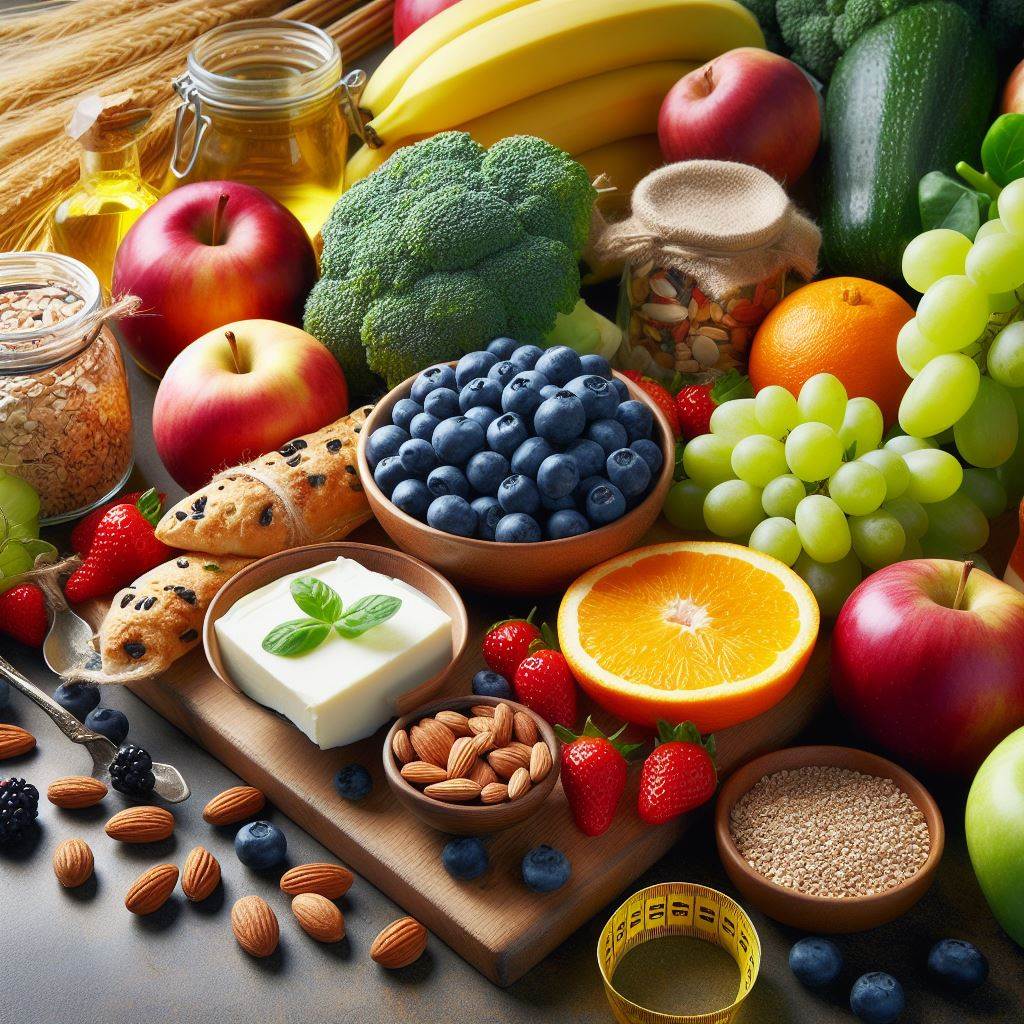

Diet plays an essential role in weight loss and specific nutrients are a focus for people with fatty liver disease.
Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic, but is often associated with central obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and insulin resistance. These health problems can cause a variety of other symptoms, such as lack of energy, mood swings, and disrupted sleep. Weight loss can help improve these symptoms and conditions.
Weight loss aimed at reducing daily calorie intake is an important part of managing fatty liver disease. Moderate weight loss, about 3-5% of body weight, can reduce liver fat, some people lose as much as 10%.
Because fatty liver disease is often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, weight loss is one of the main goals, and diet can help address this.
A fatty liver diet includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Portion control is another important aspect of any fatty liver diet. Exercising 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week, will also help achieve your weight loss goals.
MSc. Dr. Nguyen Ngoc Dai Lam - Head of Hepatobiliary Department, E Hospital
Fatty liver condition can improve gradually if the patient changes his/her living habits, practices a scientific lifestyle combined with treatment of associated diseases.
According to Master, Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Dai Lam: The most important thing in treating fatty liver is to evaluate and determine the severity of the disease, strictly follow the doctor's instructions to reduce risk factors, and prevent possible complications.
Dietary principles for people with fatty liver disease:
A healthy diet that helps lose weight has a positive impact on fatty liver disease, such as preventing the disease from progressing. It can also lead to a reduction in blood pressure, cholesterol, lipids, and blood sugar levels. To quickly improve the condition and prevent potential health complications, people with fatty liver disease need to follow the following nutritional principles:
- Avoid sugar and limit starchy foods (bread, pasta, rice, potatoes).
- Reduce saturated fat and trans fat intake.
- Avoid foods and beverages that contain high fructose corn syrup.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Increase your fiber intake.
Diet Basics:
Most people trying to lose weight need three meals and one or two snacks a day to get enough nutrients and prevent overeating. Meals and snacks should contain fiber and protein to help keep you full longer and prevent large swings in blood sugar that lead to cravings and overeating.
- Eat whole foods: meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes and whole grains.
- Avoid sugary drinks, added sugars, processed meats, refined grains, hydrogenated oils, and other highly processed foods.
- Never eat foods that contain only carbohydrates but should include a balance of healthy fats, proteins and carbohydrates at every meal.
- Practicing the plate method can be helpful. Dedicate half your plate to non-starchy vegetables, 1/4 to lean protein like white meat chicken, fish, lean pork, turkey, and 1/4 to starchy vegetables or whole grains.
A personalized meal plan based on dietary preferences and lifestyle is important because this is not a temporary diet but a lifestyle change. If you only maintain the diet for a short period of time, your old eating habits will return and you will gain weight again, putting you at risk of fatty liver and related diseases again.
2. Essential nutrients for people with fatty liver disease
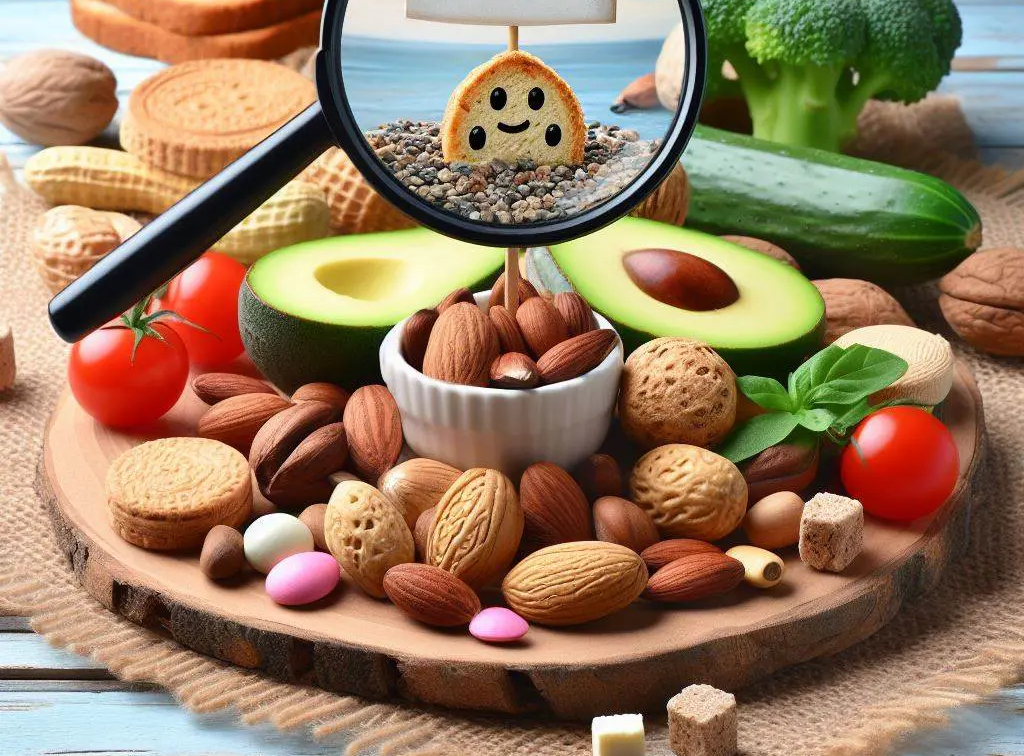

People with fatty liver disease should eat a low-carb diet and should eat unsaturated fats.
Several studies have shown that people with fatty liver disease benefit from eating a lower-carbohydrate/higher-fat diet (with a focus on unsaturated fats).
In fact, in a study in which people with fatty liver disease were randomized to a lower-calorie diet with the same amount of calories but different macronutrient ratios, those who received a lower carbohydrate (40% vs. 60%) and higher fat (45% vs. 25%) diet had improved liver function tests.
Some studies have shown that following a low-carbohydrate diet with carbohydrates that have a lower glycemic index (GI) can improve fatty liver disease. The glycemic index can be a difficult concept to understand, but simply choosing foods with a lower glycemic index (rather than counting glycemic index) can help reduce blood sugar and insulin levels.
Eating enough protein is important to ensure energy for the body, however when the liver is sick, the protein metabolism is affected. Therefore, people with fatty liver disease should eat enough and choose the right source of protein that the body needs to avoid negative effects on the liver. In addition to ensuring the body has enough energy for daily activities while still being able to maintain a reasonable weight.
Polyunsaturated fats (omega 3, omega 6) are also a focus due to their anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering properties. Sources of unsaturated fats such as margarine, olive oil, nut butters, walnuts, and fatty fish are recommended foods for people with fatty liver disease.
The Mediterranean diet is recommended by many nutritionists for people with fatty liver disease because it focuses on whole, minimally processed foods that contain unsaturated fats, as well as lots of vegetables, fruits, and legumes, which help lower total cholesterol. The DASH diet and low-carbohydrate diets can also be effective. Some people, especially those with diabetes, may also benefit from a ketogenic diet (however, this type of eating plan has not been specifically studied for people with fatty liver disease and should be guided by a nutritionist).
3. Foods that people with fatty liver disease should eat
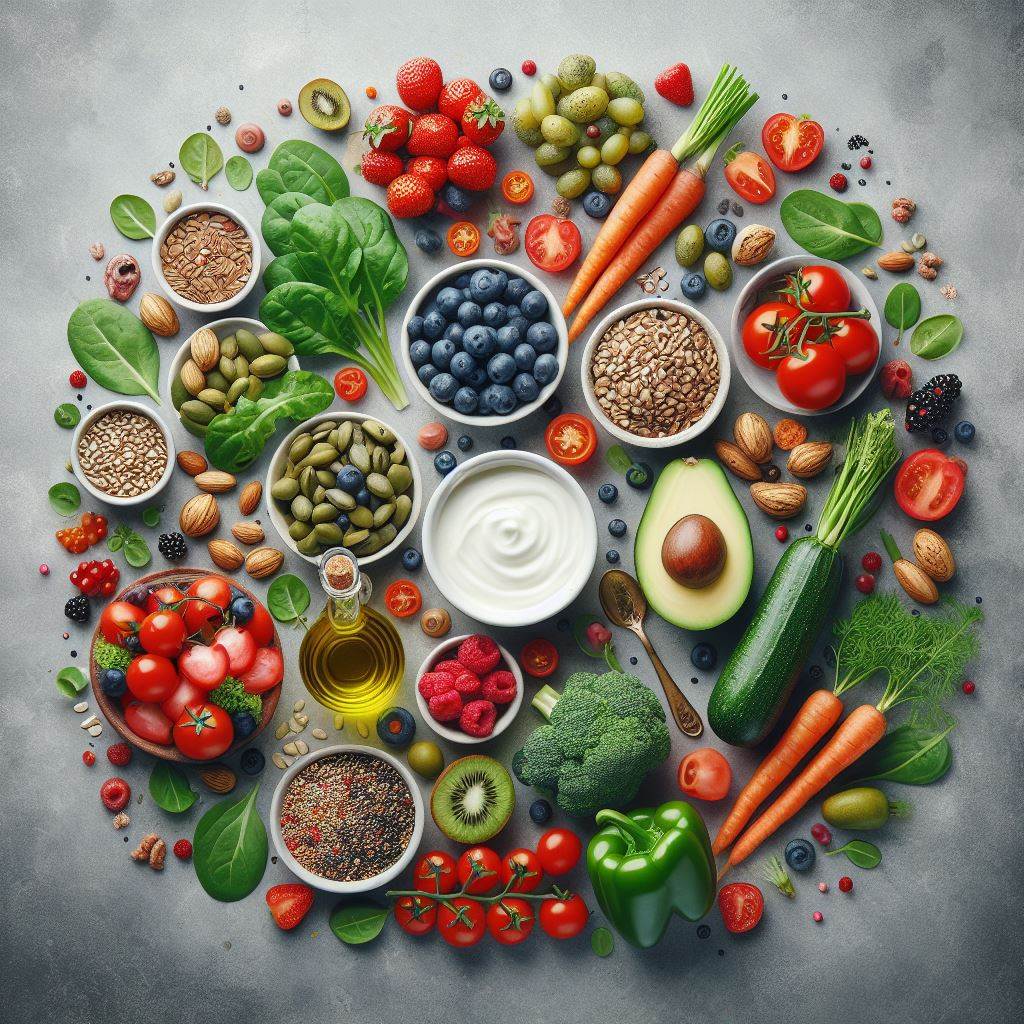

Green vegetables, fruits rich in vitamins A, C, E, antioxidants, whole grains, low-fat yogurt, olive oil... are foods that people with fatty liver disease should eat.
According to Associate Professor Nguyen Thi Lam, former Deputy Director of the National Institute of Nutrition: people with fatty liver should eat lots of green vegetables and fresh fruits to get fiber to stimulate intestinal motility, avoid constipation, and prevent atherosclerosis.
Green vegetables are also a source of many vitamins and minerals necessary for the body. On average, people over the age of 50 need about 300 - 400g of green vegetables and 200 - 300g of fruit per day.
Eat lots of green vegetables and fruits: People with fatty liver disease should increase their intake of fruits and vegetables because these foods contain lots of vitamins and fiber, which stimulate intestinal motility, reduce the risk of constipation and limit the risk of atherosclerosis. In particular, vitamins A, C, E and antioxidants in fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk of fat accumulation in the liver. Green vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, kale, onions, leeks, asparagus, artichokes, bell peppers, mushrooms, carrots, tomatoes, cauliflower. Fruits such as grapefruit, berries (blueberries, cranberries, strawberries, raspberries, etc.), lemons, oranges, pineapples, apples, pears, papaya, pomegranates, etc.
People with fatty liver should supplement at least 300g of green vegetables and 200g of fresh ripe fruit every day. People who eat a lot of fruits and vegetables tend to maintain a healthier weight.
Starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes, turnips, and yams are complex carbohydrates that are also rich in phytonutrients, fiber, and vitamins, such as vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that boosts immunity.
Whole grains: Oats, 100% milled wheat, barley, bulgur, farro, rice… Whole grains—especially those with a lower glycemic index, such as whole oats—are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They promote satiety and regular bowel movements and are a great alternative to refined carbohydrates.
Nuts: Sunflower seeds, almonds, cashews, pistachios, and walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help lower triglycerides and lipids. They may also reduce inflammation. Choose raw, unsalted options whenever possible.
Beans: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, etc. (preferably dried and not canned) are a great source of protein and fiber for vegetarians. Beans are a complex carbohydrate that helps keep you full longer and reduces large fluctuations in blood sugar. They are also low in fat.
Lean Protein: White meat chicken, turkey, eggs, pork… are protein foods that are important for muscle and help keep you full longer. Compared to higher fat proteins, lean proteins are lower in calories and saturated fat, which can help with weight loss. Swapping 85g of ground beef for 85g of chicken can save about 150 calories.
Low-fat yogurt, kefir: Rich in calcium, vitamin D, and probiotics, low-fat milk can be a healthy choice. Research has shown that probiotics can help alter bacteria in the gut, which plays a role in limiting the development of fatty liver disease associated with dangerous metabolic disorders and progression,
Healthy fats: Olive oil, peanut oil, sesame oil or fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines can help reduce triglycerides and fat in the liver.
Herbs and spices: Herbs and spices add flavor and are rich in anti-inflammatory antioxidants. They are low in calories and fat-free, such as basil, cilantro, parsley, rosemary, thyme, oregano, lemongrass, and lavender.
4. Foods that people with fatty liver should not eat
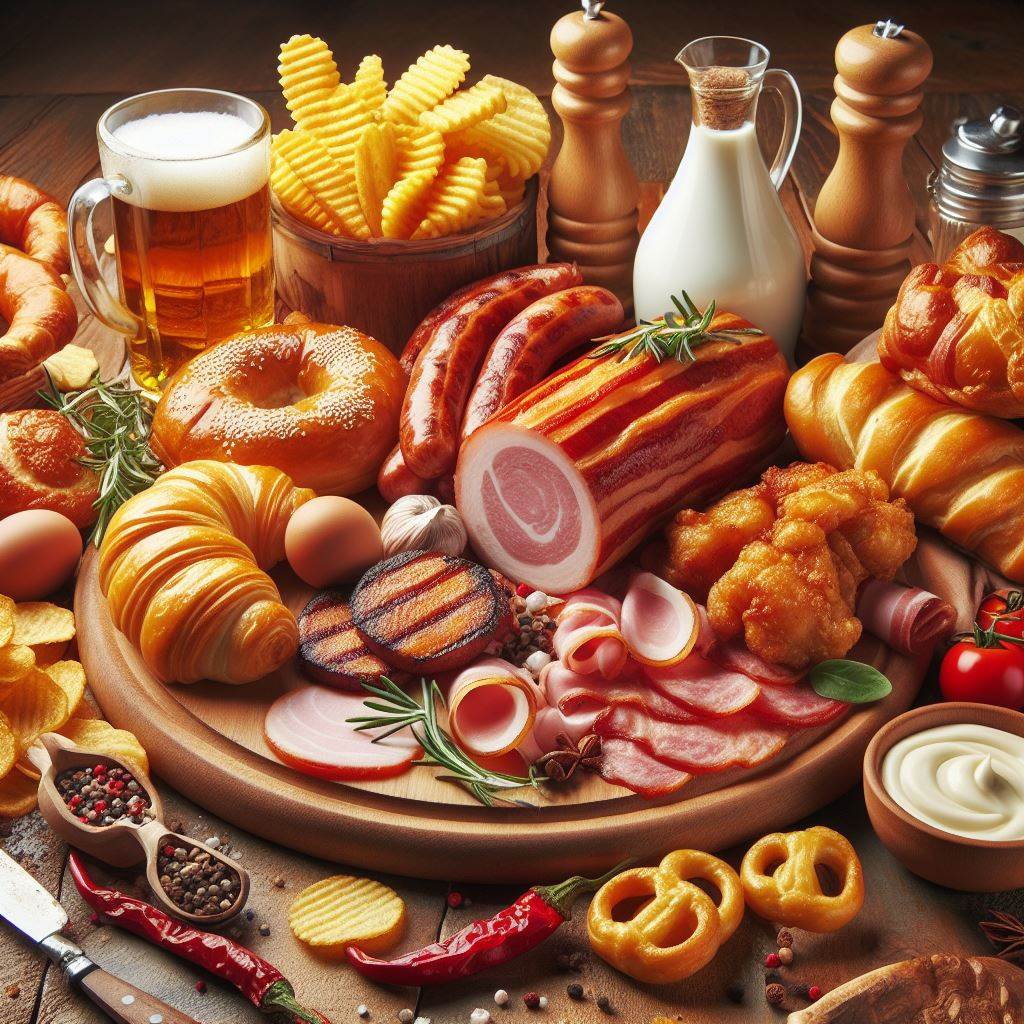

Processed foods, fried foods, alcohol, and cakes are foods that people with fatty liver should not eat.
Road:
Foods high in sugar such as candy, cookies, cakes, donuts, soft drinks, soda, sports drinks, fruit juices... are foods that fatty liver patients need to avoid. Because they cause high blood sugar levels, causing fat to accumulate in the liver.
Fruits are healthy for most people, but if you have high blood sugar or insulin resistance, avoid fruits high in fructose. Fructose is metabolized in the liver. Limiting fruits high in fructose will help reduce the burden on the liver and increase the effectiveness of treating fatty liver disease, such as jackfruit, durian, lychee, longan, dried fruits, etc., or corn syrups such as maple syrup.
Limit processed meats as much as possible.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is more likely to occur with high levels of bad cholesterol and in people who are overweight or obese. Regular consumption of processed meats can contribute to high cholesterol and other heart problems. Processed meats such as bacon, sausages, hot dogs, etc. are higher in artery-clogging saturated fat and calories.
Limit animal fat and foods rich in cholesterol
People with fatty liver should avoid animal fat, animal organs, egg yolks, etc., which are foods high in cholesterol. Limiting these foods in your daily diet helps reduce the amount of fat in the liver, which reduces the burden on the liver.
Don't eat too much red meat.
Red meats such as beef and lamb contain a lot of protein, eating too much will increase the burden on the liver. The liver cannot metabolize, causing increased fat accumulation, making fatty liver disease more serious.
Refined carbohydrates
White bread, white rice, bagels, white pasta, and packaged foods are highly processed refined carbohydrates that can raise blood sugar more than whole grains due to their lack of fiber. Limit your intake of rice.
Trans fats and saturated fats
Margarine, processed baked goods, fried foods, pastries, full-fat cheese, packaged/canned foods.
Refined, fried, and deep-fried snack foods
Potato chips, cookies, crackers, rice cakes, these are high in fat and calories.
Reduce salt
Consuming too much salt can increase your risk of fatty liver disease. It is recommended to limit sodium intake to less than 2,300mg per day.
Do not drink alcohol or beer
People with fatty liver disease should avoid drinking alcohol because it can aggravate the condition. Drinking alcohol makes the liver work harder to remove toxins from the body, greatly affecting the health of people with fatty liver disease.
In addition to building a scientific and reasonable diet, patients need to increase physical activities to improve resistance and help increase liver cell metabolism.
The exact distribution of macronutrients in a person with fatty liver disease's diet will depend on many factors, including underlying health conditions, age, activity level, weight, etc. But the goal of a healthy eating pattern for people with fatty liver disease is slow and steady weight loss (no more than 0.5kg to 1kg per week), incorporating nutrient-rich whole foods, and reducing simple carbohydrates, added sugars, and processed foods.
Source


![[Photo] Party Committees of Central Party agencies summarize the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW and the direction of the Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761545645968_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)



![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of the House of Representatives of Uzbekistan Nuriddin Ismoilov](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761542647910_bnd-2610-jpg.webp)





























































































Comment (0)