Google says it has developed a computer algorithm that shows how quantum computing can have practical applications and can generate unique data for use with artificial intelligence.
Google said the new algorithm, called Quantum Echoes, running on the company's quantum chips, is 13,000 times faster than the most complex classical computing algorithm on a supercomputer.

Quantum computers will play a key role in simulating quantum mechanical phenomena, such as the interactions between atoms and particles, as well as the structure (or shape) of molecules.
One of the tools scientists use to understand chemical structures is Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), which is the same scientific principle behind magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
NMR acts like a molecular microscope, powerful enough to allow us to observe the relative positions of atoms, thereby helping to understand the structure of a molecule.
Simulating the shape and dynamics of molecules is fundamental in chemistry, biology, and materials science; advances that help us do this better will drive developments in many fields, from biotechnology to solar energy and fusion.
Last year, Google announced the Willow quantum chip, which the company said could fix a key problem with “qubits,” the building blocks of quantum computers.
The executives said the development of the algorithm is as significant as the chip. The algorithm can also be verified using other quantum computers or through experiments. Verifiable data means it could lead to practical applications.

The Google Willow chip has already made significant strides in quantum computing.
In a proof-of-principle experiment in collaboration with the University of Berkeley, Google ran the Quantum Echoes algorithm on the Willow chip to study two molecules, one with 15 atoms and another with 28 atoms, to test the method.
The results on Google's quantum computer matched those from conventional NMR, and revealed information that conventional NMR cannot provide, providing important validation of our approach.
Just as telescopes and microscopes have opened up new worlds never before seen, this experiment is a step toward a “quantum microscope” capable of measuring previously unobservable natural phenomena.
Quantum-enhanced NMR could become a powerful tool in drug development, helping to determine how potential drugs bind to their targets, or in materials science to determine the molecular structure of new materials such as polymers, battery components, or even the materials that make up quantum bits (qubits).
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/google-dat-tien-bo-dot-pha-cho-ung-dung-thuc-tien-cua-may-tinh-luong-tu-post2149063010.html


![[Photo] Flooding on the right side of the gate, entrance to Hue Citadel](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761660788143_ndo_br_gen-h-z7165069467254-74c71c36d0cb396744b678cec80552f0-2-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man received a delegation of the Social Democratic Party of Germany](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761652150406_ndo_br_cover-3345-jpg.webp)



![[Photo] Draft documents of the 14th Party Congress reach people at the Commune Cultural Post Offices](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761642182616_du-thao-tai-tinh-hung-yen-4070-5235-jpg.webp)



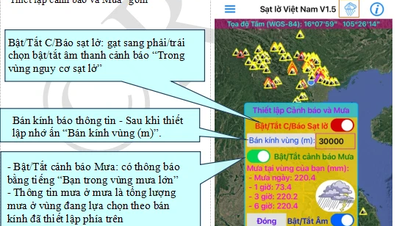















![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the 80th Anniversary of the Traditional Day of the Armed Forces of Military Region 3](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761635584312_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)












































































Comment (0)