Below are some typical experiences from countries leading this trend.
Denmark
Denmark has become one of the world's leading countries in green transformation , setting an ambitious goal to become the greenest country in the world by 2035. The country's transition is driven by investment in renewable energy, sustainable urban planning and strong environmental policies.
Denmark is a pioneer in wind energy, with wind power accounting for more than 50% of total electricity consumption. It was one of the first countries to invest heavily in offshore wind farms, with notable projects such as Horns Rev and Anholt Offshore Wind Farms. In addition to wind power, the Danish government is also focusing on investing in green hydrogen projects as an important energy source for industry and transport.
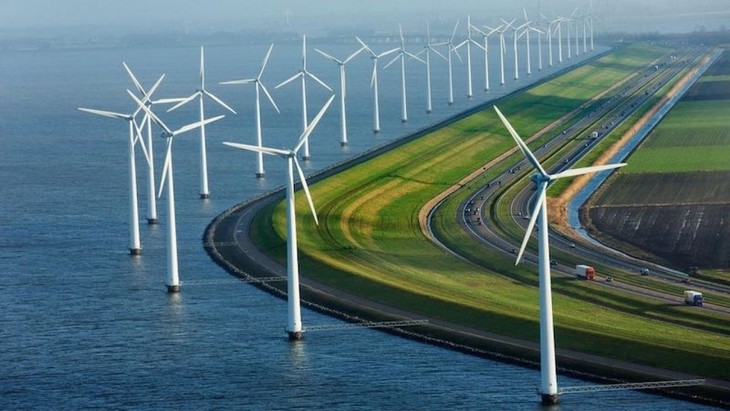 |
| Denmark is a pioneer in wind energy. Photo: Renew Economy. |
Urban planning and sustainable transport are also a prominent part of Denmark’s green transition strategy. Danish cities have a bicycle-friendly infrastructure. More than 40% of Copenhagen’s residents commute by bicycle thanks to dedicated lanes, bicycle bridges and policies that encourage sustainable transport. Public transport in Denmark is being developed in a low-emission way, with the expansion of electric buses, metro systems and hydrogen-powered ferries to reduce carbon emissions in urban areas.
Waste management is a key aspect of the green transition. Denmark has strict regulations to reduce landfill waste, encourage recycling and push businesses to adopt circular economies . These regulations are supported by a well-funded network of waste-to-energy plants. Denmark has some of the most efficient waste-to-energy plants in the world, notably CopenHill, which converts waste into electricity and heat for thousands of homes.
On the government policy front, Denmark has implemented a high tax on carbon emissions, encouraging industries to transition to cleaner technologies. The country also actively cooperates with the European Union (EU), the United Nations and private partners to implement sustainable initiatives on a global scale.
Virtue
Germany is one of the world's leading countries in the green transition, thanks to its long-standing commitment to renewable energy , sustainable policies and industrial innovation. Germany's Energiewende (Energy Transition) strategy plays a key role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and promoting a low-carbon economy.
The Energiewende initiative aims to transform Germany's energy system through:
- Expanding renewable energy: Renewable energy accounts for more than 46% of Germany's electricity production, focusing on solar, wind and biomass.
- Phase out nuclear and coal power: Germany closed its last nuclear power plants in 2023 and aims to completely phase out coal-fired power by 2038.
- Decentralized energy system: Encourage households and small businesses to produce and store their own renewable energy.
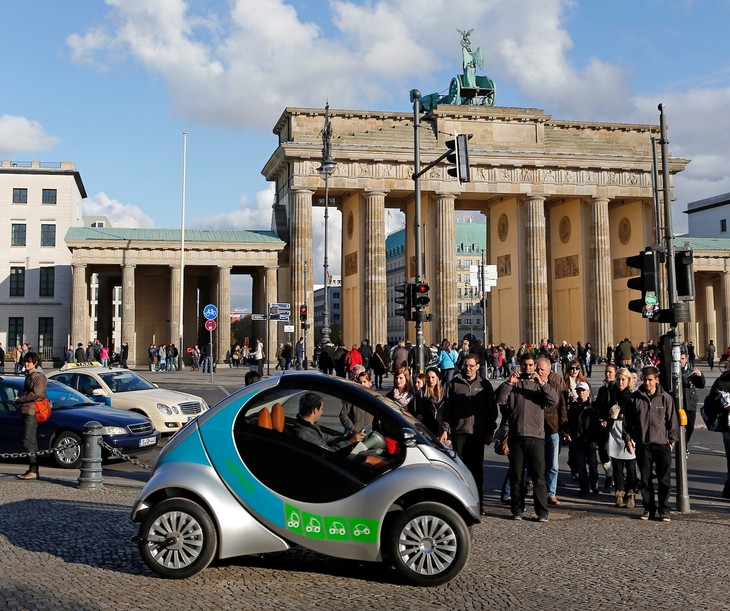 |
| The German government promotes electric vehicles by offering subsidies and tax exemptions to encourage their use. Photo: Phys.org. |
To develop sustainable transportation, the German government promotes electric vehicles (EVs) with subsidies and tax exemptions to encourage the use of this type of vehicle. Major car manufacturers such as Volkswagen, BMW and Mercedes-Benz are leading the trend of switching to electric vehicles. Regarding public transportation, the German government invests heavily in high-speed trains, hydrogen-powered buses and cycling infrastructure to reduce carbon emissions. CO₂ emission regulations for cars and industries are strictly applied in Germany.
Germany has introduced many policies to reduce waste and encourage recycling and green manufacturing. Thanks to strict regulations on waste classification and reuse, Germany now has the highest recycling rate in the world (67%). Industries in Germany are shifting to energy-saving technology, with many government incentives for businesses adopting carbon-neutral technology. The German government has issued green bonds to raise capital for renewable energy projects, energy efficiency and sustainable infrastructure.
Korea
South Korea is making significant strides in its green transition, aiming to be carbon neutral by 2050. Through ambitious policies such as the Korean Green New Deal and heavy investment in renewable energy, green technology and sustainable industry, South Korea is becoming one of Asia's leading countries in the transition to sustainable production.
Launched in 2020, Korea's Green New Deal is a comprehensive policy framework to promote green growth, with focuses on:
- Expanding renewable energy: South Korea aims to increase the proportion of renewable energy to 30-35% by 2040, focusing on solar power, wind power and hydrogen energy.
- Investing in green infrastructure: The government renovates old buildings to improve energy efficiency and builds smart cities that integrate sustainable technology.
- Integrating digital economy and green economy: Korea applies artificial intelligence (AI) and digital technology to optimize energy and resource use.
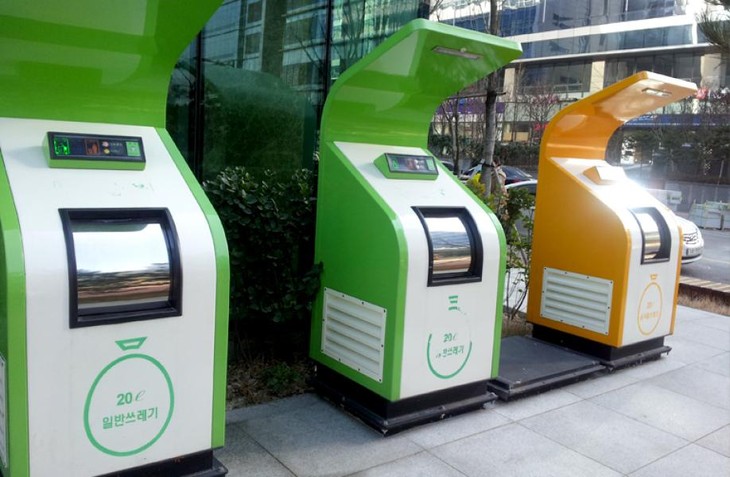 |
| The waste management system in Korea is considered the most advanced in the world. Development Asia. |
South Korea is building one of the world's largest offshore wind farms, aiming for 12GW of wind power by 2030. South Korea is also a pioneer in building a hydrogen economy, with major investments in hydrogen-powered vehicles, charging stations and hydrogen fuel cells. To gradually reduce its dependence on coal, South Korea is investing in cleaner and safer nuclear power technology.
The South Korean government is encouraging its citizens to use electric and hydrogen vehicles. South Korea is home to leading electric and hydrogen vehicle manufacturers such as Hyundai and Kia, with a target of producing 4.5 million electric vehicles and 200,000 hydrogen vehicles by 2025. The government is investing in environmentally friendly hydrogen-powered buses, electric taxis and high-speed trains. Urban bicycle infrastructure has also been rapidly developed in recent years.
South Korea’s waste management system is considered one of the most advanced in the world. The country has a high waste recycling rate (over 60%), with strict waste sorting policies and a ban on single-use plastics in place. Cities like Seoul and Busan are applying AI technology to waste management to reduce waste and optimize recycling.
To encourage the development of a circular economy and green industries, the Korean government provides subsidies to businesses that adopt low-carbon production technologies. The Korean financial system is promoting green bonds and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments to support sustainable projects.
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/nhin-ra-the-gioi-kinh-nghiem-chuyen-doi-xanh-cua-cac-nuoc-post267168.html


![[Photo] Party Committees of Central Party agencies summarize the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW and the direction of the Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761545645968_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of the House of Representatives of Uzbekistan Nuriddin Ismoilov](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761542647910_bnd-2610-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] The 5th Patriotic Emulation Congress of the Central Inspection Commission](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761566862838_ndo_br_1-1858-jpg.webp)









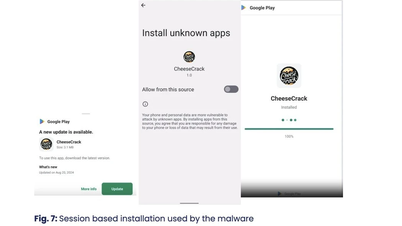

































































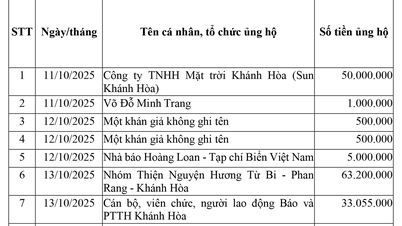

























Comment (0)