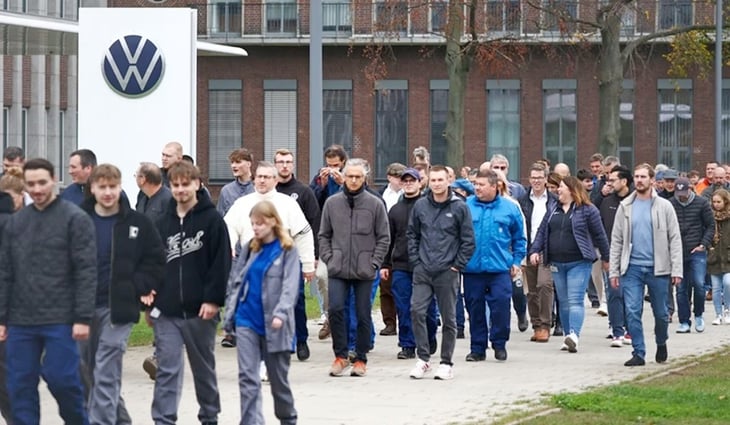

Volkswagen workers protest at the company headquarters in Wolfsburg, Germany, in late October 2024 - Photo: BLOOMBERG NEWS
According to the forecast of the EU Economic Commissioner Valdis Dombrovskis, the economic output of the European Union will decrease by 0.2% by 2027 if President Donald Trump applies all the announced tariffs. However, this is just the "last straw" when the EU's leading economy is facing a severe recession.
German economy weakens
Germany’s economy is facing serious internal problems. Aging infrastructure and technology, and bureaucracy have slowed Germany in responding to the rise of rivals from China and the United States over the past decade.
China’s economic model is shifting from low-cost manufacturing to high-quality goods, a traditional strength of Germany. The rise of Chinese manufacturers such as BYD and Nio in AI and electric vehicles, with better-equipped and cheaper models, is threatening a key German industry.
China's increasing competitive advantage in the electric vehicle sector puts Germany at a disadvantage when exporting to this billion-people market.
At the same time, Germany has no way out of the 25% import tax on cars in the US, causing the price of German cars to nearly double. In terms of market value, Elon Musk's electric carmaker Tesla is now worth four times more than the entire German auto industry.
This situation is leading to serious consequences. Volkswagen - Europe's largest carmaker - is considering closing factories for the first time in its 87-year history. In February 2025, the unemployment rate in Germany reached 6.4% and is forecast to continue to increase until 2026, while the same period in 2023 was only about 3%, according to Statista.com.
Labor crisis
Germany is facing a high-quality labor crisis due to its aging population. Asylum and immigration policies, along with excessively high tax and insurance policies, have reduced investment attractiveness and talent attraction, causing social burdens since the end of Chancellor Angela Merkel's term in 2020.
Social injustice is manifested when the burden is concentrated on the middle working class - the creators of material wealth - who have to pay social contributions of up to 45 - 50% of their income.
High-quality immigrants were initially welcomed, but then found themselves invited to share this responsibility, leading many to resort to "personal resistance" such as taking a leave of absence from work and receiving benefits once they had obtained residency and German citizenship.
Deep government intervention in labor laws to limit layoffs, coupled with overly detailed professional structure policies, leaves companies facing operational bloat and a lack of competitive edge.
Faced with a wave of massive layoffs from leading European businesses such as BMW, Volkswagen, Continental, Bosch - expected to reach 140,000 people in the next two years (according to EY research) - it seems like an opportunity to attract talent for startups, but the reality is the opposite.
Knowledge and experience in electric car technology, AI and programming skills are not integrated into the same workforce, creating a major barrier for startups to take advantage of human resources from large companies. This will be a major challenge for the German Ministry of Labor, which has to spend a huge amount of money on building training programs to reuse labor resources.
“There is no other way but to invest,” Siemens CEO Roland Busch told Bloomberg TV. A shrinking population clearly means more immigrants need to be integrated and trained. But the right-wing populist AfD party — now Germany’s second-largest political force — will do everything it can to prevent this, leaving the country’s economy and politics deeply divided.
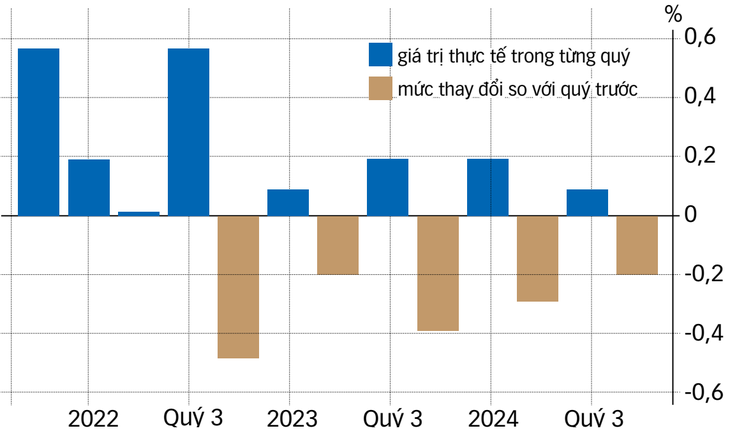
Germany's GDP in the last 3 years, down to -0.2% in 2024 - Source: Trading Economics - Data: PHUONG NGUYEN - Graphics: N.KH.
Vietnamese community also faces difficulties
Immigrants from Vietnam are mainly active in the restaurant and food trade. A small number are involved in beauty services, finance, insurance and investment.
The overseas Vietnamese community is facing many challenges: high taxes, a decline in personal consumption index due to the trend of working from home after the COVID-19 pandemic, consecutive inflation (from 2022 to 2024, respectively 6.9%, 5.9% and 2.9%), along with energy and food supply crises.
These factors have caused heavy losses to the Vietnamese restaurant industry. Many restaurants were forced to increase prices twice in 2022 and 2023 (up to 20-30%) and in 2024 (3-5%).
According to survey interviews from the Vietnamese community in Berlin, declining revenues, business closures and unemployment are threatening related service industries, leaving them in a precarious situation.
Faced with the risk of the US increasing import taxes, this industry is indirectly affected by the decline in purchasing power, putting people in a dilemma: input costs increase according to the new basic wage (12.82 euros/hour from the beginning of 2025, compared to 12.41 euros/hour in 2024), but they do not dare to increase selling prices.
Many people decided to temporarily downsize their businesses, use family labor and wait for looser tax policies from the new government of Chancellor Friedrich Merz.
Accordingly, on April 9, the three-party coalition of the ruling CDU, CSU and SPD quickly reached agreements: in early 2026, the VAT rate for food will be permanently reduced from 19% to 7%; the reduction of electricity tax will help reduce electricity prices by 5 cents/kWh; and from early 2028, the corporate tax will be gradually reduced from 15% to 10% over 5 years.
It can be seen that while Washington is always proactive in creating international strategies to treat internal economic weaknesses and using political and economic measures as a measure to realize the strategy, EU politicians are often in a passive position.
The EU is caught up in the Ukraine war and the energy crisis, forcing it to depend on the US for half of its liquefied natural gas imports. Faced with this dangerous dependence, the EU must focus on internal reform, accept its own internal pain, be ready to negotiate and only respond when "forced". This is what makes the US even more eager to seize the opportunity to put pressure on the EU in the current tariff war.
EU's weakness
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen announced at noon on April 10 (Berlin time): "We want to give the negotiations a chance. If the negotiations do not lead to a positive result, our countermeasures will come into effect."
This shows that EU countries have agreed to be able to respond to tariffs of 10-25% depending on the product imposed by the US, while still prioritizing a diplomatic solution. However, the current economic recession with Germany's GDP falling to -0.2% in 2024 (according to Trading Economics) puts the EU in a weak position in this negotiation.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/thue-quan-my-bua-vay-kinh-te-duc-20250413231930851.htm



![[Photo] Ready for the top competitions of Vietnamese table tennis](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/9c547c497c5a4ade8f98c8e7d44f5a41)
![[Photo] Many young people patiently lined up under the hot sun to receive a special supplement from Nhan Dan Newspaper.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/6f19d322f9364f0ebb6fbfe9377842d3)






















![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam visits exhibition of achievements in private economic development](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/18/1809dc545f214a86911fe2d2d0fde2e8)

































































Comment (0)