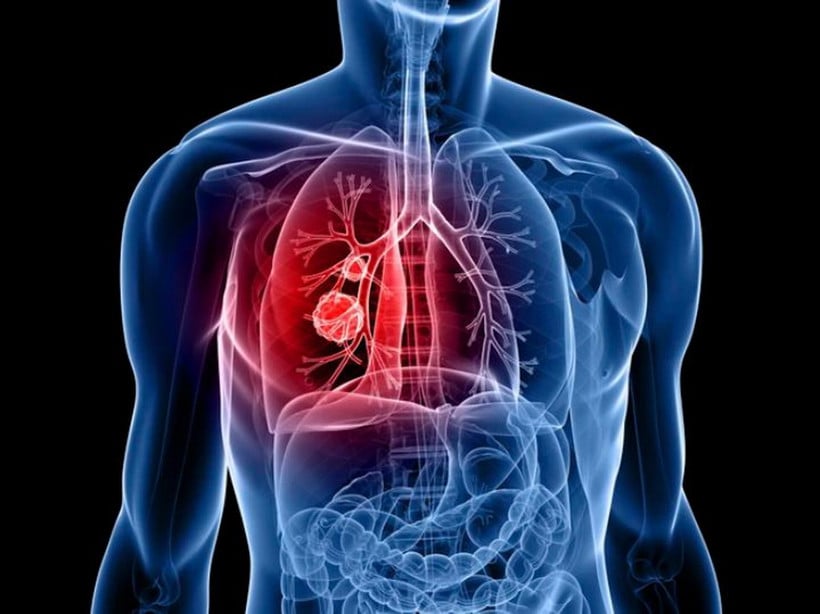
(Illustration photo. Source: Getty images)
Every year, lung cancer claims the lives of more than 30,000 people in France and nearly 50,000 new cases are detected.
What is worrying is that more than half of cases are diagnosed at a late stage when the chance of cure is very low, while if detected early, surgery to remove a lobe or segment of the lung can cure 80% of patients.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to help change this situation by promoting large-scale screening programs.
The current standard of care is low-dose chest CT, which does not require contrast agents, is less risky, and is more accurate than conventional X-rays.
Two large studies - NLST in the US (2011) and Nelson in Europe (2020), have demonstrated that screening heavy smokers can reduce lung cancer mortality by at least 20%.
However, widespread screening also carries the risk of overdiagnosis and false positives, leading patients to undergo unnecessary biopsies or even surgery.
Professor Marie-Pierre Revel, head of the radiology department at Cochin Hospital, said the problem of false positives became more serious when moving from small-scale studies to large-scale screening. Ms. Revel stressed the need to minimize the risk of harm for the more than 98% of people who have chest CT scans and do not have any malignant lesions.
Advances in AI are opening up new approaches. Tech companies have used the NLST study’s massive image database – millions of scans and one million nodules in 200,000 patients – to train algorithms to identify malignant nodules.
French company Median developed the “Eyonis LCS” solution based on this data platform and has demonstrated its ability to help radiologists make more accurate diagnoses. The company now expects to receive FDA approval and CE Marking certification (certification of product compliance with European Union law) by 2026.
In the market, Optellum was the first to be approved by the FDA for its “Virtual Nodule Clinic” software in 2021. From 2023, this AI analysis will be paid by the US up to 650 USD/time, a level considered as evidence of the health system’s trust in the role of AI in reducing costs and reducing deaths from lung cancer.
The US has expanded screening targets since 2021 and further relaxed the criteria in 2023, bringing the number of eligible people to 19 million. However, actual participation rates remain below 20%. Meanwhile, Europe launched the Solace program in 2023 to study how to reach high-risk but hard-to-reach groups such as women, low-income people and ethnic minorities.
According to Professor Revel, Europe is cautious but not slow. Previously, AI was not reliable enough, yielded many false positives and the screening strategy was unclear; but now the technology is ripe for deployment. Croatia took the lead in 2020, followed by Poland, the Czech Republic, the UK (from last October) and Germany (from April 2026).
In France, the National Cancer Institute (INCa) is running a pilot program called Impulsion to determine the appropriate screening process before rolling it out nationwide. The program will assess whether negative diagnoses by AI-assisted radiologists need to be read by a second expert. INCa wants to “re-test” the AI before it is widely adopted.
Professor Revel asserted that AI is only suitable for the role of a second reader and cannot replace radiologists because AI still misses some types of cancer.
The Impulsion study is scheduled to start in 2026 with 20,000 patients being scanned initially, then again in years one and three. Final results will only be available by the end of 2029, meaning that the large-scale rollout of screening in France could be further delayed.
In parallel, data from the Cascade study on lung cancer screening in women will be used to compare existing AI solutions, including “aView LCS” from the Korean healthcare company Core:Line, which has been selected by Germany and France for its added ability to detect coronary artery calcification. Experts propose the creation of the Solace2 project to unify minimum and optimal performance criteria for AI screening in Europe.
Regardless of the chosen option, experts emphasize that screening must be accompanied by a smoking cessation support program because 80% of lung cancer cases originate from smoking habits. In the long term, the fight against tobacco remains the most important foundation for reducing the incidence and mortality of lung cancer./.
(TTXVN/Vietnam+)
Source: https://www.vietnamplus.vn/tri-tue-nhan-tao-mo-ra-ky-vong-moi-cho-sang-loc-ung-thu-phoi-post1076931.vnp





![[Photo] Unique architecture of the deepest metro station in France](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/14/1763107592365_ga-sau-nhat-nuoc-phap-duy-1-6403-jpg.webp)































![[Photo] Unique art of painting Tuong masks](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/14/1763094089301_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Special class in Tra Linh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/14/1763078485441_ndo_br_lop-hoc-7-jpg.webp)








































































Comment (0)