Fiscal Disagreement and a New Cycle of Instability
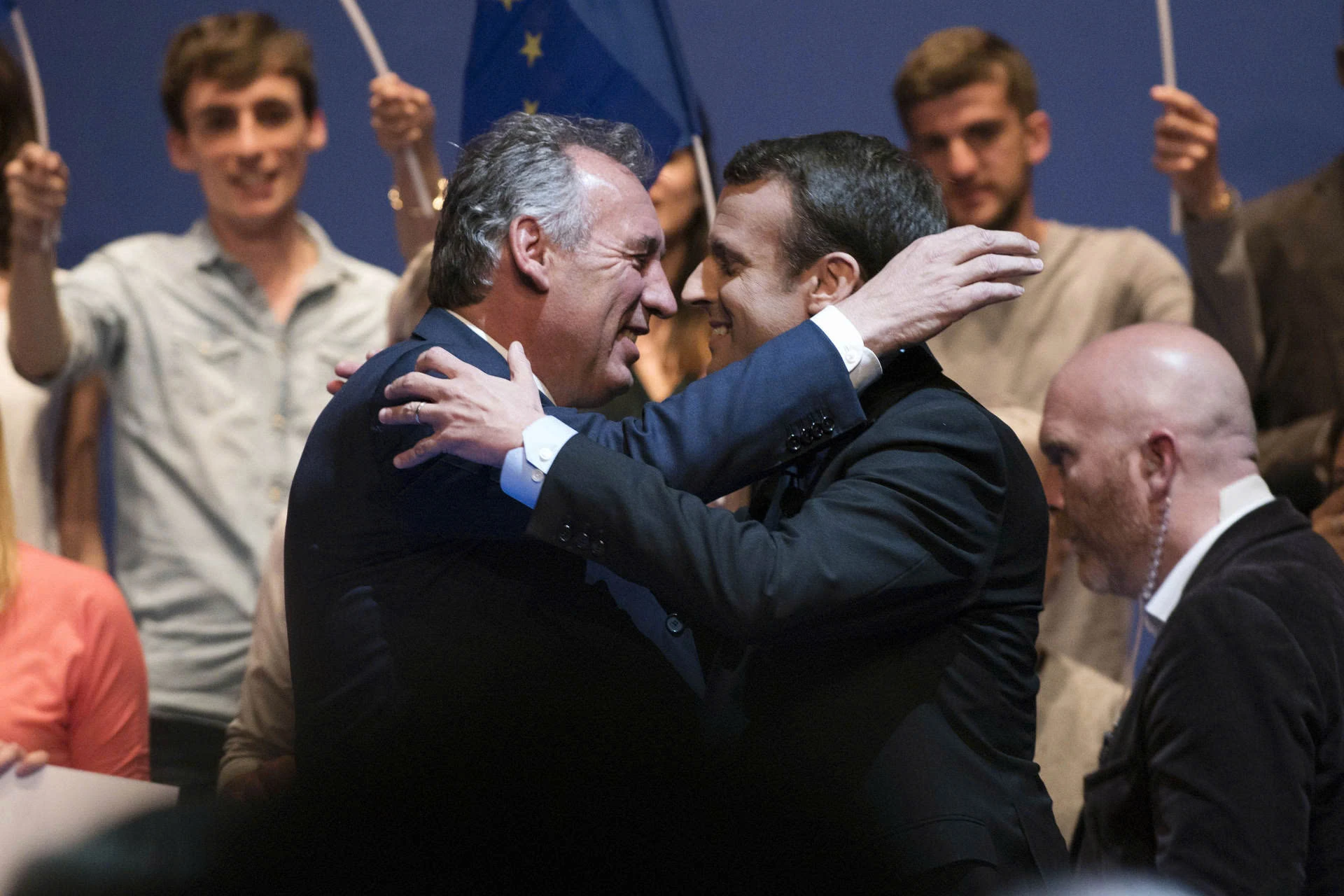
The current crisis erupted after Prime Minister Francois Bayrou proposed a plan to cut public spending to control the rising public debt. However, the plan failed to receive support from political blocs in the National Assembly, leading to a no-confidence vote that brought down Bayrou's government.
In that context, President Emmanuel Macron quickly appointed Defense Minister Sebastien Lecornu as the new Prime Minister. However, the personnel change did not solve the core problems: the current National Assembly is deeply polarized, with no faction holding a majority, causing the legislative process to almost be paralyzed.
Government collapses are no longer a rare phenomenon in French politics today. This is the third time in less than two years that a government has resigned after failing to find consensus in the National Assembly. This situation reflects a worrying reality: the French political system is gradually losing its ability to operate stably in an increasingly fragmented multi-party environment.
According to France 24, the centrist coalition led by President Macron is no longer strong enough to play a central role in the National Assembly. Instead, opposition forces are taking advantage of this instability to increase their influence, although they do not have enough forces to run the government.
In such a context, it is inevitable that the National Assembly will fall into a state of “division and deadlock”. Parties can unite to veto government policy proposals, but cannot build a sustainable alternative.
The collapse of the Bayrou government has caused a wave of mixed reactions in French society. Some people took to the streets to celebrate in front of city halls as an act of protest against the government. These reactions show that the public's dissatisfaction is growing, especially when socio-economic problems such as inflation, the cost of living and deteriorating public services have not been effectively resolved. The disconnect between the political leadership and the real lives of the people is the underlying cause of the continued decline in public trust in the government.
A difficult situation for President Emmanuel Macron
According to the New York Times, this crisis has put President Emmanuel Macron in a difficult position. With his reputation severely reduced (only about 15% of voters trust him, according to a survey by the Verian Group), he is facing high-risk choices.
The first option is to continue appointing a new prime minister, as in the case of Sebastien Lecornu, to maintain stability in the short term. However, if Mr. Lecornu cannot build a majority in the National Assembly, the scenario of another government failure is entirely possible.
The second option is to call early parliamentary elections. However, given the current split in the electorate and the tendency to support opposition parties, this could be a dangerous gamble for the government and President Macron's position.
The final and worst option for President Macron is to resign. While there is no clear sign that Mr. Macron will follow this path, calls for his resignation have been growing from opposition parties, including Jean-Luc Mélenchon’s France Undaunted party and some moderate politicians who once supported President Macron.
Many political experts believe that the current crisis is not simply a temporary incident, but a manifestation of structural weakness in the French institutional system.
Dr. Alexander Kamkin, of the Financial University under the Government of Russia, said that the Bayrou government's failure to adopt fiscal policy was a direct result of the lack of consistency in its governing strategy. He pointed out that President Macron's personal image had undermined his credibility both domestically and internationally, affecting both investor sentiment and the country's credit rating.
Meanwhile, Associate Professor Dmitry Levi, St. Petersburg State University, warned that the frequency of changing prime ministers in a short period of time is a sign of a deep institutional crisis that could last until the upcoming presidential election. In addition, another notable factor is that foreign policy is prioritized while domestic issues are neglected, causing President Macron's traditional voter base, especially the middle class and moderate left, to increasingly distance themselves from him.
With traditional parties on the defensive, far-right forces, especially Marine Le Pen’s National Rally (RN), are emerging as a potential force in the upcoming elections. It is entirely possible that this party could increase its influence in the National Assembly, or even successfully run for the presidency, if the trend of instability continues to spread.
The current political crisis in France is not only an internal event, but also a sign of the difficulties and challenges that many European countries are facing. When public trust is declining and the effectiveness of the current administrations in state management is questioned, comprehensive reform becomes inevitable.
France's political future, as well as President Emmanuel Macron's standing, depends on his ability to present a vision that reconciles interests, meets voters' expectations and restores stability to a shaky political system.
Hung Anh (Contributor)
Source: https://baothanhhoa.vn/chinh-truong-phap-truoc-nhung-thach-thuc-moi-261084.htm




![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of the House of Representatives of Uzbekistan Nuriddin Ismoilov](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761542647910_bnd-2610-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Party Committees of Central Party agencies summarize the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW and the direction of the Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761545645968_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)

































































































Comment (0)