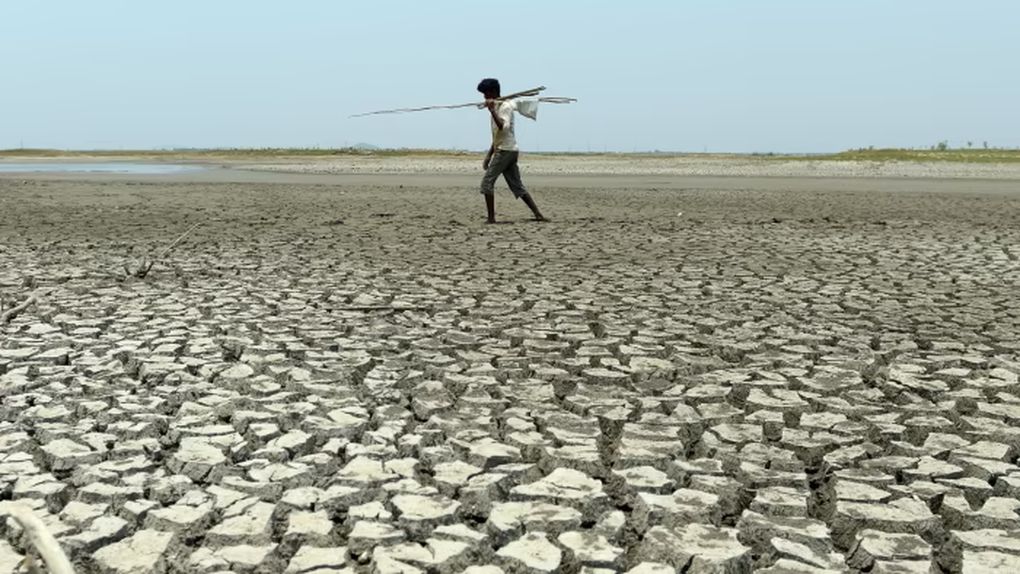
An Indian man walks through a dry lake bed on the outskirts of Chennai, India (Photo: AFP).
Very few people live longer than a century. So if no one had children, there would probably be no humans left on Earth within 100 years. But before that happens – even if all births suddenly stopped – the process would still begin with a slow decline in population.
The elderly will die, while no more children will be born. Eventually, there will not be enough young people left to do essential work, such as producing food, providing health care, and other minimal tasks required to ensure the survival of human society.
This could cause societies around the world to rapidly collapse.
Professor of anthropology Michael A. Little at Binghamton University, USA – an expert in human behavior, biology and culture – commented: “Eventually, civilization will collapse.
It is likely that there will not be many people left in 70 or 80 years, rather than 100, due to the lack of food, clean water, medicine and everything else that you can easily buy now and need to survive.”
Disasters can lead to sudden changes
It is certainly very unlikely that reproduction will suddenly stop, barring a global catastrophe.
Here's a potential scenario that writer Kurt Vonnegut explored in his novel Galapagos : A highly contagious disease could render everyone of reproductive age infertile.
Another possibility is a nuclear war, leaving no one alive. This theme has been explored in many horror movies and novels.
In the 1960s and 1970s, many people worried that there would be too many people on Earth and that this would cause major disasters. These scenarios became the focus of many works about dystopias – dark, problem-ridden societies.
Future of 10 billion people
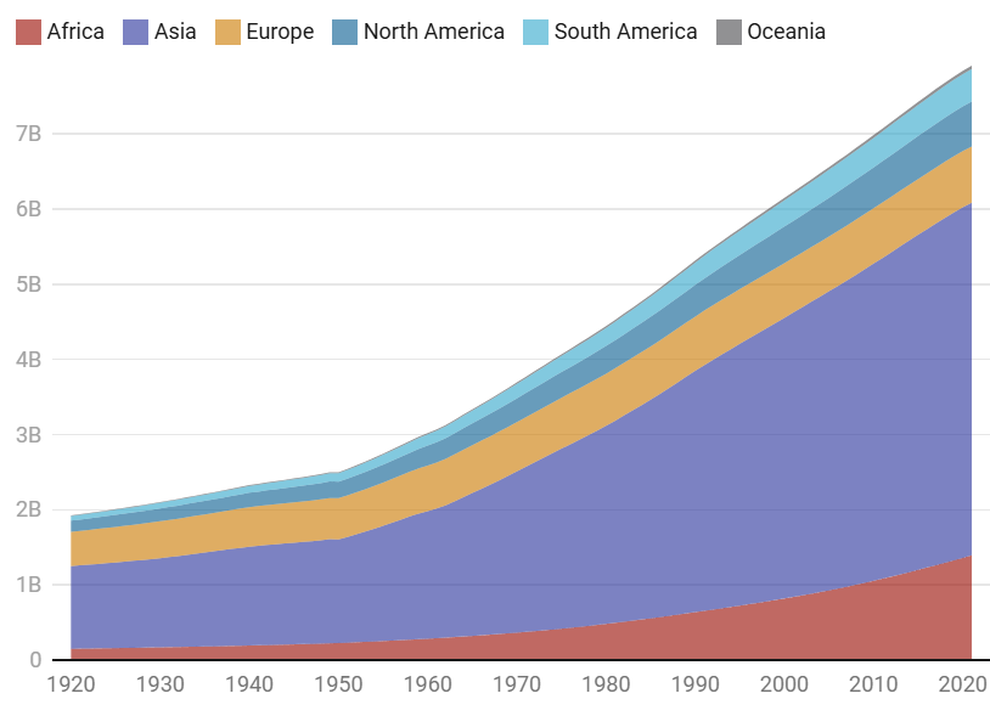
The reality is that the world's population is still growing, although at a slower rate. Population change experts predict that the global population will peak at 10 billion around the 2080s.
In 2024, there will be 132 million babies born worldwide – down from 139 million in 2014. Meanwhile, the number of global deaths in 2024 will be 62 million, compared to 56 million in 2014. Thus, after 10 years, the ratio of deaths to births has increased from 40% to 47%.
A key factor as population trends change is whether a society can maintain a balance between the young and the old. Young people are often the driving force of society – they are the key force in creating everything we use every day.
In 1974, the world had 4 billion people. The United Nations estimates that the current global population will double, exceeding 8 billion by 2022, in just 48 years (Photo: OWID/UN).
Declining birth rate
In many countries, women are having fewer children during their reproductive years than they did in the past. The decline is most pronounced in countries like India and South Korea. Today’s declining birth rates are largely due to personal choice – many people are deciding not to have children, or not to have as many as their parents.
At the same time, many men are also facing fertility problems. If this situation worsens, it could contribute significantly to population decline.
Neanderthals became extinct
Modern humans – Homo sapiens , or upright humans – have been around for at least 200,000 years. While that’s a long time, like every other species on Earth, we face the risk of extinction.
Consider the fate of the Neanderthals – a close relative of Homo sapiens . Neanderthals appeared at least 400,000 years ago, living alongside the ancestors of modern humans. However, they gradually declined and became extinct about 40,000 years ago.
Some scientists believe that Homo sapiens were more successful because they were better able to raise their children and reproduce more.
If humans were to become extinct, it would open up opportunities for other animal species to thrive. But at the same time, it would be a great loss – all the achievements of human art, science and civilization would disappear.
According to scientists, to ensure a long-term future for humanity, we need to take concrete steps such as controlling climate change, avoiding war, and especially conserving nature.
A healthy planet for all living things, including humans, depends on a balance between species, from animals to plants. Protecting nature is protecting ourselves.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/con-nguoi-se-bi-tuyet-chung-sau-bao-lau-neu-ngung-sinh-con-20250617175037890.htm







![[Photo] Opening of the 14th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762310995216_a5-bnd-5742-5255-jpg.webp)
















![[Video] Not Alone - Online Safety Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762347906381_sequence-0100-00-17-02still001-jpg.webp)












![[Photo] Panorama of the Patriotic Emulation Congress of Nhan Dan Newspaper for the period 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762252775462_ndo_br_dhthiduayeuncbaond-6125-jpg.webp)







































































Comment (0)