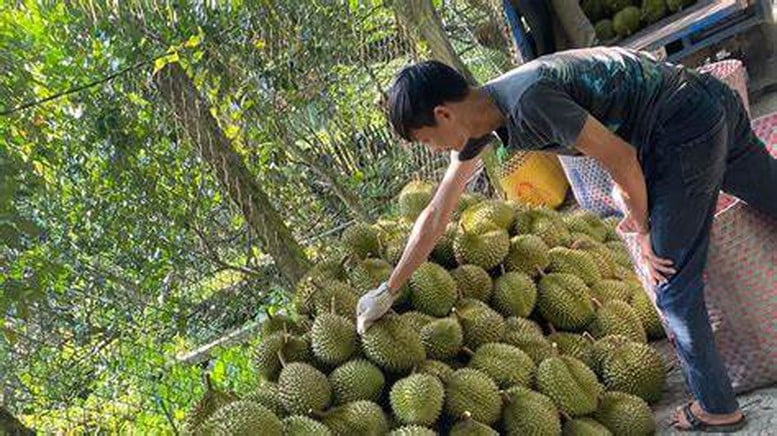

The issuance of 960 codes is a great motivation for Vietnamese durian, reducing export bottlenecks.
This decision is updated periodically every 3 months and sent to China for approval, opening up great opportunities for durian exports, while also setting strict requirements for quality control and sustainable management.
Since the Protocol on Plant Quarantine for Fresh Durian was signed on July 11, 2022, the Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection has coordinated with localities to disseminate regulations and build standard growing areas and packaging facilities.
To date, the Department has proposed 1,604 growing areas and 314 packing facilities, of which 708 growing areas and 168 packing facilities were previously approved. However, some codes have been suspended due to violations of cadmium and yellow O residues. The issuance of 960 new codes demonstrates the efforts of the Ministry, localities, businesses and farmers to meet Chinese standards - a market that accounts for 80% of Vietnam's durian export turnover.
Mr. Huynh Tan Dat, Director of the Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection, emphasized: "The code is not only a management tool but also a brand, asset and reputation associated with durian quality". The issuance of new codes reduces pressure on production, harvesting and trading, while effectively coordinating border gates and reducing congestion - a lesson from the backlog of Thai durian at the Chinese border.
Transparent growing area codes
To maintain sustainable exports, the Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection has built a national database on agricultural exports, transparently managing information from growing area codes, output, acreage, to the production - packaging - export chain. Only shipments with complete information, matching the system, will be cleared after inspection at the border gate. The Department is also drafting a circular on durian management from production to export and submitting a government telegram with a comprehensive solution to serve market expansion negotiations.
To overcome pollution from nitrogen, chemical residues and heavy metals such as cadmium, the Department also deployed 7 models in Tien Giang (Cai Be, Cai Lay) with 3 key solutions: using biological fertilizers, soil improvement fertilizers (biochar, microorganisms) and crop rotation with metal-absorbing plants. The results will be replicated, combined with food safety monitoring programs and heavy metal distribution maps. In particular, the Department recommends limiting fertilizers containing high levels of Carbendazim, requiring the content to be declared on labels and controlling 100% of imported fertilizer batches, with businesses and local agricultural departments monitoring quality.
Regarding yellow O and Ethofumesate – banned substances, the Department has coordinated with the police to handle violations, requested the cleaning of packaging facilities, and proposed 23 laboratories to test Carbendazim (12 accredited) and 13 laboratories to test Ethofumesate (8 accredited). This system, in coordination with the Department of Quality, strengthens inspection throughout the production chain, ensuring the rate of variation in test results within acceptable limits.
Durian contamination is caused by Carbendazim residues in the soil, low soil pH, and excessive fertilizer use in new growing areas. The Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection has conducted a survey in the Southwest, identified the causes, and coordinated with the Institute of Soil and Fertilizers to develop safe cultivation procedures. Solutions include balanced fertilization, good agricultural practices, and avoiding the use of Ethofumesate. Substandard shipments, often returned due to contract or import standard violations, are handled according to plant quarantine regulations.
The Department is also stepping up training and education for farmers, guiding them to comply with cultivation processes, fertilize properly and use pesticides properly. Cultivation standards and food safety control are being developed, combined with a model linking farmers - businesses - exporters to trace the origin transparently. Businesses are supported with quarantine in growing areas and packaging facilities, with human resources arranged at border gates to shorten procedures.
The Department also conducts surprise inspections of agricultural materials, closely monitors prohibited activities, and develops plans to combat counterfeit and substandard goods. These measures not only protect the market but also enhance the reputation of Vietnamese durian.
The issuance of 960 codes is a great motivation for Vietnamese durian, reducing export bottlenecks and consolidating its position as the "king of fruits". With a strict management system, business support, and quality commitment, the durian industry promises sustainable development, bringing Vietnamese agricultural products to the international market. With a heavy metal monitoring program and sustainable growing area planning, Vietnam aims to diversify its markets (EU, Japan, Korea), aiming for 5 billion USD by 2030.
Do Huong
Source: https://baochinhphu.vn/loi-mo-cho-phat-trien-ben-vung-nganh-sau-rieng-102250522163705631.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's special meeting on law-making in May](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/1c880aae96fd4e0894abc47a46fe19ba)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs a working session with the Central Internal Affairs Commission](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/3b7790f499da45b2803d8ae253207ef1)















































































![[Podcast] Week introducing more than 500 OCOP products in Hanoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/22/d144aac2416744718388dbae3260e7fd)





Comment (0)