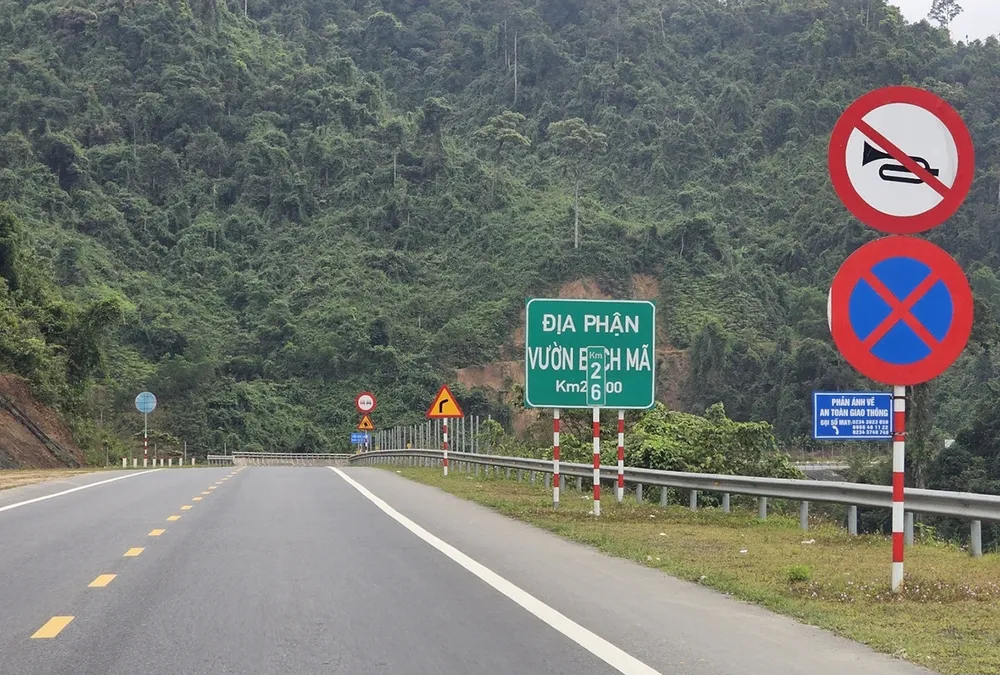
The immediate measure is to put up signs prohibiting honking when cars pass through Bach Ma National Park. Photo: MINH PHONG
Habitat fragmentation
Phase 1 (2015-2022) of the La Son - Hoa Lien expressway project has 9.5km going through Bach Ma National Park, with the area of forest land recovered up to 64.9ha. The section from Km26+500 to Km36+000 is arranged with 6 viaducts and 10 stream crossings. However, these works are not enough to maintain the connectivity of the habitat. Gibbons and red-shanked doucs, which depend heavily on the continuity of the forest canopy, are clearly affected.
A representative of Bach Ma National Park ( Hue City) said that immediately after the highway was put into operation, high-speed traffic created double impacts such as noise, night light, dust and exhaust fumes. These are factors that disrupt the natural behavior of animals such as changing feeding habits, mating, and migration. In particular, the fence along the route becomes a "separation wall", forcing animals to find a detour or risk crossing the road, increasing the risk of collision with vehicles.
Also here, the small forest patrol route (old provincial road 14C) was used as a material transport route. After the project was completed in 2022 with a 5m wide roadbed and graded stone surface, after only three rainy and stormy seasons, the drainage system was severely damaged. As a result, the patrol route connecting Huong Loc Ranger Station and Khe Mo Rang was cut off, significantly reducing the effectiveness of forest management, protection and forest fire prevention and fighting.
In phase 2, the project was expanded from 2 to 4 lanes. The area of implementation was mainly within the converted land area, so no additional forest area was encroached. However, the environmental pressure was not reduced. The doubling of traffic also meant increased noise, dust, and light, directly affecting the wildlife population living along the route.
In Kim Ngan commune ( Quang Tri province), upstream of An Ma lake, many birds were blinded by the headlights of vehicles, flying straight into the vehicles, endangering the drivers and reducing the number of wild birds. Some wild chickens panicked at the sound of the engine and headlights, ran out onto the road and were crushed to death.
Urgent need for ecological corridors
According to a survey by SGGP Newspaper reporters on the North-South expressway from Ha Tinh to Da Nang, many sections of the expressway pass through dense forests and economic forests, creating many requirements for wildlife conservation.
Mr. Nguyen Vu Linh, Director of Bach Ma National Park, said that ecologically, a feasible solution is to plant trees along the route and build ecological corridors connecting the two sides of the road. Constructions such as green overpasses, tree-covered underpasses, wet sewers for amphibians, and rope bridges for primates need to be added, and more native tree species must be planted to attract animals to move through these constructions instead of crossing the road. An equally important task is to renovate and upgrade the Huong Loc - Khe Mo Rang patrol route.
When phase 2 is completed, ranger motorbikes will not be allowed on the highway, while the turning points are too far away (one in Huong Phu, one in Hoa Lien). Without an alternative patrol route, forest protection, forest fire prevention and fighting, and rescue will be in a passive position.
In terms of technology, experts recommend investing in a system of watchtowers with smart cameras, infrared sensors and automatic surveillance. Thanks to that, the authorities can detect and warn early cases of illegal forest encroachment, hunting or forest fire risks. In parallel, it is necessary to deploy wildlife warning signs, limit speed in sensitive areas, install noise-reducing walls and directional lighting.
Conservation expert Nguyen Luong said: “Currently, many highways in Vietnam go through natural forests and economic forests, fragmenting habitats, making it difficult for wildlife to migrate. The first solution is to plan routes that avoid the core of forests and sensitive buffer zones, prioritizing detours or building long overpasses to maintain ecological connectivity. If forced to go through, it is necessary to design ecological crossings such as overpasses covered with trees, wide natural underpasses, small, damp culverts for amphibians, or rope bridges for primates. Accompanying them are directional fences and camera trap monitoring systems, AI warnings.”
This expert also recommends that for forests with highways passing through, it is necessary to combine off-route biological corridors, restore forest cover, and continuously connect between forest stands; and build biodiversity monitoring stations to monitor long-term impacts. It is important to assign responsibility for maintaining works beyond ecological boundaries, and to coordinate with local authorities and forest rangers to both develop infrastructure and conserve biodiversity.
MINH PHONG - VAN THANG
Source: https://www.sggp.org.vn/duong-cao-toc-bac-nam-qua-bac-mien-trung-nghien-cuu-thiet-lap-hanh-lang-bao-ve-dong-vat-hoang-da-post813014.html








![[Photo] Cutting hills to make way for people to travel on route 14E that suffered landslides](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/08/1762599969318_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-2025-11-08t154639923-png.webp)





































![[Video] Hue Monuments reopen to welcome visitors](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762301089171_dung01-05-43-09still013-jpg.webp)



































































Comment (0)