As it entered the Philippine-controlled ocean area, Mawar (known as Betty in the Philippines) reached winds of up to 270 km/h, far exceeding the “above level 17” level on the extended Beaufort scale used by Vietnam. The Independent quoted the Philippine weather agency as saying that on May 28, the storm maintained its strength as it continued to move north, prompting the country to issue warnings of thunderstorms and landslides in some areas.
Previously, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the US National Weather Service predicted that the hurricane season in the central Pacific Ocean - the area north of the equator of this ocean - will have a more than 50% chance of above-normal activity. A near-normal hurricane season in this region will have about 4-5 tropical cyclones - including tropical depressions, tropical storms and typhoons - while the total number of tropical cyclones in the season from June 1 to November 30 this year could reach 7.
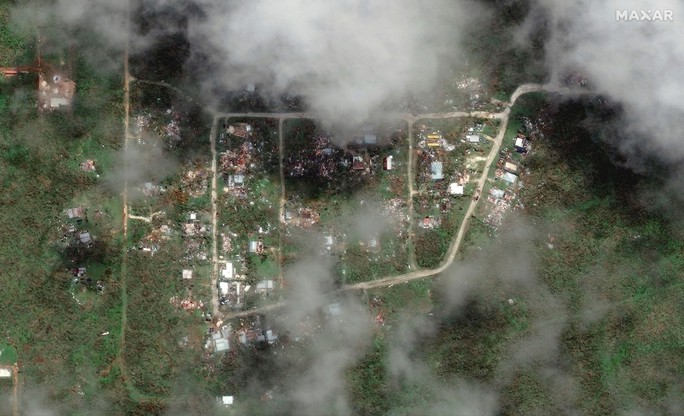

Satellite images show the devastation caused by super typhoon Mawar on Dededo village in Guam - US on May 26. Photo: REUTERS
"A key factor influencing our forecast is the emergence of El Nino. This could start this summer, and El Nino typically contributes to increased tropical cyclone activity in the Pacific Ocean ," said hurricane forecaster Matthew Rosencrans of NOAA's Climate Prediction Center. NOAA stressed that the forecast is a general guide to tropical cyclone activity, not a prediction of whether storms will affect a specific area of the Pacific Ocean, including Hawaii.
NOAA also forecasts a 40% chance of a near-normal Atlantic hurricane season, 30% above normal, and 30% below normal, with 12-17 named storms in the region, including 1-4 major storms. El Nino typically keeps hurricanes in the Atlantic, but some regional conditions, including warmer seas due to climate change, are fueling storms.
Source


![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City holds funeral for former President Tran Duc Luong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/24/9c1858ebd3d04170b6cef2e6bcb2019e)


![[Photo] The Government Standing Committee works with ministries and branches on the real estate market situation.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/24/e9b5bc2313d14c9499b8c9b83226adba)



















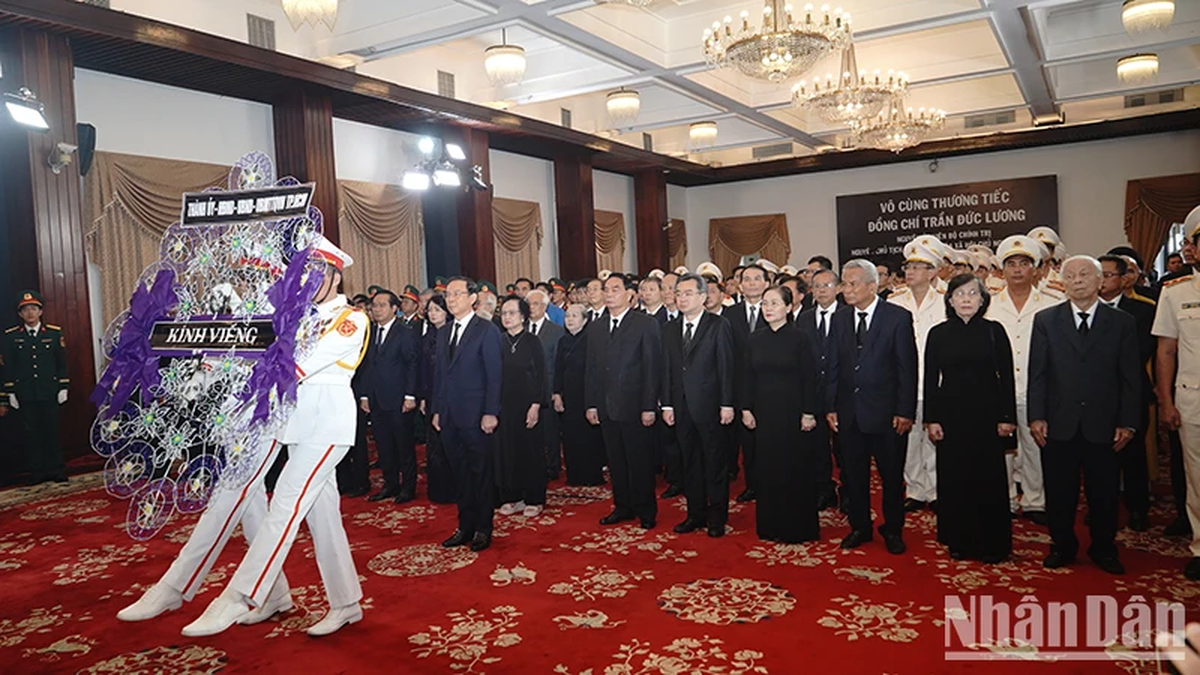
![[Photo] Party and State leaders visit former President Tran Duc Luong](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/24/960db9b19102400e8df68d5a6caadcf6)







































































Comment (0)