The eternal flame can be considered a special case of gas leakage from a deep underground reserve, according to Giuseppe Etiope, a geologist at the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology in Rome, Italy.
When natural gas from reserves deep underground escapes through cracks in the rock, it can spontaneously combust for thousands of years.
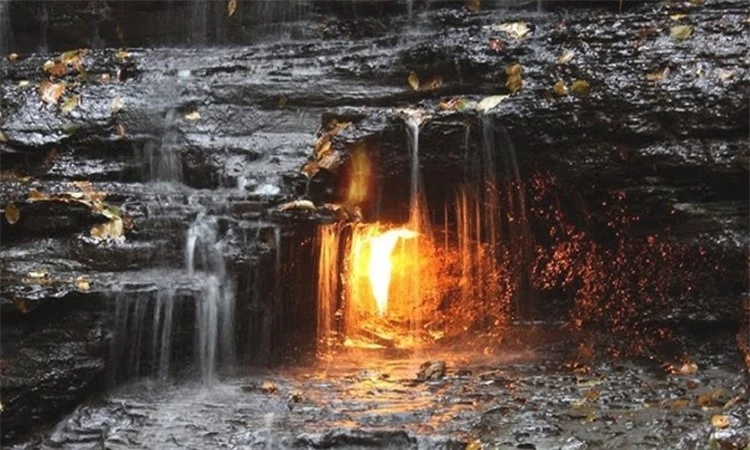

A gas leak occurs when naturally occurring flammable gases underground, primarily methane, ethane, and propane, move to the surface from pressurized reserves through cracks or holes in rock. In extreme cases, when the gas reaches the surface in high enough concentrations of methane, it can spontaneously combust. Fueled by continuous gas emissions, some fires can burn for thousands of years, earning them the name eternal flames.
Ethiopia estimates there are fewer than 50 eternal flames worldwide, typically found near oil wells. They exist in countries including the United States, Romania, Italy, Turkey, Iraq, Azerbaijan, Taiwan, China, India, and Australia. Some may have been growing for thousands or tens of thousands of years, or even as far back as a million years.
A famous flame lies beneath a 32-foot waterfall in Chestnut Ridge County Park in New York. The flame is between 3 and 8 inches high, depending on the weather and season. “It glows behind the hanging curtain of water,” Arndt Schimmelmann, an earth scientist at Indiana University, described it. Ethiopia also said it was the most beautiful natural eternal flame he had ever seen.
Although some have burned for millennia, eternal flames can be extinguished. “The name ‘eternal flame’ is a bit misleading because the geological history of Earth suggests that nothing is eternal,” Schimmelmann says. Some flames can be extinguished by rain, depending on the intensity of the gas leak and ground conditions, and then spontaneously rekindle.
At Chestnut Ridge, splashing water into a small cave can extinguish the flames. “I’ve done this myself a few times when I’ve taken gas samples for geochemical analysis. It’s always a challenge to reignite the fire without getting drenched by the waterfall,” Schimmelmann says. In fact, the fire could disappear due to natural erosion as the waterfall recedes. Losing the cave’s cover would cause the fire to go out regularly, even if the gas flow is uninterrupted.
Geologically induced hydrocarbon seeps, including eternal flames, are a source of natural greenhouse gases such as methane and photochemical pollutants such as ethane and propane. The Chestnut Ridge fire releases about a kilogram of methane per day. There are so few eternal flames that their environmental impact is small compared to the thousands of gas leaks worldwide. Gas drilling can extinguish nearby eternal flames by lowering the pressure of the gas field that fuels them. The eternal flames in Chestnut Ridge Park exist today because no drilling occurs in that area.
According to Intellectual Property
Source: https://doanhnghiepvn.vn/cong-nghe/ly-giai-khoa-hoc-phia-sau-ngon-lua-vinh-cuu/20241201120845994





![[Photo] Da Nang: Hundreds of people join hands to clean up a vital tourist route after storm No. 13](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/07/1762491638903_image-3-1353-jpg.webp)











































































































Comment (0)