Parents need to remember some notes when giving their children milk to ensure providing a healthy source of nutrition for their children.
Milk plays an important role in children's nutrition, from infancy, toddlerhood to adolescence. According to Master, Doctor Nguyen Anh Duy Tung - Nutrihome Nutrition Clinic System, there are many different types of milk, providing nutritional content from birth to developmental stages in a child's life. Types of milk that children can drink include: cow's milk (including whole milk, 2%, 1%, fat-free or low-fat and flavored like chocolate milk); goat's milk; milk substitutes (such as rice, almond, soy, coconut, cashew and oats).
In particular, cow's milk provides a variety of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that children need to support growth and development. Of which, cow's milk naturally contains protein, calcium, potassium, and vitamin B12; cow's milk has vitamin D (added during processing) and vitamin A added to low-fat and non-fat milk. These nutrients are important for growth and development, so the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that younger children drink 2 cups of milk a day and older children 3 cups.
Dr. Tung emphasized that cow's milk or cow's milk products provide nutritional benefits for children after 12 months of age (without milk allergy). The recommended dose for young children is: 2-3 glasses of milk equivalent to about 400-600 ml of milk per day. In addition to drinking milk, children also need to eat some other foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to achieve the recommended daily amount of vitamin D, equivalent to 600 IU.
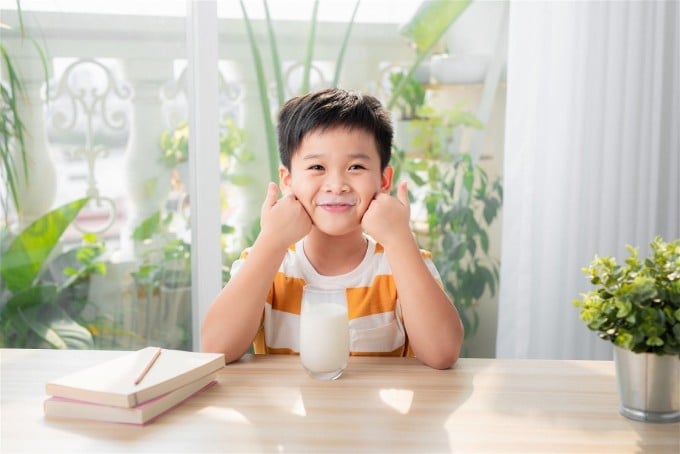

Milk provides a variety of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients that children need to support growth and development. Photo: Freepik
If your child does not drink milk, parents can choose alternative dairy foods that still have equivalent nutritional value, such as cheese, yogurt or other foods rich in calcium and vitamin D. Dr. Duy Tung said that children can still be provided with enough daily nutritional needs without drinking milk through a healthy planned diet. For children who do not like liquid cow's milk or have lactose intolerance, parents need to feed their children nutrients from other cow's milk alternatives.
"The diet of children who cannot drink milk must include foods rich in protein, calcium, potassium and vitamins A, B12 and D to ensure growth and development," said Dr. Tung.
Additionally, children with milk allergies or lactose intolerance need to use specialized milk. Signs of milk allergy in children can include rashes, wheezing, vomiting, diarrhea or even anaphylactic shock. Some children may outgrow milk allergies as they grow older.
Lactose intolerance is a condition where a child can eat some dairy products but experiences gas, diarrhea, abdominal pain and nausea if they eat too much. Unlike a milk allergy, lactose intolerance means that the child cannot fully digest the lactose in milk because they do not have enough of the necessary enzyme.
In this case, children can usually tolerate a certain amount of milk (the amount depends on each child). For example, children only show symptoms if they drink more than 300 ml of milk, but drinking 200 ml is fine. In cases of allergy or intolerance to milk, parents should take their children to see a specialist so that a specialist can give nutritional recommendations appropriate to the child's condition.
Bao Bao
Source link



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam received the delegation attending the international conference on Vietnam studies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761456527874_a1-bnd-5260-7947-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres attend the Press Conference of the Hanoi Convention Signing Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761391413866_conguoctt-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the opening of the 47th ASEAN Summit](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/26/1761452925332_c2a-jpg.webp)

























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/25/1761390815792_ctqh-jpg.webp)











































































Comment (0)