Pneumonia usually requires only a short course of treatment. However, it is not uncommon for children to have persistent, recurring pneumonia, many of whom are so seriously ill that they require hospital treatment.
Persistent, recurrent pneumonia in children can cause death or severe complications related to mechanical ventilation, hospital infections, malnutrition, anemia... leading to high treatment costs, increased medical burden, prolonged treatment time, and severe illness will cause stress for the patient's family.
Finding the cause and treating these patients is always a challenge. Therefore, preventing pneumonia and persistent, recurrent pneumonia is extremely important.
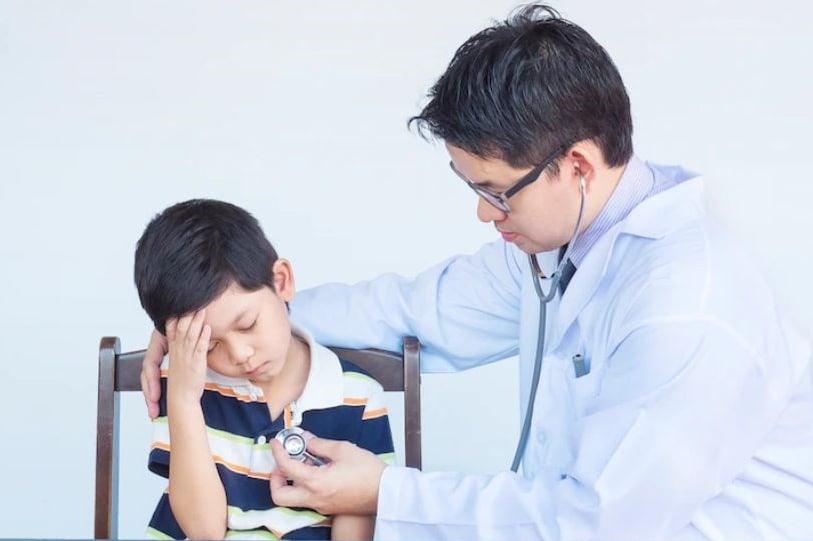
Pneumonia is a common disease in children and is one of the leading causes of death in children. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in children, especially children under 5 years of age in developing countries. A high proportion of children with pneumonia will progress to persistent, recurrent pneumonia, posing significant challenges for pediatricians and respiratory specialists.
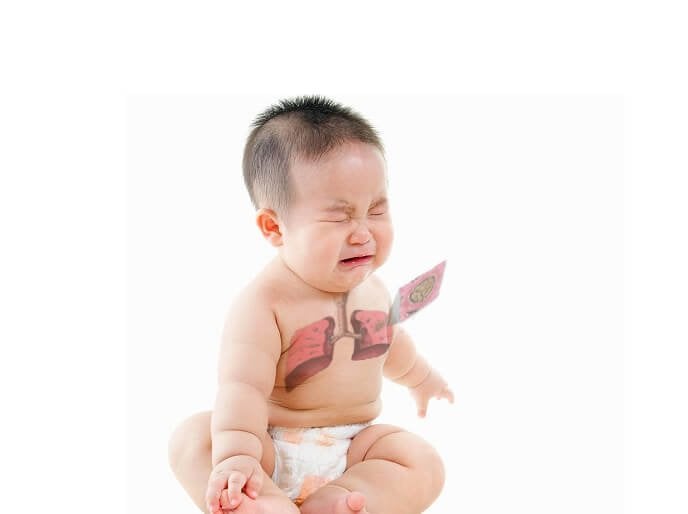
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma. Illustration photo
Persistent, recurrent pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung parenchyma. Persistent pneumonia is pneumonia with clinical symptoms and pneumonia lesions on X-ray, lasting for 30 days or more, despite treatment with antibiotics for at least 10 days.
Recurrent pneumonia is a child with 2 or more episodes of pneumonia in a year, or 3 or more episodes of pneumonia at any time; there are no more clinical symptoms and pneumonia lesions on X-ray between episodes of pneumonia.
Causes and risk factors for persistent and recurrent pneumonia
There are many causes of pneumonia, which can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi... However, there is a certain percentage of children with prolonged pneumonia of unknown cause. For recurrent pneumonia, there are many causes such as secondary infection of asthma, foreign bodies in the airways, airway obstruction due to tumors, bronchial stenosis, immunodeficiency, congenital heart disease... especially when the living environment is polluted.
The common risk factor is in children under 1 year old, having had pneumonia twice and having to be hospitalized, meaning that the child is in the group with unstable resistance. Usually, children under 6 months old rarely get sick, because they still have antibodies passed on from their mother. After 6 months, children are more susceptible to illness.
Living in a humid environment is also the cause of children being infected with the syncytial virus, reducing resistance, making them susceptible to pneumonia. If children are frequently hospitalized for pneumonia, it is likely that they have an allergic constitution, and the disease will become more severe when the weather changes.
Pneumonia is a common disease in children and is one of the leading causes of death in children. (Illustration photo).
5 steps to prevent persistent, recurring pneumonia in children
Thus, we must focus on preventing pneumonia, as well as persistent and recurrent pneumonia in children.
- Need a clean environment, the child's living place should avoid exposure to cigarette smoke, the child's room temperature should not be too cold, too hot or too humid. Should improve environmental factors in the house such as keeping the house clean, not letting it be polluted by cigarette smoke, house dust, dog and cat hair...
- Children need to be breastfed, given adequate nutrition to improve resistance, and vaccinated according to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health .
- Pay attention to the room temperature, it must be warm enough in cold weather, cool enough in summer. When the weather changes, if it is cold, keep the child warm, if it is hot, use a fan or air conditioner.
- Pay attention to the fan, keep the speed low, rotate in all directions, do not let the fan blow directly into the child's nose and mouth, because this will dry out the airways. The air conditioner should be set at a temperature above 26 degrees Celsius and do not let the child lie where the cold air is emitted directly.
- It is necessary to treat diseases as prescribed by a doctor. Due to the habit of many parents, they often arbitrarily buy antibiotics or cough suppressants for their children. Not having much knowledge and buying such drugs for children will lead to a decrease in resistance and increase the possibility of pneumonia recurrence in children. Therefore, the best solution is for parents to take their children to the nearest health facility for timely diagnosis and treatment. When children have respiratory diseases, they need to be treated early and on time to avoid dangerous complications of pneumonia.
According to SK&DS
Source

























![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man visits Vietnamese Heroic Mother Ta Thi Tran](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/20/765c0bd057dd44ad83ab89fe0255b783)





































































Comment (0)