Korea is known as a strong industrial country, but in order to move towards a balanced and sustainable economy , the Government of this country also attaches great importance to agricultural development. Korean agriculture impresses with its professionalism and modernity based on technology and has a close connection between production, processing and consumption.
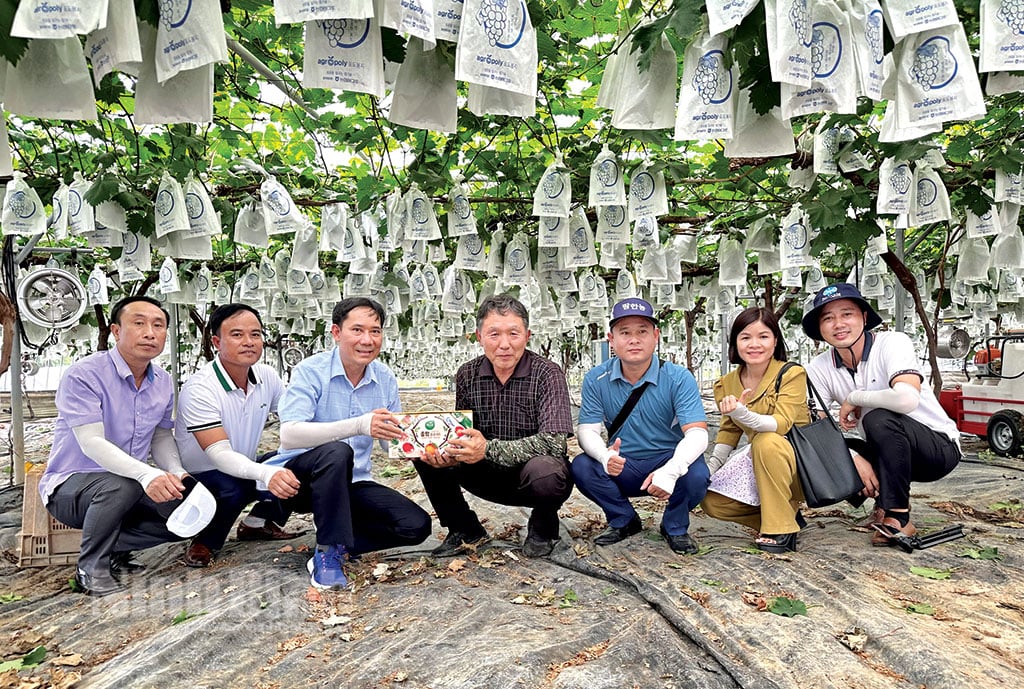

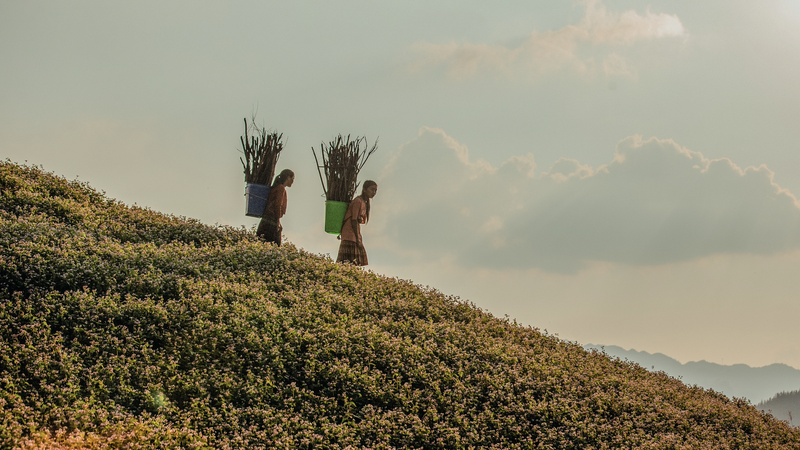
Ninh Binh province delegation visited the organic grape growing model in greenhouses in Asan city (Korea).
A series of promotion policies
Korea attaches great importance to agricultural development and cares for the lives of rural residents. This is evidenced by the fact that the Government has invested up to 6% of GDP in agriculture, although agriculture only contributes about 2% of GDP. Facing difficulties, resource limitations, climate change, labor shortages, etc., Korea has a series of policies and measures to promote agricultural development, bringing many benefits to farmers.
Specifically, regarding land policy, the Government encourages and facilitates the maximum use of existing land funds. Land is privately owned. Korea has abolished the limit on agricultural land since 1999 to facilitate the expansion of production scale. Agricultural land owners are required to use the land for agricultural production and must not leave it fallow for more than one year. Land owners who do not produce agriculture but still want to own it can entrust the land bank to lease it.
The State has a policy of adequate compensation for farmers when reclaiming land. Compensation is carried out in two ways. First, the State and farmers agree on the compensation price according to the market price. Second, if the two parties cannot agree on the compensation price, there will be an independent price appraisal unit, but in principle it must be equal to or higher than the market price.
Regarding credit policy, the State lends capital to farmers at preferential interest rates from 0% - 2.0%, the highest rate is only 50% of the commercial loan interest rate. Farmers can borrow preferential loans up to 70%, even 100% of capital for investment in high technology applications, purchase of machinery, agricultural production equipment, greenhouses, and construction of product preservation facilities.
Regarding science and technology policy, research and development, especially research on improvement, creation of new varieties, and new technologies for production, processing, and preservation of agricultural products, are given special attention. Korea has 240 scientific research facilities, which are institutes and centers. The government invests about 1 billion USD/year in research and development. For staple products such as rice, beans, tomatoes, apples, pears, etc., the State orders research facilities to select and produce high-yield, high-quality varieties that suit consumer tastes to supply to farmers. Research and extension officers are assigned to directly advise each group of farmers, helping farmers promptly resolve difficulties in production.
The Korean government also plans to conduct soil improvement projects for all farmland at least once every six years. Based on soil surveys and predictions for the nutrition of each crop, mineral-rich fertilizers will be provided for farmers to use optimally for each individual plot of land.
Korea has a Price Stabilization Fund for Strategic Commodities to ensure income for farmers and benefits for consumers. It compensates farmers when market prices are lower than the Government-guaranteed price or supports farmers when the Government requires farmers to reduce production scale. Farmers are supported by the State with 80% of agricultural insurance premiums, 50% of pension insurance, etc.
Advanced technology-based agriculture in Asan
Recently, participating in the working delegation of Ninh Binh province to exchange and learn about the agricultural development experience of Asan city, Chungcheong Nam province, we had the opportunity to learn more about the agricultural sector of this locality as well as of Korea.
Asan is known as a key agricultural production center of Korea with main crops being rice, pears, green onions, cucumbers... The agricultural land area is not too large (nearly 15,600 hectares), the labor force in this field is also limited (more than 17 thousand people, accounting for about 5.4% of the population) but the agricultural production value in Asan is very high. This is thanks to the locality focusing on applying high-tech agriculture, through applying modern means and techniques in production, increasing product value in each stage of the production value chain.
Visiting rice fields, pear, apple, grape, blueberry farms... we saw that almost all agricultural production activities are done by machines, from tilling the land, planting, fertilizing, irrigating to harvesting. Most of the farmers here are in their 60s and 70s, but they still cultivate 1-2 hectares of crops without any difficulty. Mr. Im Hong Soon, 72 years old in Mbong-myeon (Asan), who owns a 2-hectare pear garden, shared: "As long as I can hold scissors, I will continue farming because everything can be replaced by machines, very leisurely."
Mr. Nam Yoon Gil, Asan City Agricultural Technology Center said: The center is operating an agricultural machinery rental bank with 571 machines and 91 types of machines. When the season comes, farmers who need to use any type of machine just need to register to rent and will be trained and brought home to use. The center only charges a very small fee for maintenance.
At the PPS Seed nursery, the Agricultural Association Corporation, which specializes in producing and breeding melons, we were impressed by the fact that all management and operation processes are closed in the greenhouse. The steps from mixing soil, sowing seeds, and packing pots are all done by machines. There is a system of machines to measure soil and air humidity, analyze the plant's fertilizer needs, irrigation water... and can suggest solutions to help solve pests and diseases (if any) thanks to data analysis. In particular, the nursery has a heat collection system in the ground at a depth of 180m to provide optimal temperature for plants, thanks to which seedlings are produced continuously regardless of the season.
In addition to focusing on the application of mechanization and automation in production, Asan City is also very interested in the development of sustainable agriculture. Since the 1970s, the Association of Healthy Farms and the Association of Organic Farming Research have been established here. Currently, to reduce environmental pollution caused by chemicals used in agriculture, the amount of chemicals used is reduced by using them effectively and cautiously. The Integrated Pest Management (IPM) program has been introduced to encourage the effective use of chemicals. Fertility-enhancing methods are applied based on land survey results to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers to protect the soil. The quality of agricultural products is strictly controlled through the application of high-quality standards, traceability systems, strict sanctions, and public information on violating units and individuals in the media.
To support farmers in preserving, distributing and consuming agricultural products, the locality has established a local agricultural product circulation system. Accordingly, it will support farmers in connecting food supply for meals in schools and public facilities; rural-urban exchange; promoting export activities as well as developing the agricultural processing industry.
The preservation and processing technology here is developed at a very high level. For example, in the case of rice processing, it is not just simply milling and packaging, the rice processing factories here also supplement nutrition, distribute processed rice in the form of instant rice; moreover, they can automatically package based on the volume and type of each customer, according to the requirements of each customer, then send it to the necessary address without the need for human hands. For pear products, the preservation technology is so good that pears harvested in October can still maintain their quality for sale in May of the following year.
What experience for Ninh Binh?
In fact, agricultural production in Ninh Binh and Asan currently has many similarities as they are both facing many difficulties in climate change, shrinking production areas, labor shortages, etc. Therefore, developing high-tech agriculture is an important solution, a decisive factor in the quality of agricultural economic restructuring, creating a large amount of environmentally friendly products; reducing product costs, reducing manual labor, and reducing dependence on the weather, etc.
Comrade Lam Van Xuyen, Vice Chairman of Yen Khanh District People's Committee, Head of the delegation of cadres and typical farmers of Ninh Binh province attending the Agricultural Development Training Program in Asan last July shared: This is a very meaningful study trip, with many good issues about policies, advances in varieties, techniques, mechanization, organic production, environmental friendliness... for us to learn and apply to our production. In particular, studying your experiences clearly shows the role of State investment capital in many different aspects of the agricultural and rural development program. The State needs to have appropriate policies to support farmers to create favorable conditions for production and increase the competitiveness of agricultural products. It is necessary to develop plans for the development of high-tech agricultural zones and high-tech agricultural regions with appropriate scales. It is not necessary for every place to develop large-scale production, but the most important thing is to know how to exploit the potential and strengths of each locality. It is necessary to advise and support farmers in agricultural production in the direction of specialized cultivation to create large-scale commodity production areas. At the same time, more attention should be paid to converting production towards safety and sustainability, and strict management of the use of chemicals in agriculture to ensure food safety.
Mr. Le Dang Thoa, an officer in charge of agricultural production, Duc Hung Transport and Trading Company Limited (Tam Diep City) shared: Although the trip lasted only 2 weeks, it helped him learn a lot of knowledge, especially the opportunity to access high-tech agricultural production. He was very impressed by the technology of seed production research and post-harvest processing technology of the other side. In particular, through this trip, he learned the techniques of pruning branches, pruning fruits, fertilizing, and watering tomatoes and cucumbers in high-tech greenhouses to apply at the Company.
Farmer Pham Van Huong (Khanh Hoa commune, Yen Khanh district) said: Rice productivity in Asan is very high, averaging about 7.6 tons/ha (in Ninh Binh it is only about 6.2 tons/ha). To achieve this productivity, in addition to good varieties and synchronous technical infrastructure, perhaps your side has a long-term, systematic program to improve the soil, based on the results of soil surveys and forecasts for the nutrition of each crop, mineral-rich fertilizers are provided to optimally fertilize each individual field. We farmers really hope that the State will have such practical research and support.
According to the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development, since 2015, the People's Committee of Ninh Binh province and the government of Asan city, Korea have signed a Friendship and Cooperation Agreement between the two units. Accordingly, in the field of agriculture, up to now, Ninh Binh province has sent 5 delegations of agricultural officials and typical farmers of the province to study and acquire experiences in management and application of high-tech agriculture. Many technical advances from our side have been successfully applied by us. Specifically: Applying the method of making hanging trellises for melon plants in net houses and greenhouses; the method of grafting cucumbers on pumpkin roots; propagating Korean black oyster mushrooms from mushroom varieties from Asan-Korea; some varieties of vegetables, flowers and fruits from Asan such as cucumbers, lettuce, mustard greens, chrysanthemums... have also been tested in Ninh Binh with good yield and quality.
Hopefully "a day of travel teaches a lot", the study trips and the sharing and cooperation from Asan will help the cadres and typical farmers of Ninh Binh have a new, modern and progressive perspective, to apply to their production life, to come up with good models for other farmers to learn and develop together.
Article and photos: Nguyen Luu
Source: https://baoninhbinh.org.vn/an-tuong-nong-nghiep-han-quoc/d20240806075436548.htm






![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attend the 80th Anniversary of the Traditional Day of the Vietnamese Inspection Sector](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/17/1763356362984_a2-bnd-7940-3561-jpg.webp)































































































Comment (0)