The research group successfully developed a process for fabricating novel image-contrast nanofluid systems based on Fe₃O₄, Gd₂O₃, Bi₂O₃, and ultra-small Fe₃O₄–Gd₂O₃ and Fe₃O₄–Au hybrid structures. The group also developed surface modification methods using biocompatible polymers and amino acids to improve the dispersion stability and biosafety of the materials. These materials are designed to meet the requirements for high-level MRI (T1, T2) and CT image contrast enhancement, supporting research into next-generation contrast agents.
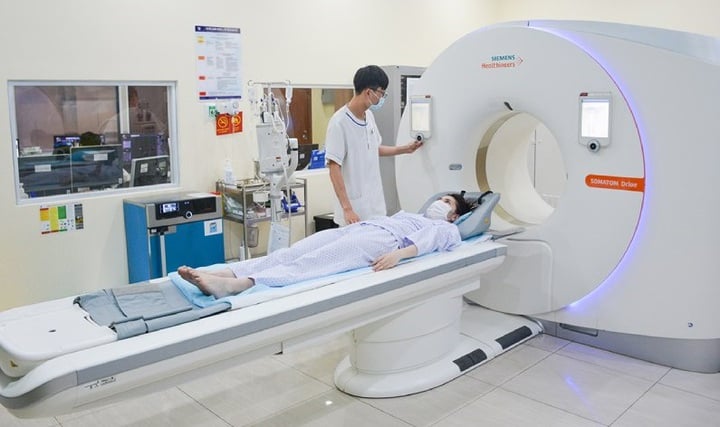
The research topic focuses on perfecting the process of creating nanofluid for MRI and CT.
The project perfected several key technological processes, including the process of creating nanofluid for MRI and CT, the MRI imaging process using the fabricated materials, and the experimental CT imaging process and contrast performance evaluation. The research team conducted in vitro and in vivo experiments on animals (rabbits/mice), evaluating the cytotoxicity, biotoxicity, and image contrast enhancement capabilities of the nanofluid samples. The experimental results were compared with commercial drugs such as Dotarem, Ferumoxytol (MRI), and Ultravist (CT), showing significant application potential.
The project has produced 3 types of nanofluid for MRI, 1 type for CT, 1 technological process for fabricating stable core-shell nanomaterials, 2 optimized MRI and CT imaging procedures based on the fabricated materials, and numerous in-depth scientific reports.
This research has made significant contributions to developing new methods for producing high-quality nanofluid materials. (Illustrative image.)
This research has made significant contributions to developing new methods for creating high-quality, ultra-stable nanofluid solutions. These are essential foundational data for the development of MRI and CT contrast agents domestically, aiming towards the establishment of pilot production projects for nanomaterial systems used in diagnostic imaging.
The socio -economic effectiveness of the research is demonstrated in its ability to reduce dependence on imported contrast agents, meet the urgent need for early detection and treatment of cancer, and contribute to the development of the biomedical technology sector in Vietnam. The report affirms that if further implemented in practice, the products of the project could have a positive impact on the biomedical materials market and the healthcare system.
Source: https://mst.gov.vn/che-tao-chat-long-nano-tuong-phan-anh-mri-va-ct-trong-y-hoc-197251211115125662.htm































































































Comment (0)