Quang Tri province identifies digital transformation in agriculture as the process of integrating and applying digital technology into all activities of the agriculture and rural development sector, changing the way of managing, producing and consuming products from traditional to modern and smart.

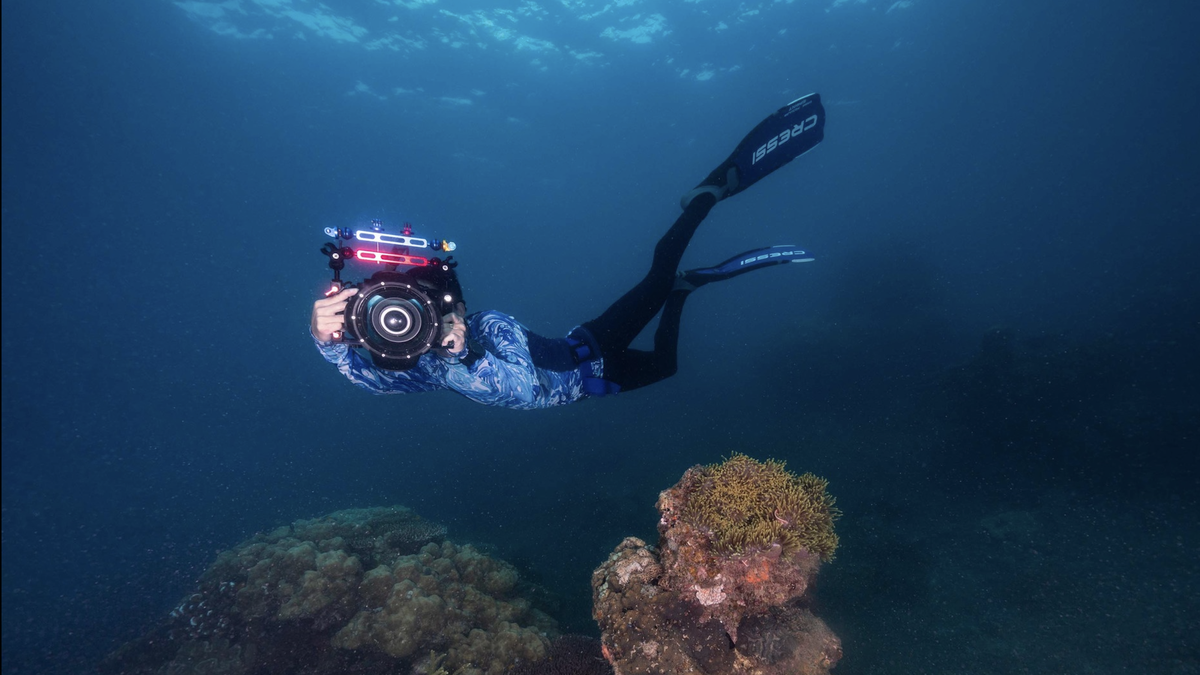
People apply scientific and technological advances to high-tech shrimp farming in Vinh Linh district - Photo: HT
According to Deputy Director of the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development Nguyen Phu Quoc, in the context of international integration, climate change, and epidemics, digital transformation in the agricultural sector is the "key" to sustainable development of the agricultural sector. By focusing on digital transformation in agriculture, many advanced technologies have been applied to production practices, forming models of applying intelligent automation technology, and applying a number of databases to the fields of forestry, irrigation, and fisheries.
Accordingly, the IT infrastructure in the agencies and units under the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development has been relatively complete, basically meeting the work requirements. Administrative procedure reform associated with digital transformation has also received attention and focus. Specifically, the digitization rate of records upon receipt reached 83.4% (7,520/9,017 records); the digitization rate of records upon return of results reached 62.74% (5,648/9,002 records).
Currently, the province has initially applied technology to production, creating quality, clean products to supply the market such as: more than 30 greenhouses with an area of 3 hectares applying high technology; more than 5,000 hectares of crop area applying water-saving irrigation technology and over 20 models applying high-tech processes, Internet of Things (IoT) to the production of Phalaenopsis orchids, lilies, strawberries, super sweet tomatoes, and melons have brought practical results. On the other hand, more than 5,500 hectares of rice, rubber, cassava... are cared for and protected from pests and diseases by drones.
The livestock sector has also undergone a dramatic transformation thanks to the active application of digital technology in all stages and processes. Notably, the application of the geographic information system - GIS in monitoring and controlling avian influenza and managing livestock and poultry diseases through the application of the "Vietnam Animal Disease Information System - VAHIS".
Many livestock farmers have also "caught up" with digital transformation through the use of livestock farm monitoring systems (cameras) connected to the Internet of Things (IOT) and smartphones; applying slaughter management software, traceability or applying closed barn technology with automatic barn air conditioning systems, automatic feeders and waterers, automatic poultry brooders, waste treatment to ensure environmental hygiene with microbiological products, biogas technology...
Promoting the strengths of aquaculture and fisheries exploitation, many enterprises, cooperatives and people have gradually applied automatic equipment to replace humans in shrimp farming (automatic shrimp feeding machines, oxygen warning devices, power warning devices, etc.); applied the system of monitoring and warning the water environment of aquaculture ponds connected to the internet with smartphones; applied VMS technology to monitor fishing vessel journeys to manage fishing vessels, horizontal sonar scanners in purse seine fishing, VX 1700 communication device integrated with satellite positioning, radar scanner system in gill net fishing and automatic steering system on offshore fishing vessels.
In particular, up to now, 100% of cooperative directors use smartphones with 4G/5G network connection to communicate and discuss work; over 80% of cooperatives use accounting software to apply to cooperative financial management.
In recent times, the agricultural sector has also researched, deployed, installed, exploited and effectively operated a system of 35 automatic people's rain gauge stations and automatic, visual natural disaster monitoring, surveillance and warning stations to effectively serve the work of warning, forecasting, directing and operating natural disaster response in the province.
Research, develop and deploy WebGIS technology applications, Google Earth software, Map info to create current status maps, build information and data bases on irrigation systems, rural clean water, dykes, landslides and natural disaster prevention and control.
At the same time, support OCOP stamps associated with traceability for the province's OCOP products; coordinate with the provincial Post Office to introduce and sell 115 OCOP products on the e-commerce platform postmart.vn. Up to now, over 95% of OCOP products have been traded on e-commerce platforms.
In addition to the achieved results, digital transformation and application of information technology in agriculture and new rural construction in Quang Tri still face many difficulties and shortcomings such as: infrastructure serving production and digital transformation is not yet synchronized; the volume of databases requiring digitalization is large while investment resources are still limited; lack of support experts and low digital skills of farmers; Few businesses investing in agriculture...
“The reason for the above limitations is that the budget for investment in information technology infrastructure, information technology application, e-government construction, and digital transformation has not met the actual needs of agencies and units. The information technology level of cadres, civil servants, and public employees of the unit is only at a basic level; awareness of people and businesses about public services is still limited; slow change in the habit of going directly to state agencies to resolve administrative procedures...”, Mr. Nguyen Phu Quoc added.
To promptly seize opportunities, overcome challenges, and strongly develop digital transformation in the province's agriculture in the coming years, the province needs to identify people and businesses as the center and the decisive factor in digital transformation.
In particular, it is necessary to continue to encourage businesses and young workers to participate in digital transformation; train digital transformation experts in agriculture who are good at both theory and practice; at the same time, promote communication, organize training courses, and provide skills training for farmers.
Enhance the provision of information on environment, soil and weather to help farmers improve crop productivity and quality.
On the other hand, management agencies also need to support and share agricultural equipment through digital platforms; design data management software and assign individuals and organizations in the locality to use the software to collect, update, exploit, manage and preserve the database to help improve productivity, profits, optimize production and bring many development opportunities, connect farmers with processing facilities, trade and consumers inside and outside the province, contributing to promoting the sustainable development of the province's agriculture.
Ha Trang
Source


























































































![[OCOP REVIEW] Tu Duyen Syrup - The essence of herbs from the mountains and forests of Nhu Thanh](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/5/58ca32fce4ec44039e444fbfae7e75ec)







Comment (0)