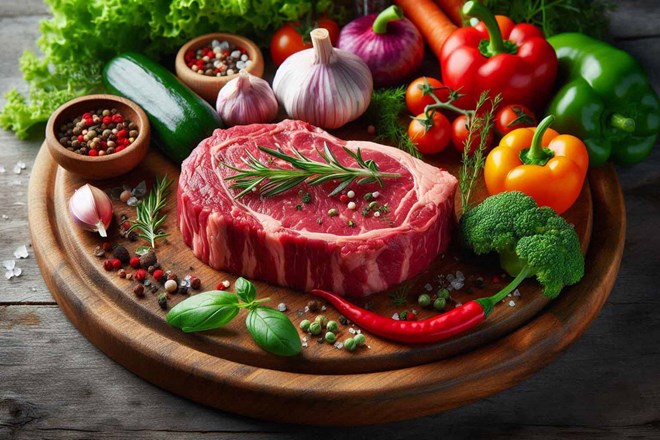

Dr. Sam Ghali - an emergency physician at the University of Florida Health Jacksonville (USA) - said that undercooked meat can cause health risks and can even cause tapeworms in the body.
The adult tapeworms live as parasites and will reproduce and lay eggs, added Mr. Sam Ghali.
Meanwhile, Dr. Pranav Honnavara Srinivasan, senior consultant gastroenterologist at Fortis Centre Bengaluru (India) - shared: "Eating undercooked meat can expose us to a variety of harmful pathogens, including bacteria, parasites and viruses, which can cause food-related illnesses."
Common pathogens found in undercooked meat
According to Dr. Srinivasan, the most common pathogens found in undercooked meat include:
- Salmonella: One of the most common bacteria associated with undercooked poultry. This bacteria can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, mild stomach cramps, and vomiting.
- Escherichia coli (E.coli): Certain strains of E.coli bacteria, especially E.coli O157:H7, are found in undercooked ground beef and can cause serious gastrointestinal upset, including diarrhea, abdominal pain and nausea.
- Campylobacter: Commonly found in undercooked poultry, this bacteria can cause campylobacteriosis, characterized by diarrhea (often bloody), fever, and abdominal pain.
Symptoms usually appear 2 to 5 days after exposure and can last up to a week.
- Listeria monocytogenes: Found in undercooked or contaminated meat. Listeria can cause serious infections, leading to meningitis or sepsis, especially in pregnant women, newborns, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms may include fever, muscle aches, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Toxoplasma gondii: This parasite is commonly found in undercooked pork and lamb. Toxoplasmosis can cause flu-like symptoms, swollen lymph nodes, and muscle aches.
Although many healthy people may not show symptoms, it can cause serious complications in pregnant women.
- Trichinella spiralis: A parasitic roundworm found in undercooked pork or game meat, causes trichinosis, which can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, muscle pain and swelling around the eyes.
How do they grow and multiply in meat?
Bacteria multiply rapidly at temperatures between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C), which is considered the 'danger zone,' Dr. Srinivasan explains.
Undercooked or improperly stored meat within this range becomes a breeding ground for pathogens such as Salmonella, E. coli and Campylobacter.
The high water content in meat creates an ideal environment for bacteria to grow. Rich in protein and fat, meat provides many nutrients for bacteria and parasites to thrive, increasing the risk of foodborne illness when undercooked.
Therefore, poor handling or storage can also cause pathogens to spread from raw meat to other foods, utensils, or surfaces.
Source: https://laodong.vn/dinh-duong-am-thuc/dieu-gi-xay-ra-voi-co-the-khi-an-thit-chua-nau-chin-1389175.ldo


































































































Comment (0)