During the week, Hanoi CDC recorded 12 dengue fever outbreaks in Bach Mai, Thanh Oai (2); Co Do, Ha Dong, Kim Lien, Phu Luong, Phuong Duc, Tam Hung, Thuong Phuc, Yen Nghia, a decrease of 6 outbreaks compared to the previous week. The cumulative total for 2025 is 192 outbreaks, with 27 outbreaks currently active.
This week, the Hanoi CDC monitored the investigation and handling of dengue fever outbreaks in four high-risk areas: Hong Son, Tien Thang, Bo De, and Dan Hoa communes.
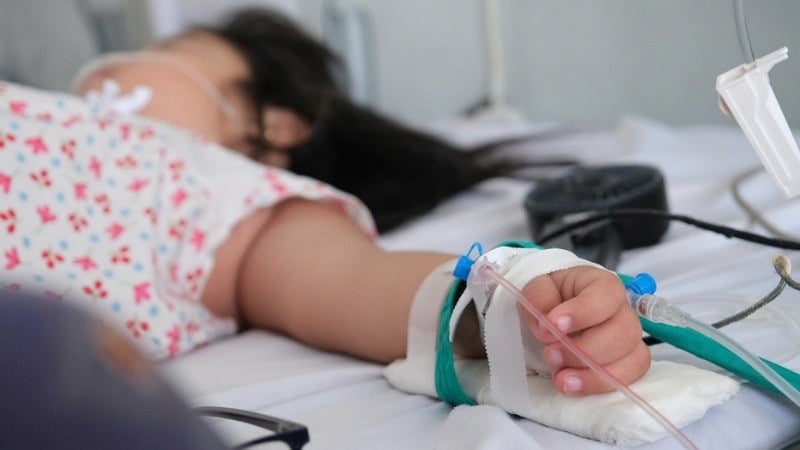 |
| The dengue fever outbreak in Hanoi is on the rise. |
Simultaneously, the Hanoi CDC, in coordination with the Department of Medical Examination and Treatment, supervised disease prevention and environmental sanitation work at the National Assembly building in preparation for the 10th session of the 15th National Assembly; inspected environmental sanitation and collected water samples at the National Exhibition Center in preparation for the 2025 Autumn Fair; and inspected environmental sanitation and collected water samples at the National Convention Center and the JW Marriott Hanoi Hotel in preparation for the signing ceremony of the United Nations Convention against Cybercrime.
In the coming week, commune and ward health stations will continue to effectively monitor and detect patients at designated health facilities, through the software system, and in the community, in order to promptly investigate and handle cases and outbreaks, preventing the disease from spreading widely.
Regularly monitor mosquito larvae and adult mosquitoes that transmit dengue fever in areas where cases have appeared, in old outbreaks, and in high-risk areas, and then implement timely response activities.
Implement proactive measures to prevent and control Chikungunya outbreaks, integrated with dengue fever prevention and control, through campaigns to eliminate mosquito larvae and pupae, and spraying chemicals to kill adult mosquitoes in high-risk areas and outbreak sites.
The Hanoi CDC, in coordination with other units, is monitoring active dengue fever outbreaks in Hoa Xa, Thuong Tin, Tay Mo, and Quang Oai districts, and strengthening health quarantine at Noi Bai International Airport to detect suspected/confirmed cases early and apply appropriate and timely disease prevention and control measures.
Last week, the Hanoi CDC recorded 187 cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease in 74 wards and communes, including 14 cases in Co Do, 9 cases in Quang Oai and Vat Lai, 8 cases in Tay Mo, and 7 cases in Dai Mo; an increase of 56 cases compared to the previous week. There were 17 cases of measles in 12 wards and communes, an increase of 10 cases compared to the previous week. One case of pertussis was recorded in Thanh Xuan, and one case of adult tetanus was recorded in Yen Hoa. No other infectious diseases were recorded during the week.
Severe warning signs that require special attention include extreme fatigue, lethargy, restlessness, abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, vomiting blood, or passing black stools.
When these symptoms appear, patients need to be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible. Importantly, under no circumstances should you administer intravenous fluids at home, as this can worsen the condition and make it more difficult to control.
In the context of the epidemic entering its peak phase, the most effective preventive measures remain proactively avoiding mosquito bites, eliminating mosquito larvae, maintaining a clean living environment, and removing items that hold stagnant water.
People should sleep under mosquito nets, wear long-sleeved clothing, and use mosquito repellent cream or spray. Additionally, for those who are eligible and in high-risk groups, dengue fever vaccination is an effective way to minimize the risk of contracting the disease and serious complications.
Currently, there are two types of vaccines that have been pre-qualified by the World Health Organization (WHO) and licensed for use in several countries: CYD-TDV (Dengvaxia, Sanofi), for seropositive individuals aged 9 years and older, which has been discontinued in many markets; and TAK-003 (Qdenga, Takeda), licensed by the Vietnamese Ministry of Health in May 2024, indicated for individuals aged 4 years and older, requiring no prior serological testing, and administered in two doses three months apart.
The protective efficacy of TAK-003 against dengue fever, determined by virology, reached 80% after 12 months, and its effectiveness against hospitalization was 90% after 18 months.
With its advantages of easy deployment and no need for serological screening, TAK-003 is expected to contribute to a rapid reduction in the epidemiological and economic burden of dengue fever in Vietnam in the coming years.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/so-ca-sot-xuat-huyet-tai-ha-noi-co-xu-huong-tang-d423317.html




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends the Conference summarizing and implementing tasks of the judicial sector.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F13%2F1765616082148_dsc-5565-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)










































































































Comment (0)