Traditional Vietnamese medicine (TM) is a crystallization of indigenous knowledge and Oriental medicine, playing an increasingly important role in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases, rehabilitation and community health care. World trends open up opportunities for international integration of TM.
- 1. Current policy and legal framework on Traditional Medicine
- 2. Major shortcomings that need to be overcome
- 3. International experience
- 4. Proposal to perfect the legal framework for integration
However, legal and technical barriers (registration, testing, standards, intellectual property, post-audit, market) prevent Vietnamese YDCT products and services from penetrating deeply into demanding markets (EU, USA, Japan); export value is still modest and mainly in the form of raw materials. Completing the legal framework is a prerequisite for Vietnamese YDCT to soon integrate internationally.
1. Current policy and legal framework on Traditional Medicine
Law on Pharmacy No. 105/2016/QH13 (issued in 2016) and Law No. 44/2024/QH15 amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Pharmacy, passed by the National Assembly on November 21, 2024; Decree No. 163/2025/ND-CP dated June 28, 2025 detailing a number of articles and measures to organize and guide the implementation of the Law on Pharmacy (effective from July 1, 2025); Law on Medical Examination and Treatment (amended in 2023)... Circulars on drug registration, management of traditional medicines - medicinal herbs, testing. Strategy for development of traditional medicine and pharmacy to 2030, vision to 2045; instructions on conservation - development of medicinal herbs, integration of traditional medicine in the health system.
These policy frameworks create the basic management foundation for the production, circulation and practice of traditional medicine. However, there is a lack of specialized laws for traditional medicine; registration procedures for traditional medicine are still "uniform" with pharmaceutical chemicals; there is a lack of a complete set of national standards for indigenous medicinal herbs; the capacity for testing and mutual recognition is still weak; the protection of traditional knowledge and benefit-sharing mechanisms have not been legalized; there is a lack of a legal framework for knowledge export and international OEM cooperation in traditional medicine.

World trend prioritizes natural medicine.
2. Major shortcomings that need to be overcome
Registration and evaluation of traditional medicines: The multi-component and multi-target characteristics make it difficult for traditional medicines to meet the testing model like pharmaceutical chemistry. The dossier often lacks clinical data according to international standards, leading to a shift to health protection foods, reducing the medicinal value. Accordingly, a mixed evidence framework is needed: Medical literature + practice ≥ 20 years + modern pharmacology + adaptive clinical research (pragmatic trials).
Standardization of medicinal materials - testing: Vietnam's medicinal materials are diverse but lack qualitative and quantitative standards for many native species; lack of traceability and control of impurities (microorganisms, heavy metals, pesticide residues, natural toxins). The testing network that meets GLP/ISO 17025 is uneven; lack of DNA barcoding (identification of unknown biological species by comparison with DNA sequences in gene banks), LC-MS/MS, NMR for identification and purification.
Intellectual property and traditional knowledge: There is currently no adequate legal mechanism to register, protect and share benefits for folk remedies, precious medicinal plants and "family secrets". The risk of loss, unfair exploitation or appropriation of biological knowledge - biopiracy still exists.
International trade and standards integration: Lack of equivalent recognition mechanism (MRA), GACP-WHO and GMP standards have not covered the chain; technical documents have not met EMA/FDA; national brand for YDCT has not been formed, leading to low export value.
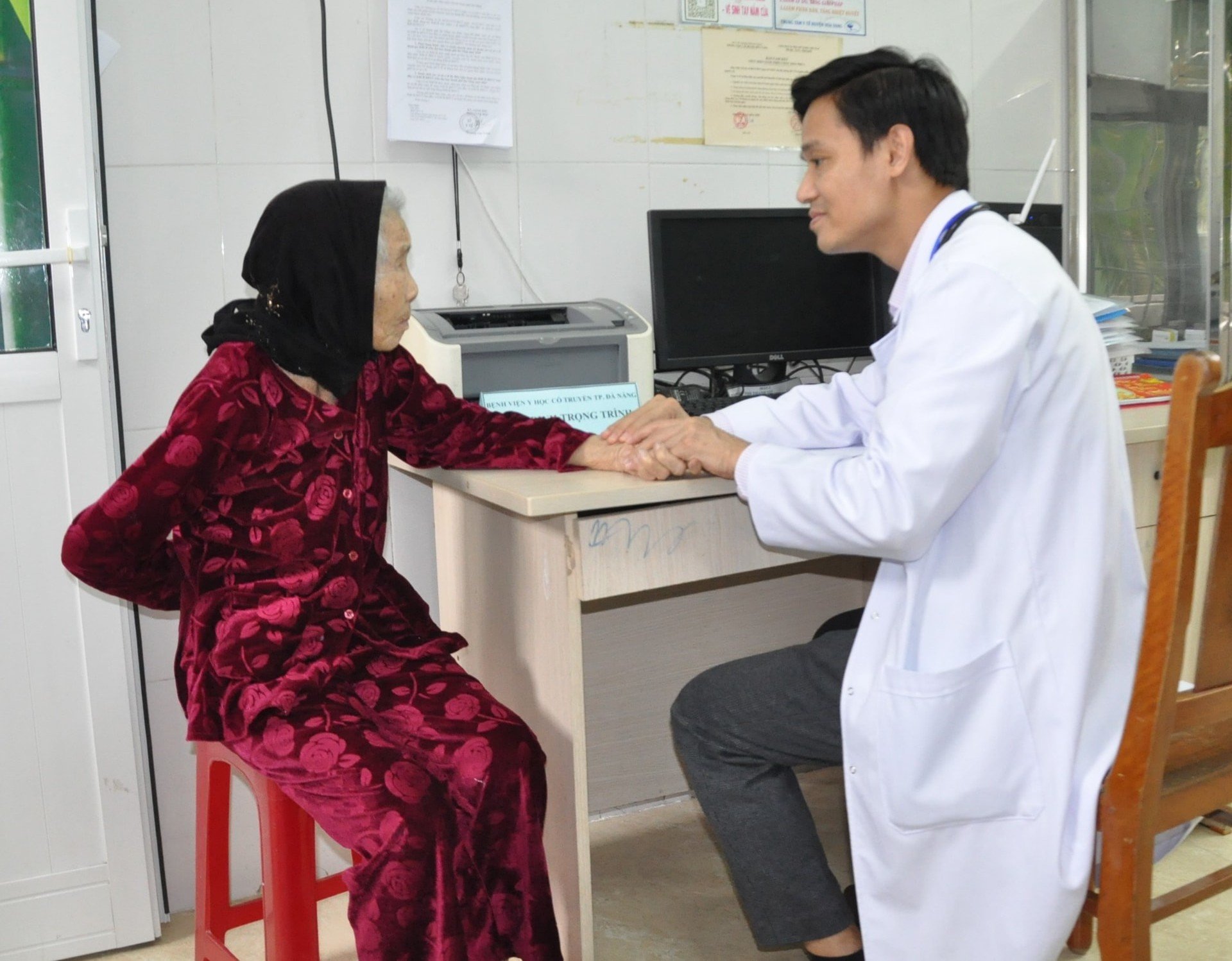

Traditional medicine is increasingly chosen by many people.
3. International experience
China: Traditional Chinese Medicine Law (2017), strong pharmacopoeia system, GMP/KM standardization (quality control of medicinal materials/traditional Chinese medicines); promoting clinical research and internationalization of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
India: Ministry of AYUSH, separate registration and testing framework, knowledge protection with Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL), Ayurveda knowledge export strategy.
South Korea: Korean Medicine Act; standardization of training and testing; positioning of the "K-Medicine" brand and signing of MRA (Mutual Recognition Agreement) in the region.
International experiences have provided lessons for Vietnamese traditional medicine: There must be separate laws, standardized pharmacopoeias, digital data of traditional knowledge, and a synchronous brand strategy - MRA.
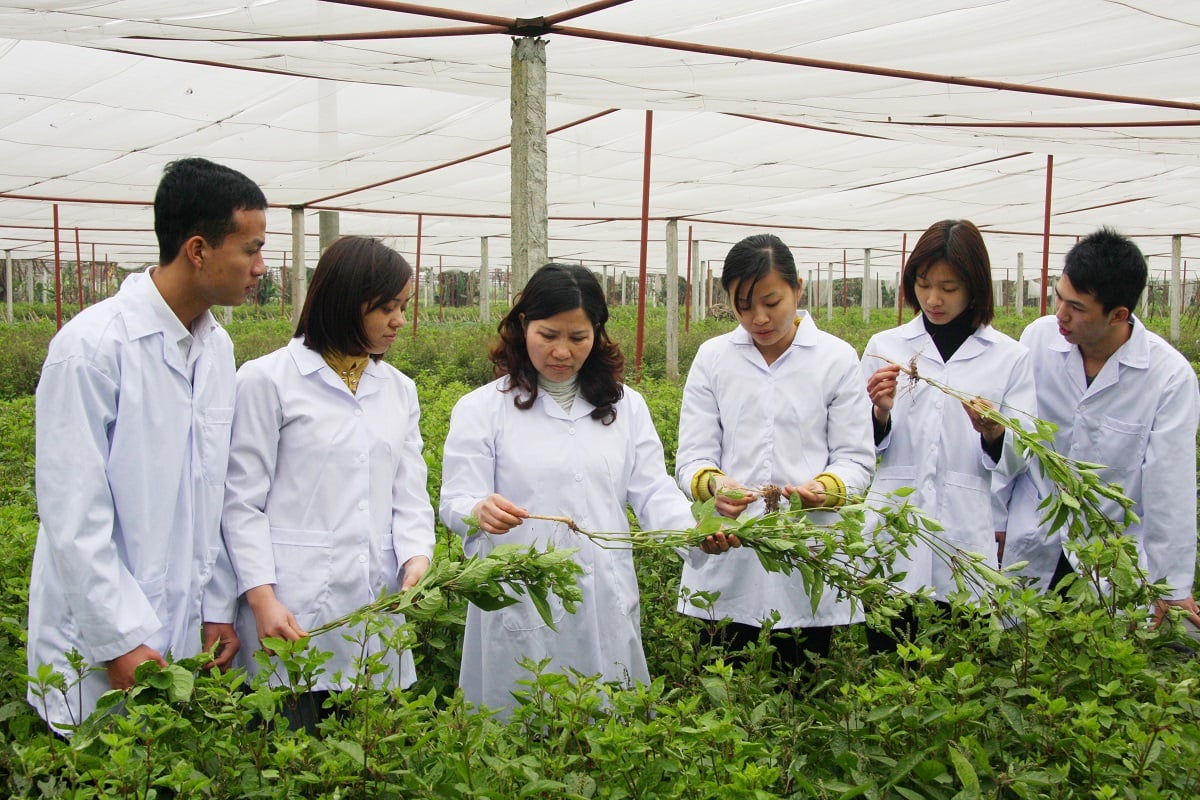

Developing herbal growing areas, raising the level of plants with high economic value, aiming for export.
4. Proposal to perfect the legal framework for integration
Promulgating the Law on Traditional Medicine of Vietnam: Comprehensive regulations on practice, training, research, production and circulation of traditional medicine, knowledge preservation, intellectual property protection, benefit sharing and technology transfer. Establishing clear roles and responsibilities of the Ministry of Health, the Department of Traditional Medicine Management, the Oriental Medicine Association, institutes and schools, businesses and the community.
Amending regulations on registration and appraisal of traditional medicines: Developing separate registration guidelines for traditional medicines such as mixed evidence mechanism (medical literature + practice ≥ 20 years + preclinical safety + adaptive clinical; shortened roadmap for traditional medicine/experience with good safety data; specialized e-Submission portal; defined appraisal period; "one-stop" mechanism with the Traditional Medicine expert council.
Standardization of medicinal materials - testing: Promulgate the expanded Vietnamese Pharmacopoeia (add ≥ 500 indigenous ingredients), apply DNA barcoding, HPLC/LC-MS/MS, impurity - toxin - microbiology standards; build a regional testing network that meets GLP/ISO 17025, a national reference center; mutual recognition regulations in ASEAN/Asia; mandatory digital traceability (QR/Blockchain) from GACP-WHO growing areas to GMP finished products.
Protection of traditional knowledge and benefit sharing: Legalize the registration of medicinal recipes - methods - medicinal plant varieties in the national traditional medicine knowledge database, linked with WIPO/TKDL. Benefit-sharing mechanism when commercializing, the community/"knowledge holder" shares finance - copyright - scientific credit. Regulations on confidentiality, licensing of knowledge use for R&D/OEM/franchising purposes.
Legal framework for knowledge export – OEM – technology transfer: The Decree on Traditional Medicine Knowledge Transfer defines knowledge products (formulas, processes, remedies, treatment methods), documentation standards, safety/ethical control.
Model contract for OEM/franchise for traditional medicine – medicinal food; IP, QC, traceability, confidentiality, dispute resolution (VIAC) terms. Step-by-step MRA mechanism with ASEAN, Korea, Japan; roadmap to meet EMA/FDA for appropriate segments.
Financial mechanism - insurance - national brand: The National Traditional Medicine Development Fund sponsors clinical research, testing centers, GACP-GMP conversion, and knowledge digitization. Expanding health insurance payments for traditional medicines with evidence of safety and effectiveness; integrating traditional medicine at the grassroots level. The national brand "Vietnam Traditional Medicine (VTM)" includes a set of criteria, certification labels, trade promotion - medical diplomacy - medical tourism.
Completing the legal framework for Traditional Medicine in international integration is not only a technical amendment, but also a strategy to elevate the industry: Preserving heritage - promoting innovation - increasing economic value - expanding the influence of Vietnamese medical culture. Specialized laws, standardization of medicinal materials - testing, protection of traditional knowledge, and the knowledge export/OEM framework will be the "four pillars" to bring Vietnamese Traditional Medicine to deep integration - sustainable development - global spread.
See more popular articles:
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/hoan-thien-khung-phap-de-phat-trien-y-duoc-co-truyen-viet-nam-trong-hoi-nhap-quoc-te-169251107182346198.htm
































































































![Dong Nai OCOP transition: [Article 3] Linking tourism with OCOP product consumption](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/10/1762739199309_1324-2740-7_n-162543_981.jpeg)













Comment (0)