Tinnitus requires special attention in the elderly because it carries many dangerous effects. Controlling underlying diseases and diseases related to tinnitus is also important in this group of people.
Risk of stroke and heart attack
Master - Doctor Le Ngo Minh Nhu, Ngu Quan Clinic (Ear, Nose, Throat - Eyes), University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City - Facility 3, said: "Tinnitus in the elderly can be a sign of high blood pressure, atherosclerosis or hemangioma. These conditions pose a risk of stroke or myocardial infarction. In addition, tinnitus can also be related to degeneration of the auditory nerve or brain such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease. Diseases such as Meniere's or acoustic neuroma are also dangerous if not diagnosed and treated promptly."

If tinnitus is accompanied by dizziness, older adults are at high risk of falling, leading to broken bones or serious injury.
Notably, if tinnitus is accompanied by dizziness, the elderly are at high risk of falling, leading to fractures or serious injuries. If tinnitus persists, it can irritate the nervous system, leading to high blood pressure or chronic headaches.
Older adults are often prone to anxiety because they do not understand the cause of tinnitus. Continuous tinnitus, especially when prolonged, can easily lead to feelings of depression and isolation, making older adults reluctant to communicate, leading to feelings of loneliness.
How to reduce the impact of tinnitus on the elderly
Regular medical check-ups : The elderly need regular ENT and cardiovascular check-ups to detect early diseases related to tinnitus. If the cause is a medical condition (such as high blood pressure or ear infection), treating the underlying disease will help reduce tinnitus. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to reduce symptoms as directed by a doctor.
Other supportive methods that may be used during the examination include:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps patients manage their emotions, reduce anxiety, and improve tolerance to earwax.
- Sound therapy: Use pleasant sounds (rain, ocean waves) to soothe tinnitus.
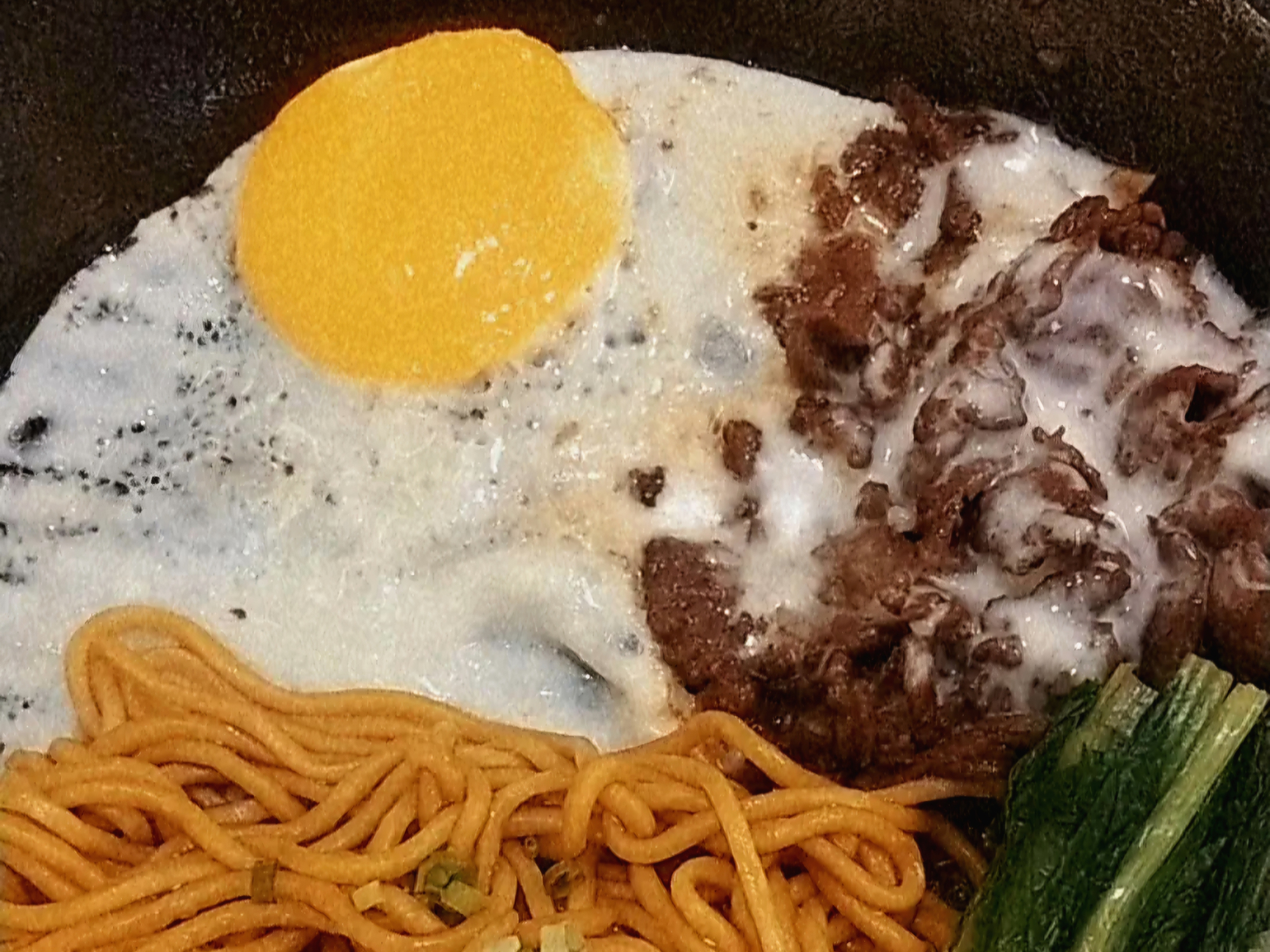

Supplement vitamins found in eggs and beef to support nerve function.
Pay attention to your diet :
- Maintain a low-salt diet to reduce the risk of fluid buildup in the inner ear.
- Supplement foods rich in B vitamins (B1, B6, B12), zinc, and magnesium, as they are beneficial for nerve health and hearing.
Use assistive devices : Hearing aids or tinnitus maskers can help relieve tinnitus.
Lifestyle changes : Avoid stimulants such as caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco. Practice relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation to reduce stress.
Control underlying medical conditions : Manage medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or vascular problems well to minimize symptoms.
Suitable living environment : Reduce noise in the surrounding environment and use pleasant sounds (such as rain or ocean waves) to soothe tinnitus.
People with tinnitus should see a doctor immediately if they have the following symptoms: Tinnitus that lasts more than a week or gets worse, accompanied by dizziness, loss of balance; ear pain, discharge, or sudden hearing loss; pulsating tinnitus, especially when lying down.
Patients need to maintain the habit of regular health check-ups to monitor the progression of the disease, especially if symptoms do not improve or are accompanied by dizziness or hearing loss.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/u-tai-co-nguy-co-gay-dot-quy-o-nguoi-lon-tuoi-bac-si-dua-ra-loi-khuyen-185250303202532686.htm


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man received a delegation of the Social Democratic Party of Germany](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761652150406_ndo_br_cover-3345-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Flooding on the right side of the gate, entrance to Hue Citadel](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761660788143_ndo_br_gen-h-z7165069467254-74c71c36d0cb396744b678cec80552f0-2-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Draft documents of the 14th Party Congress reach people at the Commune Cultural Post Offices](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761642182616_du-thao-tai-tinh-hung-yen-4070-5235-jpg.webp)



























![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the 80th Anniversary of the Traditional Day of the Armed Forces of Military Region 3](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/28/1761635584312_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)









































































Comment (0)