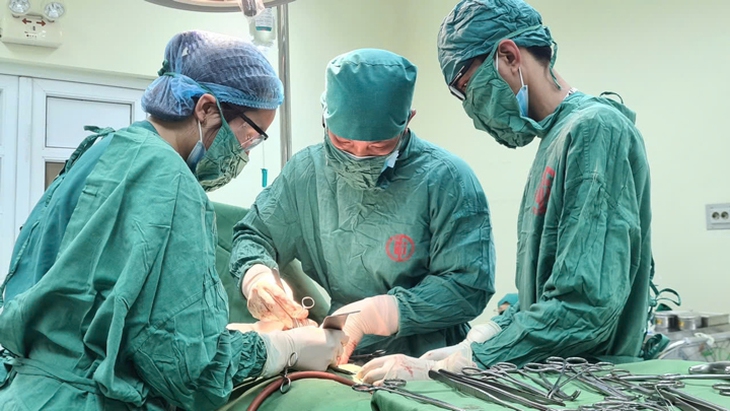
Doctors perform surgery on patients - Photo: BVCC
Ovarian germ cell cancer often progresses silently and is easily confused with other gynecological diseases.
Early detection and timely treatment increase the chance of recovery
Vietnam - Sweden Uong Bi Hospital recently received a 15-year-old female patient ( Quang Ninh ), admitted with dull abdominal pain and an abnormally large abdomen.
Through examination and paraclinical tests, the doctor discovered a large tumor occupying the entire abdomen up to the sternum. After consultation, the patient was scheduled for surgery to remove the tumor. The surgery lasted more than 1 hour, the tumor was removed and sent for histopathological examination.
Biopsy results showed that the patient had ovarian germ cell cancer - a rare form of reproductive cancer in adolescents.
Currently, after surgery, the patient is closely monitored and has a treatment plan to control and limit the risk of recurrence.
Dr. Tran Anh Tuan, K Hospital, said that ovarian germ cell tumors develop from the reproductive cells (germ cells) of the ovary. Most germ cell tumors in the ovary are benign (non-cancerous), and malignant tumors (cancerous) are rare.
Ovarian germ cell tumors usually develop in young women under 20 years of age, but they can also develop in older women. Usually, a tumor develops in only one ovary.
However, it is difficult to detect early signs of ovarian germ cell tumors. Symptoms of malignant tumors often do not appear until the cancer has progressed, some symptoms include:
Pelvic pain or tenderness : Pelvic discomfort, cramps, and ovarian pain are common symptoms of germ cell tumors.
Enlarged belly : Young women and girls may have a bulging belly, which may or may not be accompanied by weight gain in other areas of the body.
Nausea or difficulty eating .
Change in bowel habits (constipation).
Abnormal vaginal bleeding: This is a less common symptom of germ cell tumors.
Malignant ovarian germ cell tumors are a rare form of ovarian cancer. Less than 5% of ovarian cancers are malignant germ cell tumors, while 20-25% of all benign ovarian tumors are germ cell tumors.
Early treatment will be more effective.
Ovarian germ cell cancer often progresses silently and is easily confused with other gynecological diseases. If detected early and treated promptly, the chance of recovery is relatively high.
Treatment for malignant tumors includes surgery or chemotherapy. The outlook depends on the stage of the cancer, the size of the tumor, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. Most germ cell tumors are treatable.
Cancer experts measure cancer's outlook by the five-year survival rate. If the cancer hasn't spread to other parts of the body, the survival rate is 94 to 98 percent.
Cancer that has spread beyond the original tumor site has a 5-year survival rate of 73%. Overall, the survival rate for germ cell tumors is about 93%. New treatments are now available to increase a woman's chance of having children after treatment for germ cell tumors.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/bung-to-nhanh-tre-15-tuoi-phat-hien-ung-thu-te-bao-mam-buong-trung-choan-het-o-bung-20250911162209478.htm



![[Photo] The 5th Patriotic Emulation Congress of the Central Inspection Commission](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761566862838_ndo_br_1-1858-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man receives Chairman of the House of Representatives of Uzbekistan Nuriddin Ismoilov](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761542647910_bnd-2610-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Party Committees of Central Party agencies summarize the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW and the direction of the Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/27/1761545645968_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)



































































































Comment (0)