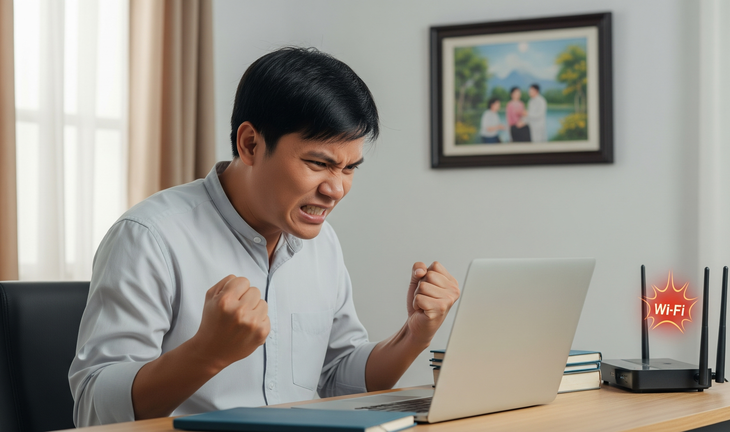

Users are frustrated because WiFi is too slow.
Many people have the habit of working, studying or entertaining in a fixed place in the house. However, even when not moving, they often encounter the situation of WiFi speed being smooth at times, then unstable at times for unknown reasons.
This is not an unusual phenomenon but an inherent characteristic of wireless transmission technology.
WiFi speed is unstable because the environment is always changing
WiFi transmits signals using radio waves. These waves travel through the air and are strongly affected by the physical environment. Obstacles such as concrete walls, glass doors, wooden cabinets, or even a person walking by can weaken or distort the signal. When the signal is deflected, reflected, or scattered, internet speeds can change from second to second.
One thing that is unique is that wireless signals are not as stable as cables . If you rotate your laptop slightly, change the angle of your phone, or open or close a door in the room, the waves can be reflected in a different direction, causing the connection speed to change without you realizing the behavior that caused the difference.
Additionally, there is a less-known factor: electronic devices in the home also emit electromagnetic waves. Microwave ovens, Bluetooth speakers, wireless headphones, air purifiers, and even smart lights all operate on frequency bands that can overlap or overlap with WiFi signals, especially in the 2.4 GHz band.
When multiple devices are running at the same time, the possibility of interference increases, forcing the router to process more complex signals, thereby slowing down the connection.
Even the number of devices accessing the network at the same time has a significant impact. If there are 5 to 7 devices using the internet in the family, the bandwidth will have to be divided among each device.
When one device suddenly loads a large amount of data, such as watching high-resolution video , updating the operating system, or syncing cloud data, the other devices will feel a noticeable slowdown even though they themselves are not doing anything.
The transmitter factor cannot be ignored. Many families still use old WiFi transmitters that are not capable of self-adjusting frequency channels or lack signal orientation technology. Meanwhile, new generation routers can automatically select channels with less interference , adjust the transmission power, or prioritize devices that are transmitting more data. Updating the router software and placing the device in an open, central location in the apartment are also important factors to maintain a stable connection.
Internet infrastructure and applications also make the network sometimes fast and sometimes slow.
From our research, not all the causes of erratic WiFi are in your home. A large part of the problem comes from the way the internet is provided and distributed by your carrier, as well as how applications access and use data.
Residential internet in urban areas often uses a bandwidth sharing model. This means that a group of households in the same area will share a portion of the transmission capacity. In the evening, when many people watch videos, study online, make video calls or play games at the same time, the entire area will experience local network congestion . At that time, even if the indoor WiFi signal is strong, the access speed is still slow because the data flow outside is congested.
In addition, not all the data you need is stored in Vietnam. Many popular services such as Netflix, YouTube, Google Drive or remote working software have servers located abroad. When the undersea fiber optic cable system has problems or international traffic is congested, the access speed of these services will decrease significantly. These factors are completely beyond the control of the user.
Additionally, modern apps and operating systems often have tasks running constantly in the background. Your laptop might be updating its software, your phone might be automatically backing up your photos to the cloud, your browser might be reloading tabs you didn't open.
All of these activities use the internet in the background, causing the total amount of data to be consumed without you even knowing it. As a result, when you open a website that seems light, it still loads very slowly because the connection is busy with other background processes.
Another technological factor is how WiFi allocates data to each device . Some high-end routers may prioritize real-time connections like video calls, gaming, or online meetings, but most low-cost devices do not. This leads to connection lag or drops even when the device is showing full signal.
Understanding 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz Wi-Fi: Which wave to choose for a faster and more stable network?
2.4 GHz is the oldest and most popular frequency band. Its advantages are wide coverage and good wall penetration , suitable for houses with many floors or rooms. However, the disadvantages are lower speeds and susceptibility to interference, as this frequency is also used by many other devices such as microwave ovens, cordless phones and Bluetooth.
5 GHz is a popular choice for high-speed needs, like watching 4K video, playing online games, or video conferencing. It has less interference, but it has trouble penetrating walls and has a shorter range . In small spaces or when you're close to your router, this is the optimal choice.
6 GHz , used in the Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 standards, is the newest band available. Due to its low number of devices, it is virtually immune to interference from other devices , while also providing greater bandwidth and extremely high transmission speeds . However, due to its higher frequency, 6 GHz waves are very poor at penetrating walls and only work effectively in the same room as the router or in open spaces .
Bottom line: If you need long-distance, reliable coverage across multiple rooms, 2.4 GHz is a safe bet. If you want a fast, smooth network in close proximity, prioritize 5 GHz or 6 GHz if your device supports it. And don't forget to place your router in an open, central location in your home, which is still key for any band to work effectively.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/vi-sao-wifi-luc-nhanh-luc-cham-du-ban-ngo-yen-mot-cho-20250616105832932.htm




![[Photo] Opening of the 14th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/05/1762310995216_a5-bnd-5742-5255-jpg.webp)
































![[Photo] Panorama of the Patriotic Emulation Congress of Nhan Dan Newspaper for the period 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762252775462_ndo_br_dhthiduayeuncbaond-6125-jpg.webp)




































































Comment (0)