Tam Anh General Hospital in Ho Chi Minh City receives at least 5 cases of diabetic complications each week due to patients eating improperly, forgetting to take their medication, or injecting too little or too much insulin.
On September 21st, Dr. Ho Ngoc Bao, from the Emergency Department, provided this information, adding that complications can worsen the condition and lead to death if not treated promptly.
For example, Mrs. Le, 85 years old, has diabetes and has been self-administering insulin for 15 years. She was admitted to the emergency room due to fatigue, tremors, sweating, and lethargy. Tests showed her blood sugar was extremely low. Doctors diagnosed her with an insulin overdose. After treatment to lower her blood sugar, she regained consciousness, her health stabilized, and she was discharged after 7 days.
Unlike Mrs. Le, Mr. Tuan (56 years old) and Mrs. Hong (54 years old) were hospitalized due to hyperglycemia. Because he forgot to inject insulin, Mr. Tuan's blood sugar increased four times the normal level, causing ketoacidosis (accumulation of acid in the blood), leading to lethargy, fatigue, shortness of breath, vomiting, and excessive thirst. He received intravenous fluids, electrolytes, and insulin, which helped alleviate his symptoms.
Ms. Hong, who has had diabetes for 20 years, recently had stable blood sugar levels and adjusted her insulin dosage based on the amount of food she ate. She experienced continuous vomiting and was admitted to the emergency room, where she was diagnosed with hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis. Fortunately, she received timely treatment, as any delay could have been fatal.
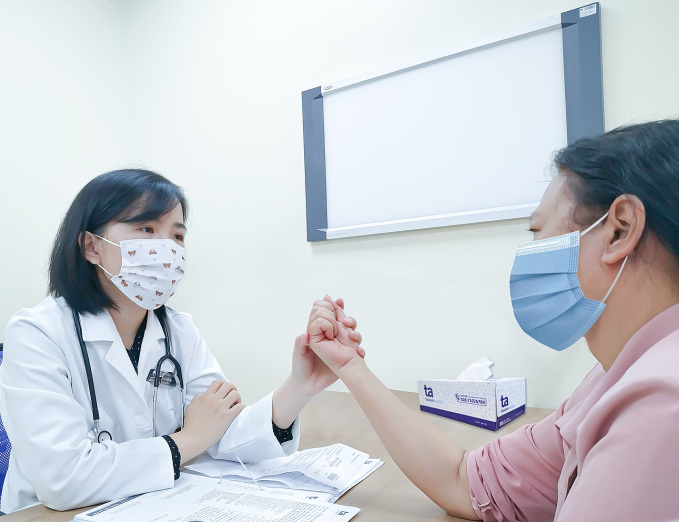

Doctor Thuy Dung instructs patients on how to measure food intake using their fist to monitor blood sugar levels. Photo: Dinh Tien
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by consistently high blood sugar levels because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin effectively. Patients need to take medication daily as prescribed by their doctor.
Dr. Phan Thi Thuy Dung, a specialist in Endocrinology and Diabetes, explained that diabetes medications fall into two main groups: insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. Insulin helps lower blood sugar and takes effect quickly, within 5-30 minutes after injection. Depending on the individual case, the doctor will guide the patient on the appropriate use of insulin.
Doctors advise diabetic patients to take their medication exactly as prescribed, without forgetting to take it or taking an overdose. Patients should also not change their medication dosage on their own, even if their blood sugar is stable, as in Mrs. Hong's case.
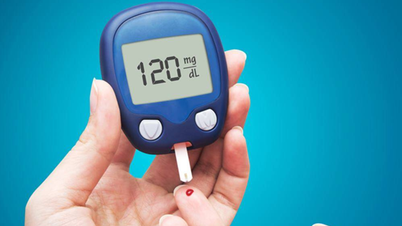
Cases like Mr. Tuan's, where patients forget to take their medication and their blood sugar spikes, are very common. Typically, diabetes medications come with labels and specific instructions on what to do if a dose is missed. If blood sugar is high, with symptoms such as excessive thirst, hunger, frequent urination, fatigue, etc., patients should go to the hospital for examination. Blood sugar levels above 250 mg/dL are considered dangerous.
Poorly controlled blood sugar can easily lead to acute diabetic complications such as ketoacidosis, coma, and hyperosmolar hyperglycemia. Other chronic complications such as damage to large blood vessels (myocardial infarction, stroke) and damage to small blood vessels (renal dysfunction, peripheral neuropathy) can also occur.
In addition to medication, to control diabetes, patients should limit their intake of starches, sweet fruits, canned foods, and foods high in sugar. They should avoid alcohol, smoking, and other stimulants. A balanced diet including meat, fish, eggs, vegetables, and fruits in three main meals each day is also important.
Regular exercise is recommended, aiming for at least 30 minutes a day, or at least two days a week, focusing on exercises that target major muscle groups including the legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders, and arms. Gentle exercises such as brisk walking, housework, dancing, yoga, swimming, and cycling are suitable. Regularly check your blood sugar at home and attend regular check-ups as directed by your doctor to better monitor and treat the condition. If any unusual symptoms occur, seek prompt medical attention.
Dinh Tien
At 8 PM on September 22nd, the online consultation program "Mistakes in managing blood sugar at home for people with diabetes" will be broadcast on the VnExpress fanpage. The program provides information on how to use medication, nutrition, and exercise to help patients effectively manage their blood sugar at home. Doctors from the Endocrinology - Diabetes Department of Tam Anh General Hospital System participating in the consultation include Assoc. Prof. Dr. Hoang Kim Uoc, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Lam Van Hoang, and Dr. Dinh Thi Thao Mai. Readers can ask questions here to receive advice. |
Source link












































































































Comment (0)