Sports injuries such as ligament tears and ankle sprains are common causes of cartilage damage, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis later on, even after treatment.
Dr. Dao Duy An Duy, MD, MSc, Head of the Orthopedics and Trauma Center, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, provided the above information, further explaining that cartilage, located between the two ends of the bones in a joint, functions to protect and reduce friction within the joint. If the articular cartilage is damaged and worn down, the ends of the bones rub against each other when the patient moves, causing osteoarthritis.
According to Dr. Duy, a torn or ruptured anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most common sports injuries. If left untreated, this condition can damage the cartilage, leading to osteoarthritis. Patients experience prolonged pain, reduced mobility, and face the risk of disability and the need for joint replacement later on.
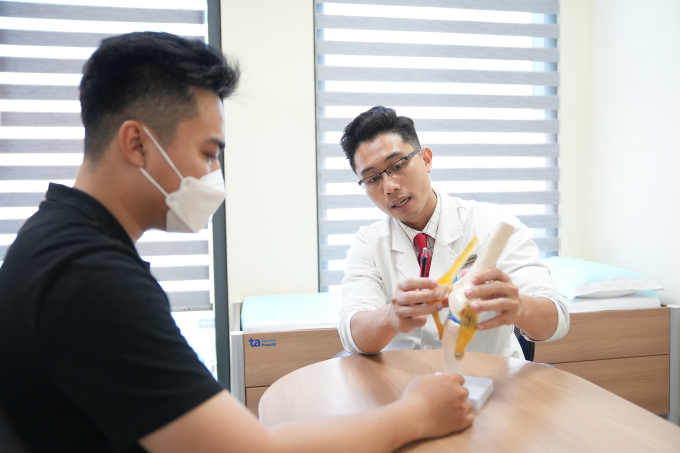

Doctor Duy provides joint health consultation to a patient at Tam Anh General Hospital. (Illustrative photo: Provided by the hospital)
Dr. Duy cited several studies showing that approximately 50% of people who completely tear their anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) develop osteoarthritis within 12-14 years afterward, even after surgery, which is three times higher than those without the injury. Even minor ligament injuries that don't cause discomfort at the time of the injury can damage the articular cartilage. Furthermore, other injuries, even if healed, that recur frequently increase the risk of future osteoarthritis.
All sports contribute to overall health, maintaining a healthy weight, and thus slowing down the process of joint degeneration. Doctor Duy notes the following ways to reduce the risk of injury when playing sports.
Choose a suitable sport : Football, basketball, etc., with their high-speed movement and frequent, sudden changes in direction, can easily lead to injuries, especially to ligaments. Practicing yoga, swimming, etc., correctly can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Yoga or Tai Chi are forms of exercise that focus on improving neuromuscular function; enhancing balance and coordination of body movements. Meanwhile, swimming or cycling help build strength, flexibility, balance, and endurance.
Exercise at a moderate intensity : Overtraining increases the risk of injury and accelerates joint degeneration. Avoid sudden increases in intensity; only increase by 10% after every one or two training sessions. Do not overexert yourself, especially when tired, in pain, or experiencing other unusual symptoms.
The body needs adequate rest and recovery time by exercising one day, resting the next, or alternating between intense and light workouts.
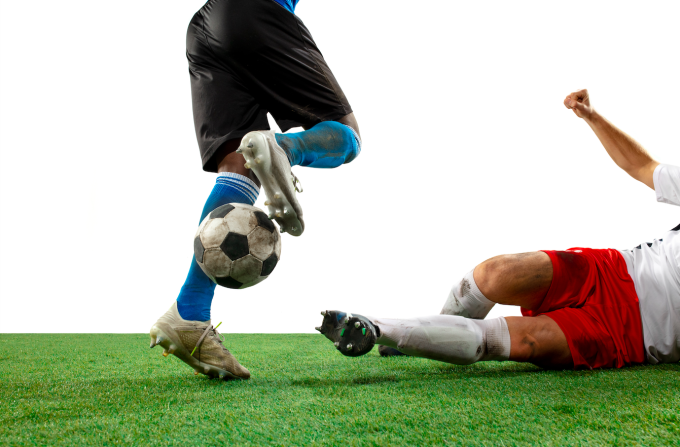

Highly competitive sports like football are prone to injuries. (Illustration: Freepik)
Adequate stretching : Warming up before exercise and cooling down afterward are effective in reducing injuries. Stretching, twisting, and low-intensity jogging help the body transition from a resting state to an active one. Heart rate, breathing rate, and body temperature gradually increase to prepare for higher-intensity physical activity.
At the end of the workout, stretching should be done again. At this time, the stretching exercises allow muscles to recover quickly, reduce post-workout fatigue, and help eliminate toxins and waste products accumulated in the muscles during physical activity.
Phi Hong
| Readers can submit questions about musculoskeletal disorders here for doctors to answer. |
Source link









































































































Comment (0)