According to Universe Today , the Nube galaxy is so faint that the famous Sloan Deep Sky Survey (SDSS) project missed it. However, scientists were fortunate when another survey program called the IAC Stripe82 Heritage Project accidentally spotted it, a nearly transparent object.
A research team led by Dr. Mireia Montes from the Canary Islands Institute of Astrophysics (IAC - Spain) has analyzed and confirmed that nubes are primarily composed of dark matter.
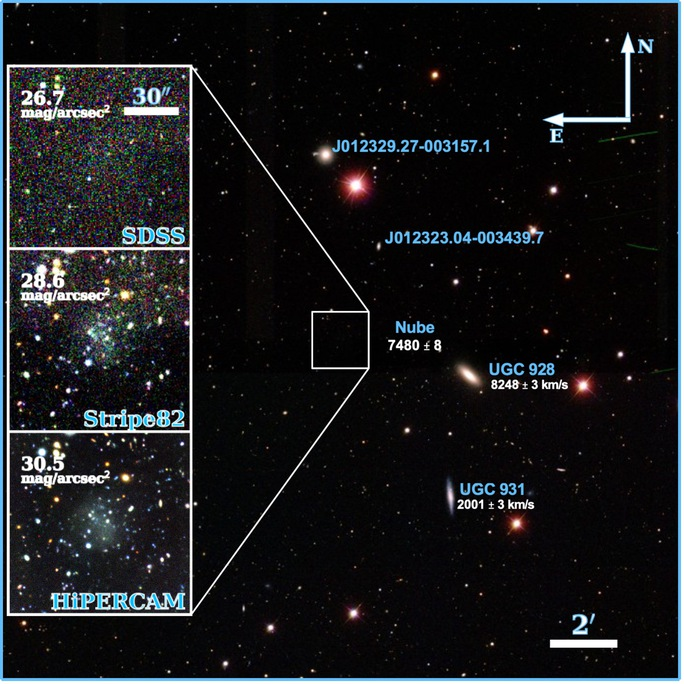
The Nube Galaxy is marked by a solid black square in the overall observation, only faintly visible in more detailed observations (Image: Montes et al).
This "ghost galaxy" is a nearly dark dwarf galaxy with a mass comparable to the Small Magellanic Cloud, and is one of the satellite galaxies of the Milky Way, to which our planet belongs.
The results, derived from additional observations using the Green Bank Telescope (located in the US), show that the "ghost galaxy" is approximately 350 million light-years away from us.
It is an extremely diffuse galaxy, 26 billion times more massive than the Sun, but its total stellar mass is only 390 million times that of the Sun, suggesting a dark, invisible entity is taking over.
That invisible thing is dark matter, a hypothetical type of matter believed to occupy a large part of the universe, and even surround Earth in a way we cannot see or feel.
Half of Nube's mass is spread across a region of space 22,000 light-years wide, making it the largest super-diffuse galaxy ever known to scientists.
According to the authors, studying the "ghost galaxy" Nube will be a great opportunity for scientists to answer questions about dark matter.
At the same time, it offers hope that there are many more dwarf galaxies of this "ghost galaxy" type, we just haven't noticed or seen them yet because they are too faint and almost transparent like a ghost.
(Source: Nguoi Lao Dong Newspaper)
Source


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)


















































Comment (0)