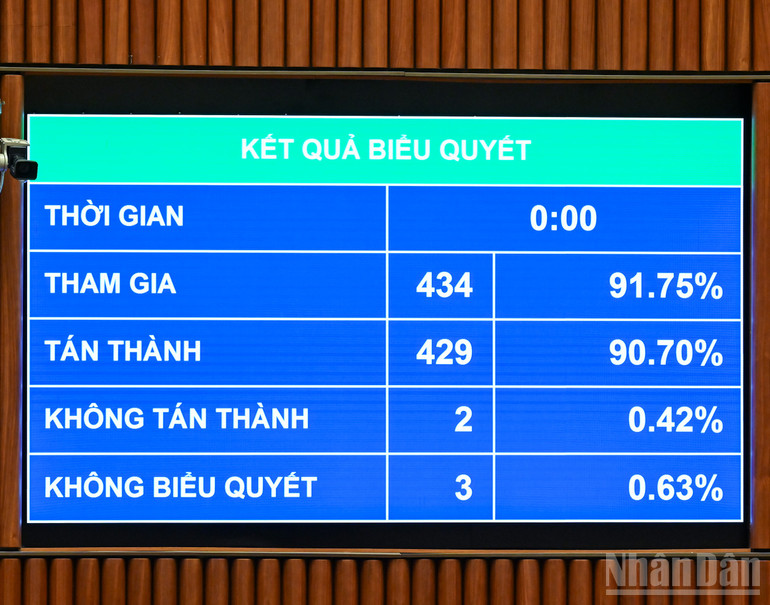
On the afternoon of December 10th, the National Assembly passed the Law on Artificial Intelligence with 429 out of 434 attending delegates voting in favor (equivalent to 90.7% of the total number of National Assembly delegates).
The Law on Artificial Intelligence comprises 8 chapters and 35 articles, regulating the research, development, provision, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence systems; the rights and obligations of relevant organizations and individuals; and state management of artificial intelligence activities in Vietnam. Artificial intelligence activities solely for national defense, security, and cryptography purposes are not covered by this Law.
4 fundamental principles in artificial intelligence operations
According to the law recently passed by the National Assembly, artificial intelligence activities must ensure compliance with four basic principles, including:
Putting people at the center, ensuring human rights, privacy rights, national interests, public interests, and national security; adhering to the Constitution and laws.
Artificial intelligence serves humanity, not replaces human authority and responsibility. It ensures the maintenance of human control and the ability to intervene in all decisions and behaviors of the artificial intelligence system; system security, data security, and information confidentiality; and the ability to inspect and monitor the system's development and operation.
Ensuring fairness, transparency, impartiality, non-discrimination, and no harm to individuals or society; adhering to Vietnamese ethical standards and cultural values; and being accountable for the decisions and consequences of the system.
Promoting the development of green, inclusive, and sustainable artificial intelligence; encouraging the development and application of artificial intelligence technologies that are energy-efficient, resource-saving, and reduce negative impacts on the environment.
Classifying and managing AI systems based on risk.
The Artificial Intelligence Law stipulates the classification and management of artificial intelligence systems according to three risk levels: high, medium, and low.
High-risk artificial intelligence systems are those that can cause significant harm to the lives, health, legitimate rights and interests of organizations and individuals, national interests, public interests, and national security;
A medium-risk artificial intelligence system is one that has the potential to confuse, influence, or manipulate users because they are unable to recognize that the interacting entity is an artificial intelligence system or the content it generates;
The remaining artificial intelligence systems are those with low risk.
The risk classification of artificial intelligence systems is determined based on criteria such as the level of impact on human rights, safety, and security; the system's area of use, especially essential areas or those directly related to the public interest; the scope of users; and the scale of the system's influence.

Prohibited behaviors in artificial intelligence operations
The Artificial Intelligence Law also stipulates prohibited acts in artificial intelligence activities, specifically:
Exploiting or hijacking artificial intelligence systems to commit illegal acts and infringe upon the legitimate rights and interests of organizations and individuals.
Developing, providing, deploying, or using artificial intelligence systems for the purpose of: committing acts prohibited by law; using falsified or simulated real people or events to deceive or manipulate human perception and behavior intentionally and systematically, causing serious harm to human rights and legitimate interests; exploiting the weaknesses of vulnerable groups, including children, the elderly, people with disabilities, ethnic minorities, or people with impaired or limited civil capacity, or those with cognitive difficulties or behavioral control problems, to harm themselves or others; creating or disseminating falsified content capable of seriously endangering national security, public order, and social safety.
Collecting, processing, or using data to develop, train, test, or operate artificial intelligence systems in violation of laws on data, personal data protection, intellectual property, and cybersecurity.
Obstructing, disabling, or distorting the human mechanisms for monitoring, intervening, and controlling artificial intelligence systems as stipulated in this Law.
Concealing information that must be disclosed, made public, or explained; erasing or falsifying mandatory information, labels, or warnings in artificial intelligence operations.
Exploiting research, testing, evaluation, or verification activities related to artificial intelligence systems to engage in actions that violate the law.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/cam-su-dung-he-thong-ai-tao-noi-dung-gia-mao-gay-nguy-hai-an-ninh-quoc-gia-post929261.html













![[Video] Application of Biofloc technology in building an industrial-scale shrimp farming model](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765415061532_1765268925610-jpg.webp)



















![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)


































































Comment (0)