Therefore, building an international cooperation mechanism in research and preservation of traditional medical knowledge is becoming an urgent requirement - not only to protect national heritage, but also to affirm the position of Vietnamese traditional medicine on the world medical map.
1. International cooperation promotes the preservation and promotion of traditional knowledge
According to the Department of Traditional Medicine Management, in Vietnam, traditional medicine is closely associated with national identity, with medicinal plants, remedies, and folk treatment methods that have been tested over time, and is a symbol of national wisdom and self-reliance.
Vietnamese Traditional Medicine can basically be divided into two systems: the academic knowledge system (with a strict theoretical system according to Eastern philosophy based on the theory of yin and yang, five elements, four diagnoses, eight bonds...) and the folk knowledge system (with a hereditary, indigenous nature, often used and passed down by traditional practitioners, traditional healers, and grandmothers).
It can be said that traditional medicine or traditional medicine is the medical knowledge crystallized by history, culture and proven by health care experience over thousands of years of human history. Preserving, inheriting and developing traditional medicine is both a responsibility and a mission to preserve traditional cultural values, while meeting the increasingly diverse health care needs of the people.
One of the solutions set out by the Party and State to develop Vietnamese traditional medicine in the new period is to strengthen international integration and cooperation, especially emphasizing the preservation and promotion of traditional knowledge, medicinal gene sources, good remedies, and precious medicinal plants.

International cooperation is needed to preserve and promote traditional knowledge in health care.
However, in the context of globalization and commercialization of medicine, this valuable source of knowledge is facing the risk of being lost, misappropriated or exploited unfairly. The challenge in the current context is the need for a unified mechanism, widely applied among countries in international cooperation to preserve traditional medical knowledge. The main reasons:
Firstly , TCM knowledge has great scientific and practical value for research, pharmaceutical development, medical examination and treatment and public health care. Establishing an international cooperation mechanism helps connect scattered knowledge sources, share data and experiences between countries, promote multi-center research and create globally valuable scientific evidence, actively contributing to promoting the approach to evidence-based traditional medicine.
Second , international cooperation is a tool for preserving knowledge and biodiversity – two elements that go hand in hand in TCM. Indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants, their processing and therapeutic uses are closely linked to the natural environment, so international cooperation helps maintain ecosystems, preserve genetic resources, prevent overexploitation, and promote the protection of intangible cultural heritage.
Third , in the context of research commercialization, international cooperation becomes an important legal barrier to ensure legitimate rights for countries and communities holding knowledge. This mechanism helps to implement the principle of "access and equitable benefit-sharing" under the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Nagoya Protocol, prevents the phenomenon of "biopiracy", and encourages responsible and transparent research.
2. Why is it necessary to build an international cooperation mechanism in research and preservation of traditional medicine?
Building an international cooperation mechanism in research and preservation of traditional medicine and traditional medicine plays an important role, specifically:
- The international cooperation mechanism plays a coordinating and connecting role between countries, research institutes, international organizations, businesses and indigenous communities: Through the cooperation network, parties can share data, standardize research processes, testing, and safety inspection of TCM methods. This is the foundation for TCM to be gradually integrated into the modern health system according to the orientation of WHO's Global Traditional Medicine Strategy 2025–2034.
- International cooperation mechanisms play a role in shaping scientific and ethical standards in traditional knowledge research: Building a common legal framework helps countries control access to genetic resources, data, and publication of research results, while protecting safety, efficiency, and respect for community culture.
Cooperation mechanisms are also a tool to promote benefit sharing and contribute to sustainable development goals: When traditional knowledge is applied to products, technologies or health services, international mechanisms help ensure that the community holding the knowledge receives commensurate benefits, which can be in the form of finance, technology transfer, training or community investment. As a result, international cooperation not only preserves knowledge but also expands livelihood opportunities and local development. Enhances the ability to integrate and participate in global value chains for medicinal herbs, natural medicine products and health care services using traditional medicine
- Contribute to enhancing the image and position of the country in the field of Traditional Medicine: Deep participation in international research programs and networks helps Vietnam affirm its role as a country with a rich heritage of traditional medicine, widely promote the strengths of Vietnamese Traditional Medicine, and at the same time help Vietnam access scientific resources, finance and global data in the field of health in general and traditional medicine in particular.
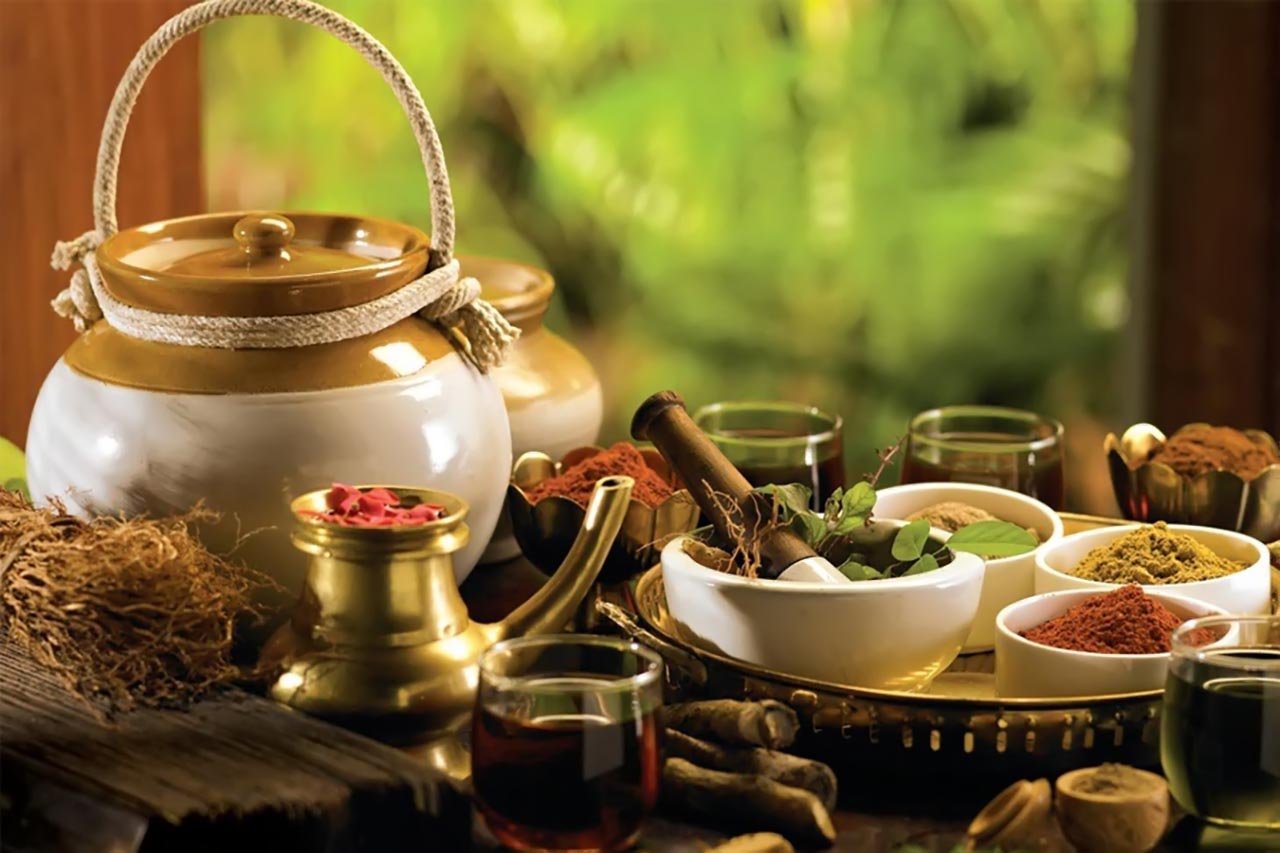

Medicines and medicinal herbs contribute to enhancing the image and position of the country in the field of traditional medicine when international cooperation is strengthened.
3. Requirements to be ensured when building an international cooperation mechanism
The Department of Traditional Medicine and Pharmacy, Ministry of Health, said that establishing an international cooperation mechanism on research and preservation of traditional medical knowledge is not only a scientific issue, but also related to sovereignty, fairness, ethics and the rights of indigenous communities. Therefore, this mechanism needs to ensure the following basic requirements:
3.1 Respect national sovereignty and the rights of knowledge-holding communities
Each traditional medical knowledge is closely linked to a specific geographical area, ethnicity, and culture. Therefore, in building an international cooperation mechanism, it is necessary to ensure:
- Access to, research and exploitation of traditional knowledge must have consensus, based on full information from the knowledge ownership community and competent state agencies.
- All cooperation agreements must comply with the principle of fair benefit sharing (MAT – Mutually Agree Terms) according to the Nagoya Protocol (2010) on access to genetic resources and benefit sharing. Ensure that the intellectual, cultural and resource sovereignty of the host country is not violated.
3.2 Ensure scientific basis, evidence and safety
International cooperation on traditional medicine must be based on the principles of science – transparency – safety. All research, clinical trials or products developed from traditional knowledge must have scientific evidence of effectiveness and safety. Sharing of data, specimens and research results must comply with international biomedical research ethics standards and Vietnamese law, protect human rights and avoid uncontrolled commercialization.
Countries need to research and develop a set of common, unified standards worldwide on inspection, quality assessment and technical records in the field of traditional medicine according to WHO guidelines (According to the orientation of the world traditional medicine strategy for the period 2025 - 2034).
3.3 Protect and share benefits fairly and transparently
This is a core requirement to ensure the sustainability of cooperation, all benefits arising from the use of traditional knowledge (e.g. commercial products, inventions, technologies) must be shared fairly with the community and country that owns the knowledge.
It is necessary to develop a financial mechanism or benefit-sharing fund – which can be technology transfer, research support, training or community development investment. Ensure information transparency and publicity according to the provisions of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
3.4 Ensuring harmony between conservation, exploitation and development
It is necessary to preserve knowledge and biodiversity associated with traditional medicine. Develop knowledge economy and community livelihoods through sustainable value chains (planting medicinal herbs, health tourism, traditional care products); avoid the trend of "over-commercial exploitation" causing resource depletion or cultural identity loss.
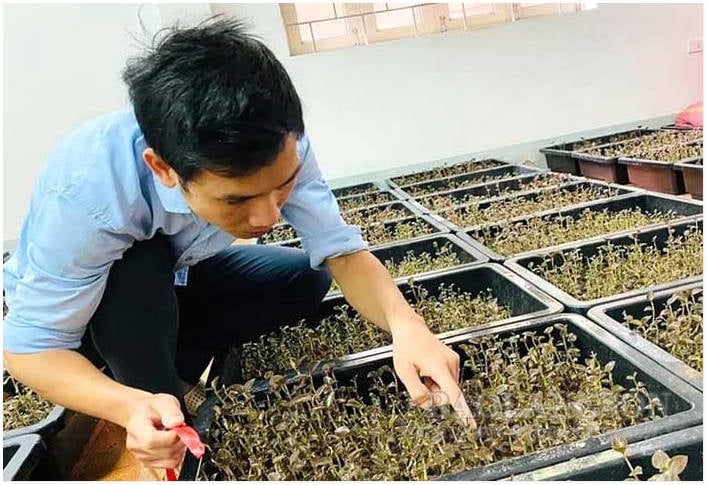

Growing medicinal herbs is one of the measures to preserve, exploit and develop traditional medicine.
3.5 Ensuring legal harmony and international standards
International cooperation must comply with multilateral conventions: CBD/Nagoya, UNESCO 2003, WIPO/IGC, WHO TM Strategy, and be compatible with the Intellectual Property Law, Pharmaceutical Law, and Medical Examination and Treatment Law of each country.
Vietnam needs to improve the legal framework for protecting traditional knowledge, including registration, licensing, monitoring mechanisms and benefit-sharing related to intellectual property.
3.6 Application of digital transformation and knowledge data management
Develop a national digital data infrastructure on traditional medicine knowledge, with a mechanism for sharing and cooperating on data internationally. This database helps to record, authenticate, and share knowledge in a controlled environment; at the same time, it is a tool to prevent illegal registration of patents and intellectual property abroad.
However, to build an effective and sustainable international cooperation mechanism, Vietnam needs to overcome difficulties and challenges such as the lack of synchronization between domestic and international legal corridors; lack of data and mechanisms to authenticate traditional knowledge; limited financial resources and research human resources; challenges in information sharing and security; and limited social and media awareness.
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/hop-tac-quoc-te-ve-nghien-cuu-bao-ton-tri-thuc-y-hoc-truyen-thong-huong-di-tat-yeu-cua-viet-nam-trong-ky-nguyen-hoi-nhap-169251102091810715.htm


![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City Youth Take Action for a Cleaner Environment](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762233574890_550816358-1108586934787014-6430522970717297480-n-1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] The road connecting Dong Nai with Ho Chi Minh City is still unfinished after 5 years of construction.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762241675985_ndo_br_dji-20251104104418-0635-d-resize-1295-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Panorama of the Patriotic Emulation Congress of Nhan Dan Newspaper for the period 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762252775462_ndo_br_dhthiduayeuncbaond-6125-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Ca Mau "struggling" to cope with the highest tide of the year, forecast to exceed alert level 3](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/11/04/1762235371445_ndo_br_trieu-cuong-2-6486-jpg.webp)



































































































Comment (0)