(NLĐO) - The society of an extinct human species may have been "ahead of its time" compared to us in some areas, for example , healthcare .
A research team led by paleoanthropologist Mercedes Conde-Valverde from the University of Alcala (Spain) re-analyzed another human fossil specimen, coded CN-46700, unearthed from the Cova Negra cave in 1989.
CN-46700 contains the remains of a Neanderthal child, dating back to approximately 273,000 to 146,000 years ago, a time when this ancient human species settled in the area.
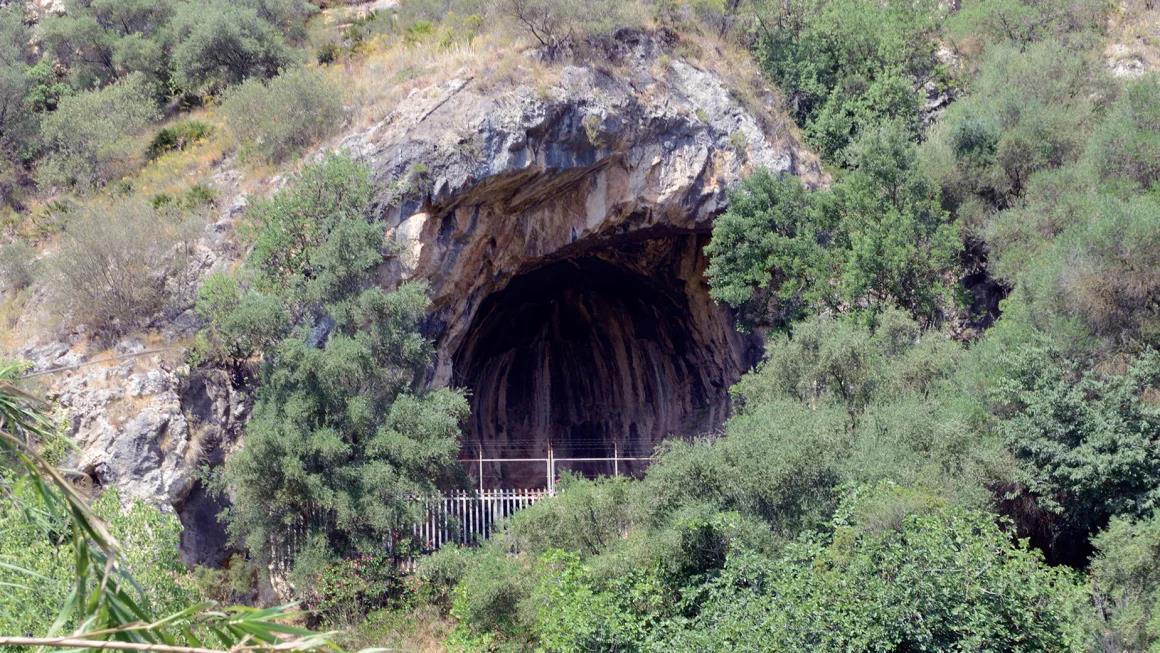

Cova Negra Cave, where ancient Neanderthals once lived - Photo: CNN
Researchers used micro-CT scanners to build a 3D model of the original fossil for analysis.
They found signs of health problems including a smaller cochlea, with abnormalities that could cause severe hearing loss and dizziness. "The only syndrome that fits the whole spectrum of abnormalities found in CN-46700 is Down syndrome," said Dr. Conde-Valverde.
Down syndrome is not unique to humans; it has also occurred in other ancient and modern hominid species.
But what was shocking about this discovery was that the child was 6 years old when he/she died.
According to Science Alert, previous archaeological evidence suggests that children with Down syndrome in the Iron Age often did not survive past 16 months of age.
In 1900, advances in medicine and healthcare systems allowed people with Down syndrome to have an average life expectancy of 9 years.
Today, thanks to numerous advances in medicine and social models, people with this disease can even live as long as healthy people.
Therefore, the idea that a child with Down syndrome hundreds of thousands of years ago could live longer than Iron Age children and nearly as long as children with Down syndrome in the early 20th century is almost unbelievable.
Down syndrome is often associated with defects affecting growth, physical and cognitive development, and motor skills.
Children with this syndrome often experience delayed walking and speech, balance and coordination problems that increase the risk of falls, and difficulty feeding due to weak muscle tone.
Thus, maternal care alone, given the primitive conditions of prehistoric life, would not have been sufficient to sustain the child to age 6. The existence of CN-46700 suggests that the child received extensive and ongoing support from the wider group.
This means that Neanderthals likely evolved much faster than we previously thought, and their social structure may even have been more complex than our own during the same period.
Previously, some evidence also suggested that this ancient human species was not wild ape-like as previously thought, but possessed many remarkable skills tens of thousands of years ago - from weaving and toolmaking to jewelry making.
Neanderthals became extinct about 30,000 years ago and belonged to the same genus, Homo sapiens, as modern humans.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/phat-hien-soc-ve-mot-loai-nguoi-khac-tien-hoa-vuot-bac-196240701112603317.htm























![[Video] Application of Biofloc technology in building an industrial-scale shrimp farming model](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765415061532_1765268925610-jpg.webp)



















![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)


































































Comment (0)