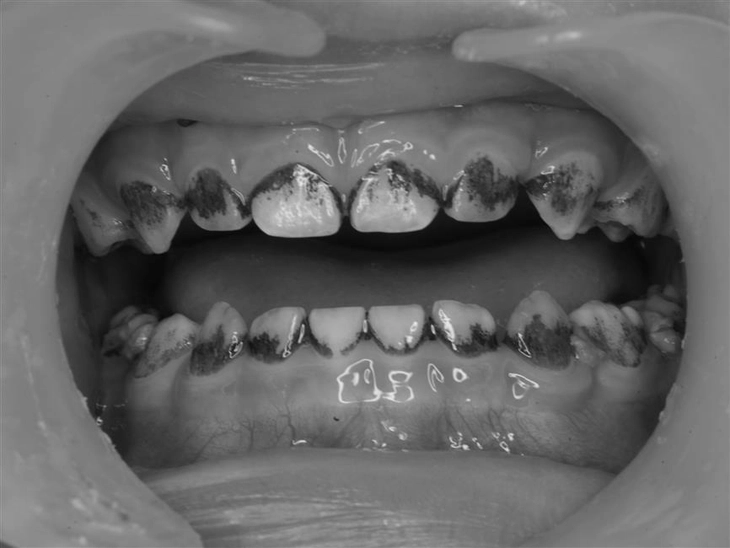
Illustrative image of a case of black plaque on teeth.
This phenomenon is called black stain or black plaque on teeth, a fairly common condition in children worldwide , including in Vietnam.
Interestingly, contrary to parental anxiety, studies show that children with black plaque on their teeth tend to have fewer cavities. This is a fascinating paradox that has been clarified by numerous scientific studies over the past 60 years.
The origin of black plaque on baby teeth
In adults, if black plaque is found on permanent teeth, we usually immediately think of it as being caused by drinking too much tea or coffee, or smoking. Babies don't have these habits, so what is this black plaque on baby teeth?
This is a type of extrinsic staining, meaning the staining substances originate from outside the tooth tissue, rather than being caused by underlying dental disease. These patches typically appear as black dots or streaks running parallel to the gum line, particularly noticeable on the inner surface of lower molars or the outer surface of upper incisors.
Black plaque adheres very firmly, is difficult to clean with regular brushing, and often recurs even after a dentist has cleaned it. Although it doesn't cause pain or weaken the teeth, this condition significantly affects aesthetics, making many children hesitant to smile and causing parents to worry.
Causes and mechanisms of black plaque formation on baby teeth.
The mechanism of black plaque formation has been studied quite thoroughly. It has been determined that it is primarily composed of insoluble iron salt compounds called ferric sulfide. This process occurs when certain types of bacteria in dental plaque secrete hydrogen sulfide gas (H₂S), which combines with iron present in saliva or gingival fluid to form black particles that adhere firmly to tooth enamel.
Common bacteria found in black plaque include Actinomyces, Rothia, Neisseria, Porphyromonas, and Prevotella.
In addition, the saliva of children with dark spots is often rich in calcium, phosphate, copper, and zinc, and has a higher pH, along with better buffering capacity, which means their teeth are less susceptible to acid dissolution and have better resistance to cavities. Diet also plays a role.
Factors that contribute to the formation of black plaque on teeth.
- Tooth enamel surface and saliva: A rough tooth enamel surface can make teeth more susceptible to black plaque buildup. Similarly, acidic saliva or dry mouth associated with mouth breathing increases the presence of plaque-causing bacteria.
- Diet: Certain iron-rich foods, soy sauce, beets, or brightly colored vegetables may increase the risk of developing dark spots.
- Iron supplements: Iron-rich supplements, often prescribed for children with iron-deficiency anemia, can lead to the appearance of dark or green plaque on the teeth.
- Prolonged swimming: Exposure to chlorine and other compounds in pool water can contribute to tooth discoloration, depending on the quality and type of enamel a child has.
- Poor oral hygiene practices: Improper brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which is easily mineralized and pigmented by pigment-producing bacteria, resulting in this type of black plaque.
To treat children's teeth safely, dentists need experience and an understanding of pediatric patients' psychology - Photo: TTD
How to identify and remove black plaque?
Early detection of black plaque is not difficult, as parents can easily see it by observing the tooth surfaces.
These black plaque deposits are stubborn stains; unlike the soft plaque caused by food residue after eating, black plaque is not easily removed by brushing with a regular toothbrush. Areas affected by black plaque may feel rough compared to the rest of the tooth surface.
When preventative measures are insufficient, various treatments can effectively manage the staining condition:
The most common treatment nowadays is for dentists to clean plaque using ultrasonic or saline systems. Saline systems clean more effectively and quickly, and are more comfortable for children.
Some studies have experimented with lasers, photodynamic therapy, biological antimicrobial agents, or probiotics as supportive treatments to limit recurrence, but none have proven to be truly effective.
Since black plaque is largely caused by bacteria in the mouth, influencing the oral environment can help prevent or reduce the intensity of black plaque formation. Some children may experience changes in their oral environment as they grow older, or these changes can be achieved through the use of antibacterial mouthwashes (for children over 5 years old).
If using mouthwash for children, choose alcohol-free options.
What preventative measures can parents and caregivers take for children?
Preventing black plaque is related to oral hygiene and eating habits. Here are some effective preventive measures:
● Brush and floss regularly: Ensure children brush their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque. Don't forget to clean their tongues as well.
● Balanced diet: Limit consumption of foods and drinks high in artificial coloring. Encourage a diet rich in fiber such as fruits and vegetables, and supplement minerals from dairy products to promote healthy teeth.
● Regular dental check-ups: Children under 5 should have their teeth checked every 3 months, and every 6 months for older children, to effectively remove plaque and monitor oral health, detect and treat dental problems early.
● Managing iron supplementation: If iron supplementation is needed, consider a liquid form that can be taken with a straw to minimize contact with teeth or subsequent brushing.
Many studies have shown that children with black plaque tend to have fewer cavities due to differences in their microbiome and saliva composition. However, for aesthetic and psychological reasons, parents should still take their children to a pediatric dentist for cleaning and advice on home care.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/tre-co-mang-bam-den-tren-rang-sua-co-gay-mat-rang-20250927094156758.htm







































![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)

































































Comment (0)