Hemorrhoids are one of the most common diseases of the anal-rectal region. The incidence in adults ranges from 5 - 25% of the population and accounts for over 50% at the age of 50, occurring in both men and women. Many people are afraid because they think that hemorrhoid treatment is ineffective or causes a lot of pain and discomfort.
Grades of hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are divided into 4 degrees based on the degree of hemorrhoid prolapse:
- Grade 1 hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids are located entirely within the anal canal.
- Grade 2 hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids fall out when straining to defecate but can retract on their own.
- Grade 3 hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids fall out when squatting for a long time, carrying heavy objects, exercising vigorously, or defecating; they do not retract on their own and must rest or be pushed back up with the hand.
- Grade 4 hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids prolapse frequently and cannot be pushed completely back into the anal canal.
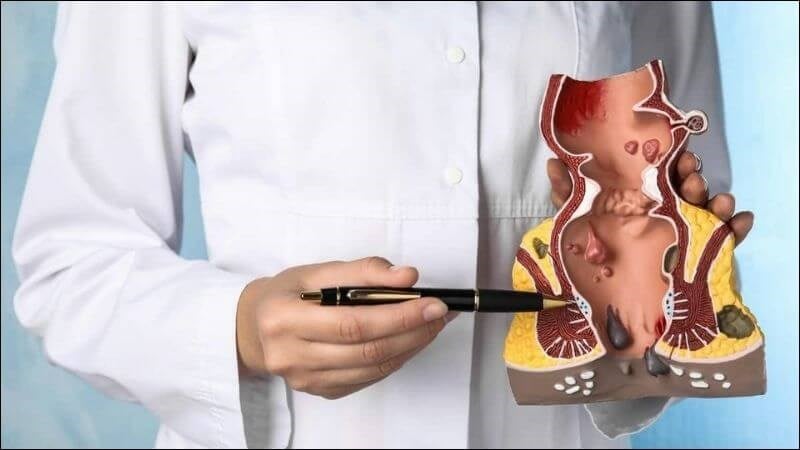
Hemorrhoids are one of the most common diseases of the anal-rectal region.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
In some mild cases, hemorrhoids can shrink on their own with appropriate changes in diet and lifestyle. However, severe cases require specialized treatment.
- Grade 1 and 2 hemorrhoids: Can be treated medically with oral, topical or suppository medications to reduce symptoms and help the patient feel more comfortable.
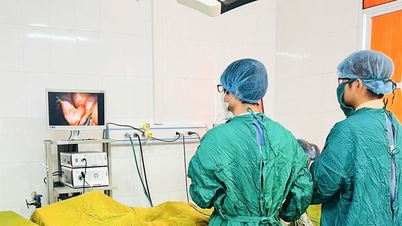
- Hemorrhoids grade 3 and above: Usually require surgical intervention or intervention. Currently, there are many modern, safe methods such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, infrared treatment, laser hemorrhoidectomy, radiofrequency hemorrhoidectomy, Longo surgery, etc.
The choice of method depends on the severity of the disease, the patient's health and financial conditions.
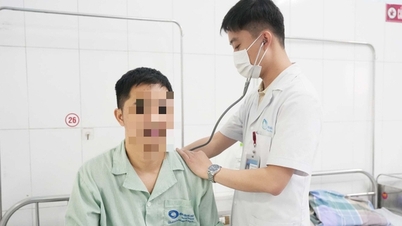
How to care after hemorrhoid surgery
After surgery, the anal area may be painful for up to 4 weeks and there may be some discharge or bleeding. After 1-2 weeks, the patient can resume normal activities but needs to adjust their habits to recover faster. Recovery time depends on each person's physical condition.
Some notes on home care
Diet
- Eat soft, easy-to-digest foods; prioritize laxative foods such as sweet potatoes, green vegetables, etc.
- Increasing fiber helps improve bowel movements and reduces the risk of hemorrhoids recurring.
- Drink enough 2 - 2.5 liters of water per day to help soften stools and avoid constipation.
- Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, beer, coffee and stimulants.
Activities and exercise
- Rest when tired, walk gently to improve circulation.
- Do not run, jump, or carry heavy loads until your body recovers.
- Bathe normally but keep the anal area clean and dry.
- May need to take 1-2 weeks off work depending on the nature of the job (especially heavy work).
- When going out, avoid squatting or sitting for too long.
Incision care
- Take medication exactly as prescribed, do not change medication on your own.
- Soak the anus in warm water for 15 - 20 minutes, 3 times/day and after defecation; can use water diluted with potassium permanganate or betadine.
- Keep the anal area clean and dry; use soft towels instead of toilet paper.
- Avoid products that can cause irritation.
- You can elevate your buttocks to reduce swelling.
Abnormal signs require immediate medical attention
Patients need to go to a medical facility when they have the following symptoms:
- Fecal incontinence
- Rectal bleeding
- Severe pain that does not subside despite medication
- Urinary and bowel disorders; pain or swelling in the lower abdomen
- Signs of infection: increased pain, swelling, heat, redness, fever, pus.
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/cach-cham-soc-sau-mo-tri-giup-phong-bien-chung-va-hoi-phuc-nhanh-169251201081328836.htm



![[Photo] Cat Ba - Green island paradise](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F04%2F1764821844074_ndo_br_1-dcbthienduongxanh638-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)






















































![[VIMC 40 days of lightning speed] Da Nang Port: Unity - Lightning speed - Breakthrough to the finish line](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/04/1764833540882_cdn_4-12-25.jpeg)















































Comment (0)