The World Health Organization (WHO) has issued global guidelines for the use of Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) therapy for the treatment of obesity. This is the first time such guidelines have been issued.
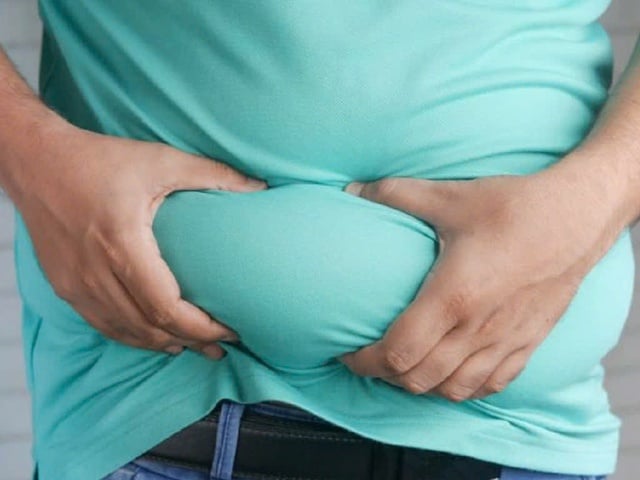

A healthy diet and appropriate physical exercise help increase the effectiveness of obesity treatment. PHOTO: PEXELS
The WHO guidelines include two main recommendations: GLP-1 therapy can be used in adults, but excludes pregnant women.
The efficacy of these therapies in treating obesity and improving metabolism has been demonstrated, but this recommendation remains limited, due to data on long-term efficacy and safety, maintenance, and discontinuation.
The development of the guidance involved extensive analysis of existing evidence and consultation with a wide range of stakeholders, including those with practical experience. The guidance will be updated as new evidence becomes available.
WHO guidelines also state that medication alone will not reverse the obesity challenge. Tackling the obesity problem requires obesity prevention policies; screening and early intervention for people at high risk of obesity and related diseases.
Along with this therapy, healthy dietary and physical activity interventions may help improve treatment outcomes.
WHO estimates that obesity affects people in every country and is linked to 3.7 million deaths worldwide (by 2024). Without drastic action, the number of people with obesity is expected to double by 2030.
Obesity, a condition of body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher in adults, is a complex chronic disease and a major cause of non-communicable diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and some cancers; and reduces treatment outcomes in patients with infectious diseases.
In Vietnam, the Ministry of Health estimates that obesity causes serious health problems related to 200 different diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, osteoarthritis, fatty liver and some cancers, especially gastrointestinal cancer...
How to calculate body mass index (BMI):
BMI (kg/m 2 ) = weight (kg)/height (m 2 ).
Assessment of overweight and obesity according to WHO standards applied to Asians: BMI from 23-24.9 is overweight, BMI 25 - 29.9 is grade 1 obesity.
Source: Ministry of Health
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/lan-dau-tien-who-co-huong-dan-toan-cau-ve-thuoc-dieu-tri-beo-phi-18525120409222613.htm







![[Photo] Cat Ba - Green island paradise](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F04%2F1764821844074_ndo_br_1-dcbthienduongxanh638-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
























































![[VIMC 40 days of lightning speed] Da Nang Port: Unity - Lightning speed - Breakthrough to the finish line](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/04/1764833540882_cdn_4-12-25.jpeg)












































Comment (0)