The liver is an organ that plays a central role in metabolism, detoxification and energy regulation.
However, the liver is also susceptible to damage from factors such as alcohol, fatty foods, drugs, chemicals and metabolic diseases. Adding green vegetables to your daily diet, especially those with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, is considered one of the natural ways to help the liver function more effectively.
Green cabbage
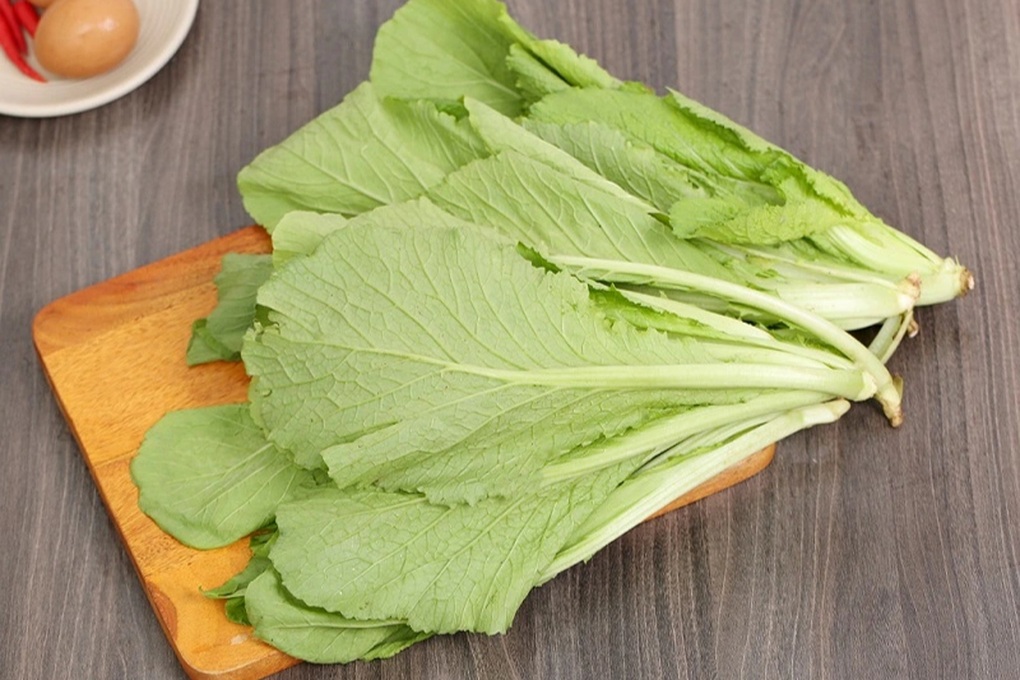

Green vegetables contain many valuable active ingredients (Photo: Getty).
Kale contains sulforaphane, a plant compound that activates phase 2 detoxification enzymes in the liver, helping to remove toxins from the body.
According to a study published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology , sulforaphane helps reduce liver inflammation, increase insulin sensitivity, and inhibit the growth of liver cancer cells in experimental models.
In addition, kale is also rich in vitamin C, E, beta-carotene and fiber. These ingredients help maintain stable liver enzymes, reduce fat accumulation in the liver and strengthen the immune system.
Fish mint
Fish mint contains many antioxidants such as quercitrin, rutin and caffeoylquinic acid which help reduce oxidative stress, one of the main causes of liver cell damage.
A study in the Journal of Medicinal Food showed that Houttuynia cordata extract was able to improve liver indices in models of chemically induced liver injury.
In addition, the anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties of fish mint also help enhance the excretion process, reducing the metabolic burden on the liver.
Gotu kola
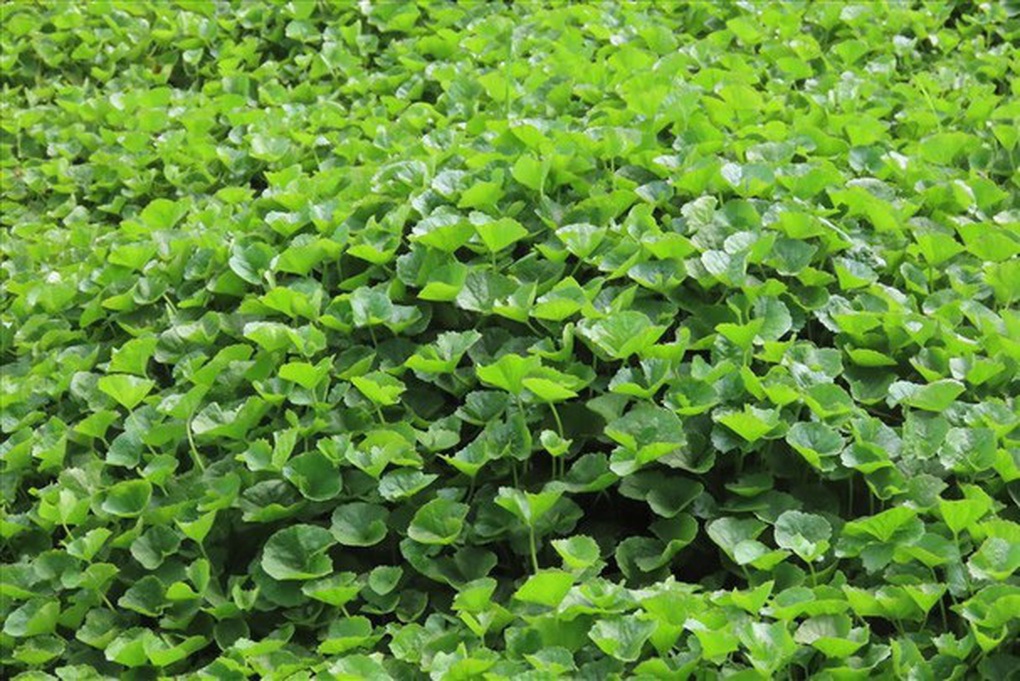

Gotu kola helps cool the liver and detoxify (Photo: Getty).
Gotu kola has the ability to support the liver in fighting the harmful effects of alcohol and toxins. Gotu kola stimulates bile production, helps improve digestion and increases the liver's ability to metabolize lipids.
The anti-inflammatory properties of gotu kola also help soothe acute and chronic inflammatory reactions in liver tissue.
One study found that gotu kola extract improved liver enzymes and reduced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in animal studies.
Artichoke
Artichokes contain cynarin and silymarin. Two active ingredients that are known to protect the liver and increase the ability to repair damaged liver tissue.
According to a study published in Phytotherapy Research, the use of artichoke extract helps reduce the levels of liver enzymes ALT, AST and GGT in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
In addition to its ability to protect the liver, artichokes also help increase bile secretion to aid in fat digestion and remove fat-soluble toxins from the body. Artichokes can be prepared by boiling, cooking soup with mushrooms, meat or used as tea.
Perilla
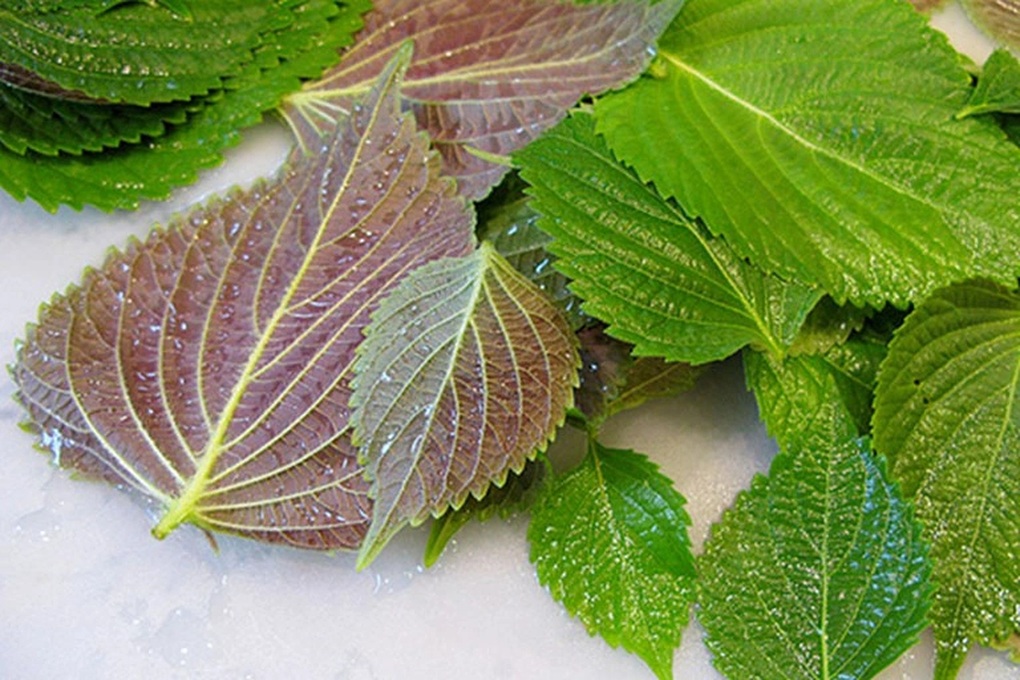

Perilla reduces the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and promotes mitochondrial production (Photo: Getty).
Perilla contains the compound perillartine, which helps regulate lipid metabolism, reduces fat accumulation in the liver, and supports blood sugar control.
A study from Kyungpook University (Korea) showed that perilla leaf extract reduces the expression of genes related to lipid synthesis and promotes mitochondrial production - helping to increase the performance of liver cells.
Strengthening liver function requires a combination of many factors, not just food. People should maintain a healthy diet, limit alcohol, increase physical activity, have regular health check-ups and get fully vaccinated to prevent hepatitis A and B.
In case of signs of high liver enzymes, jaundice, prolonged fatigue or history of liver disease, the patient should visit a hepatobiliary specialist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/suc-khoe/5-loai-rau-binh-dan-giup-tang-cuong-chuc-nang-gan-20250719094339572.htm






![[Photo] The captivating scenery of the fragrant maple forest in Quang Tri](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765353233198_lan09046-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Explore the US Navy's USS Robert Smalls warship](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765341533272_11212121-8303-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




























![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)










































































Comment (0)