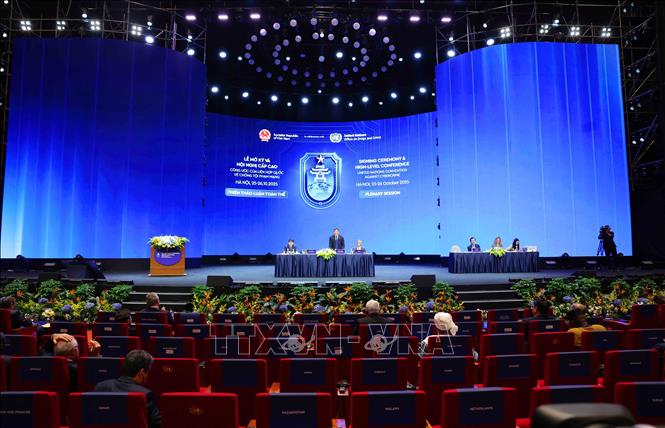

A view of the second plenary session. Photo: Phuong Hoa/VNA
According to him, what is the significance of Vietnam being chosen as the host country for the signing ceremony of the Hanoi Convention for Vietnam's international standing and role?
Vietnam's selection as the host country for the signing ceremony of the UN Convention against Cybercrime is a historic milestone in the country's diplomatic and technological development. This reflects the international community's confidence in Vietnam's growing role as a responsible partner in the global digital ecosystem. The Hanoi Convention signing ceremony not only reinforces Vietnam's image as a reliable partner in multilateral relations but also affirms its commitment to jointly addressing one of the biggest non-traditional security challenges today – cybercrime. At the same time, Vietnam can also act as a bridge between developed and developing countries towards a safer and more inclusive cyberspace.
How would you assess Vietnam's role and success in organizing the signing ceremony of the UN Convention against Cybercrime, with the participation of over 70 countries over the past two days?
First of all, I, like many other international experts, am very optimistic about the outcome of this event. This is a memorable milestone, complementing previous efforts in international cooperation on cybersecurity, especially after the Budapest Convention – which has many similarities but has not been truly comprehensive due to the lack of voices from developing countries.
In this context, Vietnam's hosting was considered a great success, demonstrating its professional organizational capacity and the positive role of a developing country that has made significant progress in digital transformation and ensuring digital sovereignty .
For the Convention to have lasting effectiveness, in my opinion, there are three key factors: First, building cross-border trust – ensuring that the new regulations still respect the data privacy rights of global users; Second, raising public awareness – because citizens are the first line of defense against cybercrime, therefore, cybersecurity education needs to be integrated into the curriculum and communication at the community level needs to be strengthened; Third, promoting the participation of the private sector and startups, alongside government agencies. Three important forces that need to be mobilized include: private businesses, with their infrastructure and data technology capabilities; research institutions, playing a role in risk analysis and policy recommendations; and technology startups, bringing innovation and new security solutions.
Furthermore, the Convention also needs to consider the role of new technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing – which present both significant opportunities and challenges. It is crucial to guide the safe and responsible use of these technologies while promoting international cooperation in cybersecurity research and governance.
I believe that if these factors are given due attention, the Hanoi Convention will be a major turning point, ushering in a more substantive phase of global cybersecurity cooperation, and Vietnam has made a very impressive start to this process.
The Hanoi Convention is expected to create a turning point in global cooperation on cybersecurity. In your opinion, what are the biggest opportunities that the Convention opens up for countries?
The Convention offers the world a rare opportunity to collectively address cyber threats. It promotes the development of a unified legal definition, standards for the exchange of electronic evidence, and mechanisms for cross-border cooperation. In particular, it provides an opportunity for developing countries like Vietnam and India to access resources for capacity building, sharing technical expertise, and collective intelligence data. This collaboration helps bridge legal gaps between nations, strengthens mutual trust and responsibility, and forms the foundation for a safer and more cooperative digital ecosystem.
Could you share more about the cooperation between Vietnam and India in combating cybercrime?
Vietnam and India have a comprehensive strategic partnership, in which cooperation on cybersecurity is playing an increasingly important role. Within this framework, the two countries can promote capacity-building programs, training in digital forensics and cybercrime investigation, as well as sharing experiences in data protection and cybercrime investigation.
Furthermore, Vietnam and India can collaborate on developing regional cybersecurity standards through ASEAN and other multilateral forums, contributing to the creation of a safe and sustainable cyberspace in the Indo-Pacific region.
Furthermore, promoting academic exchange and public-private cooperation between the two countries will also contribute to strengthening their joint response capabilities to emerging cybersecurity challenges.
Regarding future prospects, how do you assess the potential for the Hanoi Convention to become a global legal framework for combating cybercrime, and what role can Vietnam continue to play in the implementation phase?
I believe the Hanoi Convention has enormous potential to become a unified platform for international cooperation on combating cybercrime. However, that success depends on the level of transparency, cooperation, and sustained political commitment of the signatory countries.
During the implementation phase, Vietnam can play the role of a "coordinator and connector," promoting cooperation among developing countries, sharing its own digital transformation experiences and cybersecurity practices. More importantly, Vietnam can ensure that the Hanoi Convention does not just exist on paper, but is realized into concrete results: a fair, safe, and people-centered cyberspace.
Thank you, sir!
Source: https://baotintuc.vn/thoi-su/cong-uoc-ha-noi-viet-nam-khang-dinh-vai-role-cau-noi-toan-cau-trong-hop-tac-an-ninh-mang-20251027062542796.htm



















































































































Comment (0)