Bond yields in emerging East Asia rose amid growing expectations that interest rates will remain elevated for longer, according to a new report by the Asian Development Bank (ADB). Vietnam’s local currency bond market rebounded, expanding 7.7% quarter-on-quarter.
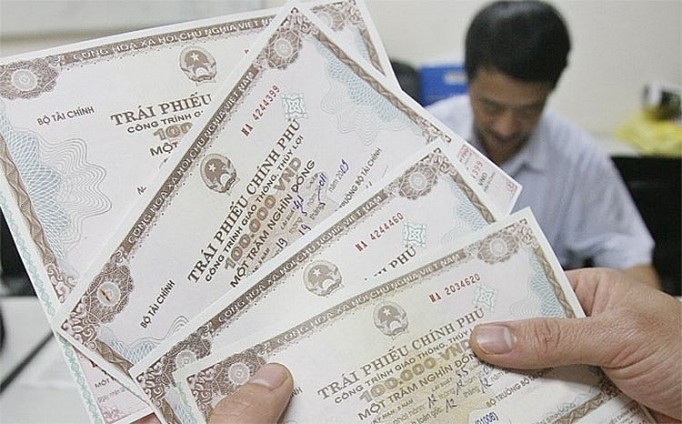 |
| Treasury bonds and other government bonds increased 3.3% quarter-on-quarter to support the government's funding requirements. (Source: VGP) |
Vietnam’s local currency bond market recovered with growth of 7.7% quarter-on-quarter, thanks to increased government bond issuance and the State Bank of Vietnam’s resumption of central bank bill issuance in March, according to ADB.
Treasury and other government bonds rose 3.3 percent from the previous quarter to support government funding requirements. Corporate bonds fell 0.9 percent due to a large volume of maturing bonds and low issuance.
The sustainable bond market in Vietnam reached a size of 800 million USD by the end of March. This market includes green bonds and sustainable bond instruments issued by individual enterprises and mostly has short maturities.
Government bond yields rose an average of 56 basis points across all maturities as domestic inflation picked up and the US Federal Reserve delayed cutting its policy rate. Vietnam’s year-on-year consumer price inflation rose to 4.44% in May, approaching the government’s ceiling of 4.50%.
The latest edition of the ADB's Asia Bond Monitor, released recently, also showed that bond outflows from regional markets reached $20 billion in March and April. Slower-than-expected deflation has reinforced the case for higher interest rates for longer and boosted short- and long-term bond yields in both advanced economies and regional markets.
Regional currencies fell against the US dollar and credit default swap spreads widened in most markets. Most regional equity markets rallied on the economic outlook, but equity markets in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) saw outflows of US$4.7 billion.
“Financial conditions in emerging East Asia remain stable, but persistent geopolitical tensions and adverse weather events pose higher risks to inflation, adding to uncertainty about the path of disinflation,” said ADB Chief Economist Albert Park. “Some regional monetary authorities may maintain higher interest rates for longer to protect their currencies amid uncertainty about the global monetary stance and reflationary trends.”
Emerging East Asia, comprising ASEAN member economies, China, Hong Kong (China) and South Korea, is expected to see its local currency bond market grow at a slower pace of 1.4% in the first quarter of 2024, reaching $24.7 trillion.
According to the ADB, a slowdown in government bond issuance in China and Hong Kong (China) has held back the expansion of the regional market. But the region’s corporate bond segment has grown, supported by strong issuance in both economies, with the Chinese government taking measures to boost the domestic economy.
Higher interest rates for longer periods also cast a shadow over sustainable bond markets in the ASEAN, China, Japan and Korea (ASEAN+3) region, leading to a decline in sustainable bond issuance in Q1 2024, reaching USD 805.9 billion at the end of March.
It remains the world’s second-largest sustainable bond market, accounting for 18.9% of the global market share, behind the European Union (EU) at 37.6%. However, sustainable bonds account for only 2.1% of the total ASEAN+3 bond market, compared to 7.3% in the EU.
Source: https://baoquocte.vn/adb-thi-truong-trai-phieu-bang-dong-noi-te-cua-viet-nam-phuc-hoi-tang-truong-77-276149.html


![[Photo] 60th Anniversary of the Founding of the Vietnam Association of Photographic Artists](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764935864512_a1-bnd-0841-9740-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the VinFuture 2025 Award Ceremony](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764951162416_2628509768338816493-6995-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)










































































































Comment (0)