- Common causes of blood clotting disorders
- Recognizing blood clotting disorders
- Note for patients with blood clotting disorders
Blood clotting disorders are conditions in which the body loses its ability to control the process of blood clotting. Normally, blood clots form when injured to stop bleeding. With a blood clotting disorder, a person may bleed excessively even without injury. For pregnant women, blood clotting disorders can be dangerous for both mother and baby.
Common causes of blood clotting disorders
- Genetics: Blood clotting disorders are inherited from parents. These include Haemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency), B (factor IX deficiency), and C (factor XI deficiency). Other causes include: Leiden V mutation, occurring in 5% of people of European descent; Pro-thrombin G20210A mutation (factor II mutation), occurring in 2% of the population; deficiencies in natural proteins that prevent blood clotting (such as Antithrombin III, protein C, and protein S); fibrinogen dysfunction or elevated levels; hyperhomocysteinemia; platelet aggregation syndrome; and an abnormal fibrinolytic system.
- Platelets: A decrease in the number or quality of platelets in the blood can cause abnormal bleeding.
- Liver disease.
- Cancers such as kidney, lung, colon, uterine, and testicular cancer can increase the risk of blood clotting disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency: people who are deficient in vitamin K.
- HIV, sepsis, or other infections.
- Nephrotic syndrome (too much protein in the urine).
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
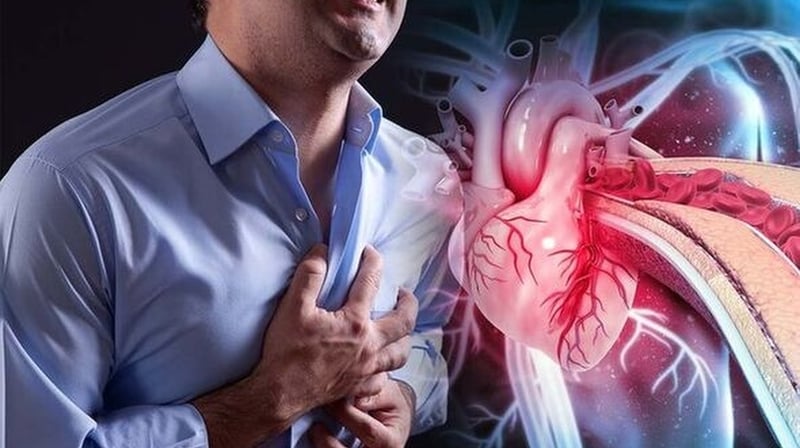
Blood clotting disorders can cause myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Recognizing blood clotting disorders
People with bleeding disorders may experience symptoms including: excessive bleeding that cannot be controlled with pressure; easy bruising; blood in the urine or stool; heavy bleeding during menstruation or after childbirth; bleeding under the skin; redness and swelling in many areas of the body; umbilical cord bleeding in newborns.
Several factors can also lead to other symptoms. For example, liver disease can cause fatigue, weakness, and loss of appetite.
Additionally, individuals with hypercoagulable states may experience symptoms depending on the presence and location of the blood clot. For example, a blood clot near the heart or lungs may cause chest pain, shortness of breath, or discomfort around the upper body. These symptoms may indicate a heart attack or pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis often include pain, swelling, and skin discoloration around the area where the blood clot is located, such as in the leg.
Untreated blood clotting disorders can have serious health consequences. Patients are at risk of blood clots forming in their veins, which can lead to complications such as heart attacks and strokes.
Pregnant women with blood clotting disorders, in particular, require close medical monitoring to avoid life-threatening complications.
Note for patients with blood clotting disorders
Patients with blood clotting disorders should pay attention to the following:
- Limit activities that carry a risk of injury or bleeding, such as extreme sports , shaving, nail trimming, and tooth extraction. Use protective equipment such as helmets, gloves, bandages, and adhesive dressings.
- Regularly check for wounds, bruises, bleeding, and infections, and treat them promptly.
- Consult your doctor before using any medication, especially those that affect blood clotting such as Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Clopidogrel, Warfarin, etc.
- Inform your doctor about your blood clotting disorder when you need surgery, tests, vaccinations, blood transfusions, etc.
- Monitor coagulation-related parameters such as INR, APTT, PT, Fibrinogen, D-dimer, coagulation factors, etc.
- Follow the schedule and dosage of blood clotting disorder medications prescribed by your doctor precisely.
In summary: If you suspect you have a blood clotting disorder, you should immediately go to a medical facility for diagnosis. In addition to a physical examination, doctors will order additional tests to determine the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/6-luu-y-cho-benh-nhan-bi-roi-loan-dong-mau-tranh-nguy-co-bien-chung-169251207182514959.htm




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)














































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)


















































Comment (0)