Betel leaves were once present in most Vietnamese households in the past, from wedding ceremonies and ancestral worship to folk remedies for coughs, headaches, and infections. In the context of increasing interest in herbal products and natural medicine, a scientific and cautious approach to betel leaves reveals their significant health potential.
1. Nutritional value of betel leaves
- 1. Nutritional value of betel leaves
- 2. Potential health benefits of betel leaves
- 3. Common ways to use betel leaves
- 4. Side effects and risks to be aware of
- 5. Who should be cautious when using betel leaves?
Betel leaf (scientific name Piper betel) belongs to the genus Piper. It is a perennial climbing plant with heart-shaped leaves, thriving in tropical and subtropical regions, including Vietnam.
The nutritional value of betel leaves includes: Water: 85-90%; protein: 3-3.5%; fat: 0.4-1%; minerals: 2.3-3.3%; fiber: 2.3%; carbohydrates: 0.5-6.1%; potassium: 1.1-4.6%; calcium: 0.2-0.5%; vitamin C: 0.005-0.01%; essential oils: 0.08-0.2%...
Notably, the essential oils and polyphenol compounds in betel leaves are considered to be the components responsible for many of its potential biological effects.
Preclinical studies suggest that betel leaves may possess several properties: antioxidant, antifungal, wound-healing, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic activity, and potential to protect cells against certain carcinogens...
However, much of the current evidence is limited to laboratory or animal studies. Major health organizations such as the WHO and NIH (USA) emphasize that herbal remedies cannot replace standard medical treatment.
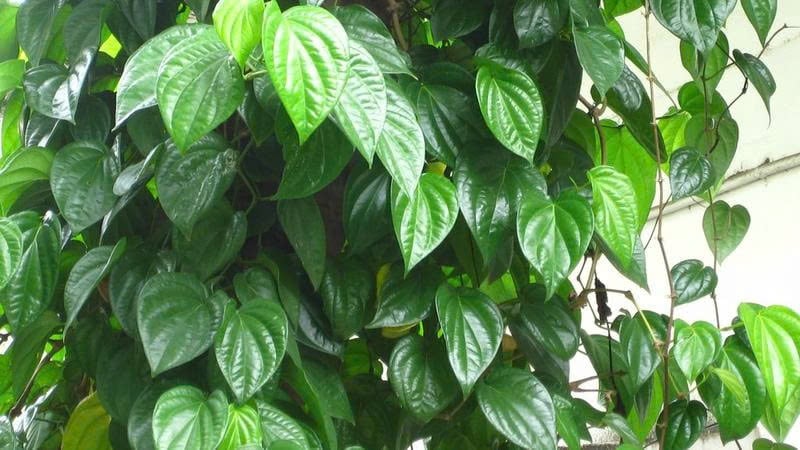

Betel leaves were once present in most Vietnamese households in the past, from wedding ceremonies and worship to folk remedies for coughs, headaches, and infections.
2. Potential health benefits of betel leaves
1. Headache relief: Betel leaves can help relieve headaches due to their natural cooling and pain-relieving effects. They are often used by crushing the leaves and applying them to the temples or the top of the head, or by using them for steam inhalation to relieve colds. The active compounds in betel leaves help relax the nerves, reduce stress, and provide a feeling of well-being, but a doctor should be consulted if the headache is severe or prolonged.
2. Potential for supporting cancer prevention: Some studies show that betel leaf extract contains phenolic compounds that can inhibit the growth of cancer cells in vitro. However, it should absolutely not be misunderstood that betel leaves can treat cancer. The WHO affirms that cancer needs to be treated with standard medical protocols, and herbal remedies can only play a supportive role if permitted by a doctor.
3. Supports treatment of fungal infections: Betel leaves can help treat fungal infections because they contain a bioactive compound called hydroxychavicol (a type of polyphenol), which can slow the growth of fungi. They are used to treat skin infections or as a mouthwash for oral thrush.
4. Stomach Protection Support: Betel leaves may support the treatment of stomach ulcers due to their protective properties. Antioxidants can enhance enzyme activity, which is beneficial for ulcers. They may also increase mucus production in the mucosa. However, there is insufficient clinical evidence to support its use as a substitute for medication in treating stomach ulcers.
5. Potential for supporting blood sugar control: Betel leaves may have health benefits for diabetes. Studies in mice suggest that betel leaves may lower blood sugar levels. However, further research is needed to evaluate the effects of betel leaves on diabetes.
The NIH notes that diabetes is a chronic disease requiring lifelong treatment, and herbal remedies should not be used as a substitute for medication.

Studies show that betel leaves can lower blood sugar levels.
6. Supports the reduction of allergic reactions: Betel leaves may help treat allergies. In laboratory studies, they were tested on human lung cells to see their effect on substances that cause allergic reactions. The results showed that betel leaves may help reduce these allergy-causing substances. However, more human studies are needed to evaluate the effects of betel leaves on allergies. If you have allergies, consult your doctor.
7. Supports wound healing: Animal studies show that betel leaves can promote epithelialization, helping wounds heal faster. Note, Large wounds and infections require immediate medical attention.
8. Relieving Constipation: In traditional medicine, betel leaves were once used to relieve constipation via rectal administration (in combination with castor oil). This method should not be used without professional advice.
3. Common ways to use betel leaves
- Chew betel leaves (without tobacco, limit betel nut and lime intake).
- Boil betel leaves in water to use as a mouthwash or for external skin cleansing...
The Mayo Clinic advises against using herbal remedies for extended periods or in high doses without medical guidance.
4. Side effects and risks to be aware of
Chewing betel nut along with lime and tobacco increases the risk of:
- Addictive
- Overstimulation, sweating, drooling
- Increased risk of oral mucosal damage.
The WHO has classified the habit of chewing betel nut along with tobacco as a risk factor for oral cancer.
5. Who should be cautious when using betel leaves?
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Children, the elderly
- People who are taking medication to treat a chronic illness...
There is currently insufficient data on drug interactions, so consult your doctor before use.
Betel leaves are a familiar medicinal herb with remarkable biological potential. However, the true value of betel leaves is only realized when used correctly, for the right people, and as a substitute for modern medicine. Understanding and using them correctly is key to protecting your health.
Readers are invited to read more:
Source: https://suckhoedoisong.vn/8-tiem-nang-chua-benh-cua-la-trau-khong-169251213215859112.htm







![[Image] Vietnam's colorful journey of innovation](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F14%2F1765703036409_image-1.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)

























































![[Image] Vietnam's colorful journey of innovation](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/14/1765703036409_image-1.jpeg)







































Comment (0)