From side sleeping, stomach sleeping to back sleeping, everyone has a favorite sleeping position.
Previous studies have shown that sleeping on your back causes several potential health problems, including high blood pressure and obstructive sleep apnea, as well as problems for those with nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux or who are pregnant. Now, a new study has uncovered another harmful effect of this sleeping position.
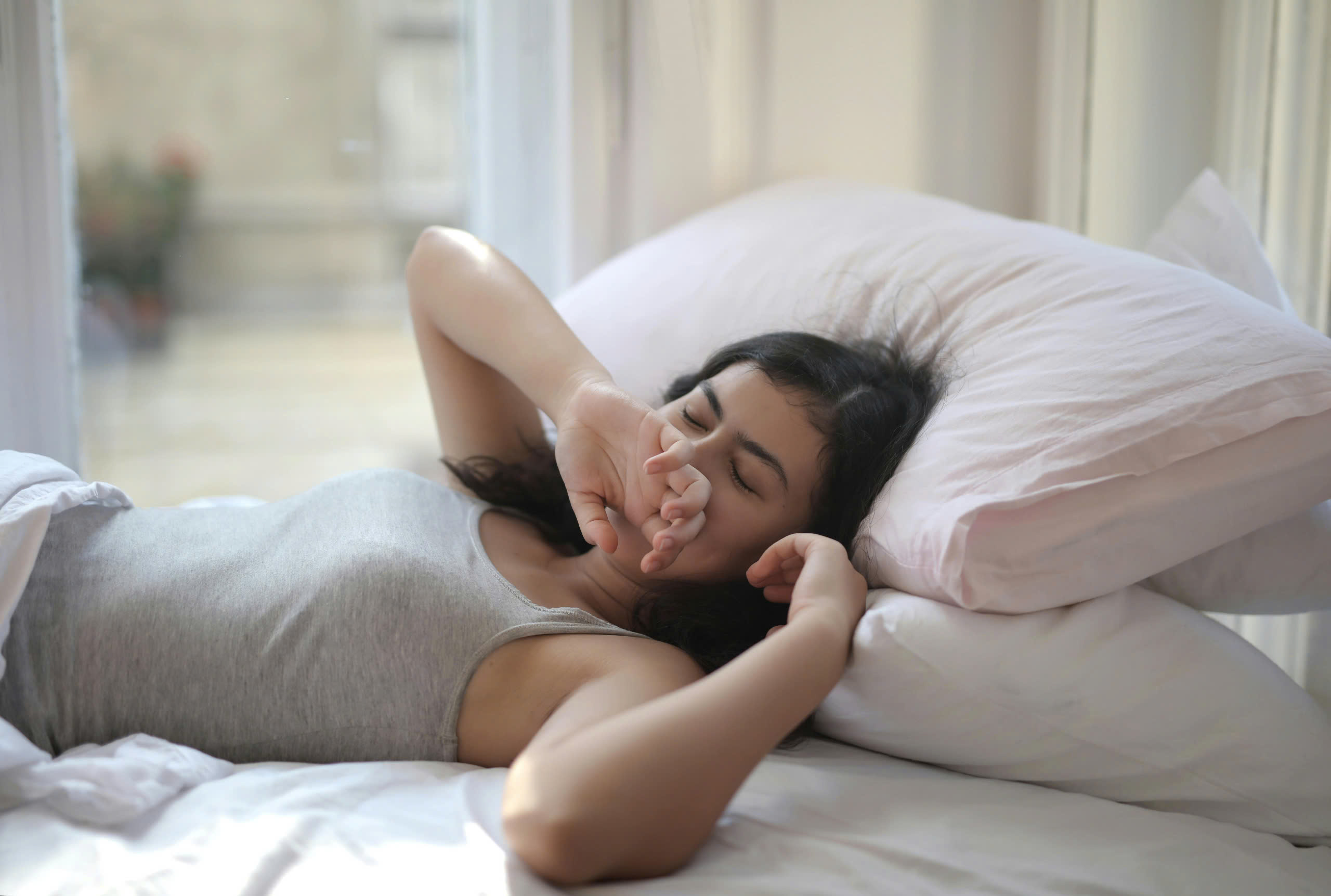

Many studies show that sleeping on your back causes some potential harmful effects on health.
New research, building on a 2019 study, found that sleeping more than two hours a night on your back increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, according to the medical news website Medical News Today.
The new study, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of California San Francisco, the Mayo Clinic School of Medicine (USA), and Saint Mary's General Hospital in Toronto (Canada), included individuals with mild cognitive impairment, progressive supranuclear palsy – a late-onset neurodegenerative disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's dementia, and a control group.
Participants wore devices to calculate the number of hours they slept in a supine position each night, and also assessed nine sleep biomarkers to differentiate the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Sleeping on your back for more than two hours is associated with neurodegenerative conditions.
Results found that people who slept more than two hours in a supine position had four neurodegenerative conditions compared with the control group.
Researchers believe this provides further evidence of a strong link between sleeping on your back and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and mild cognitive impairment.
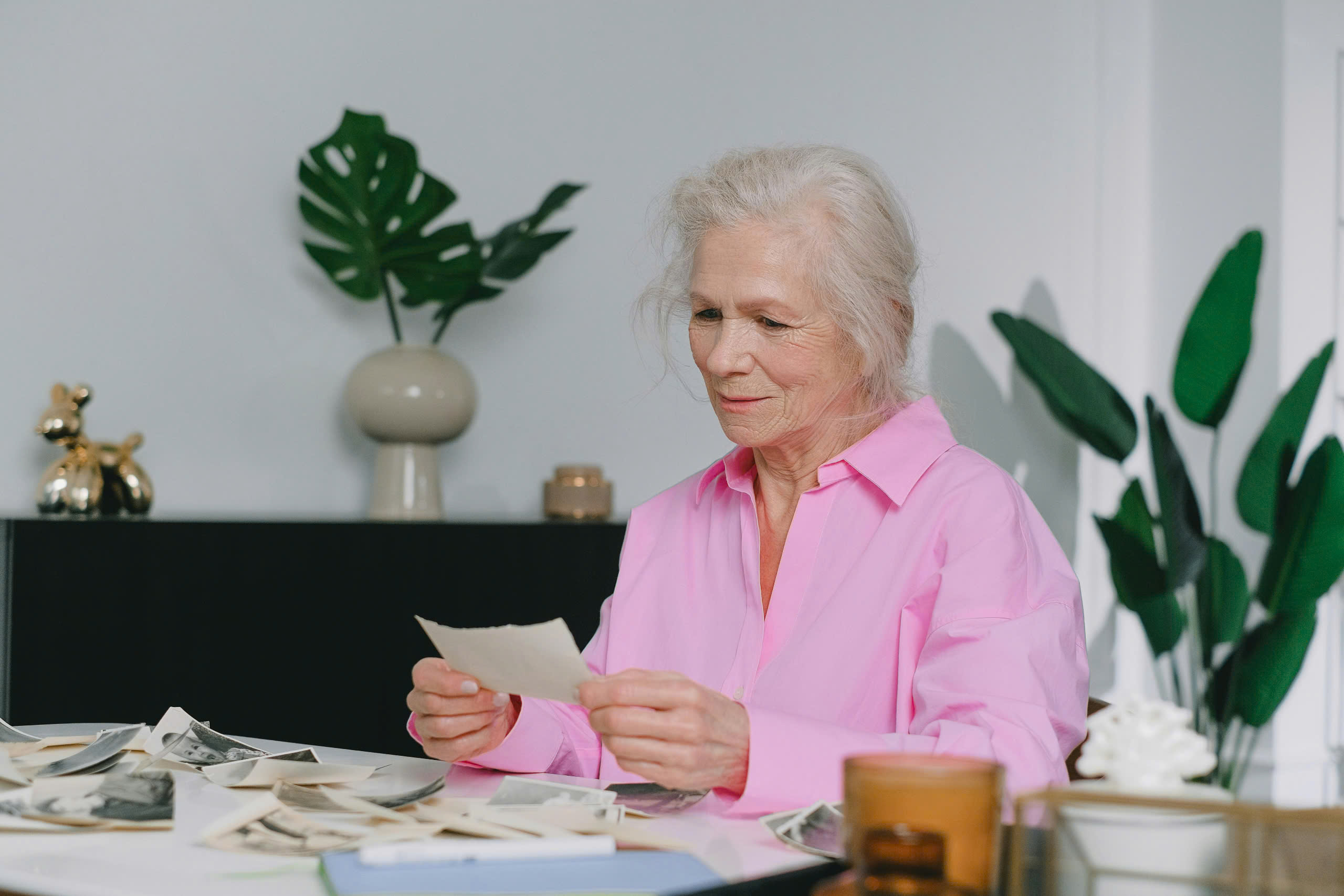

Sleeping for more than two hours each night in a supine position increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Why might sleeping on your back increase the risk?
Researchers explain that when sleeping on your back, neurotoxin clearance is less efficient than when sleeping on your side due to differences in how venous blood returns to the heart from the brain. Additionally, sleeping on your back causes more severe sleep apnea, leading to continuous sleep disruptions, which also contributes to the accumulation of neurotoxins. The new study suggests that the inefficient neurotoxin clearance resulting from years of sleeping on your back contributes to neurodegeneration.
Some emerging research suggests that sleeping on your side may help the brain remove waste products, which could theoretically reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, the authors added.
In summary, while sleeping posture is important for brain health, prioritizing good sleep hygiene and lifestyle factors in general is even more crucial to reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases, according to Medical News Today.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/khoa-hoc-chi-ra-tu-the-ngu-co-the-gay-hai-nguoi-lon-tuoi-nen-tranh-185240914201733219.htm


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)


















































Comment (0)