What is derivative?
According to the Math 11 textbook, volume 2, part of the "Connecting Knowledge and Life" series, the derivative of a function is one of the important concepts in mathematics. The derivative represents the rate of change of a function at a point or an interval.
Formula for the derivative of a function at a point
The derivative of a function at a point indicates the degree of change of the function at that point.

Derivatives of common functions
These are the simplest forms of power functions – the foundation for calculating derivatives for many more complex functions later on.

Derivatives of sums, differences, products, and quotients.
Derivatives of sums, differences, products, and quotients are important rules that help us calculate the derivatives of complex expressions from simple functions. Instead of having to prove them again from the definition of a limit, we can simply apply these formulas and rules to simplify the process.
Specifically, the derivative of a sum or difference is equal to the sum or difference of its derivatives; the derivative of a product follows the rule "derivative first, then multiplication; addition first, then derivative"; and the derivative of a quotient follows the rule "numerator derivative multiplied by denominator, subtraction numerator multiplied by denominator derivative, division by denominator squared". These formulas will be clearly presented below, with illustrative examples, to help students easily remember and apply them to exercises.
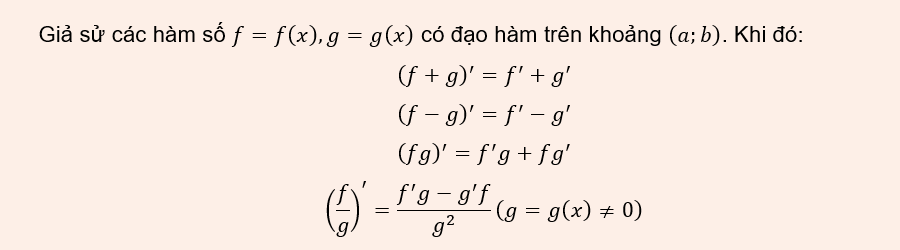
Derivative of a composite function
The derivative of a composite function is used when the function is formed from multiple nested functions. Applying the chain rule, the derivative of the composite function equals the derivative of the outer function multiplied by the derivative of the inner function.

Derivatives of trigonometric functions
The derivatives of trigonometric functions help us understand the rate of change of functions such as sin(x), cos(x), or tan(x) as the value of x changes.
By mastering the derivatives of sin(x) and cos(x), we can deduce the derivatives of other trigonometric functions, as they can all be expressed in terms of sin and cos (using the quotient rule).
In the following section, we will prove the derivative formulas for sin(x) and cos(x). From there, we can calculate derivatives for other trigonometric functions as well as extend this to inverse trigonometric functions and some other special formulas.

Derivative of an exponential function
The derivative of an exponential function tells us the rate of change of functions of the form a x (with a>0, a≠1) or especially e x . Among these, e x is considered the most important exponential function because its derivative is equal to itself.

Derivative of a logarithmic function
The derivative of a logarithmic function indicates the rate of change of functions of the form loga (x) (with a>0, a≠1), the most important of which is ln(x) - the natural logarithm base e.
Knowing the derivative formula for ln(x), we can easily deduce the derivative of loga (x) using the change of base formula.

Second derivative
The second derivative is the derivative of the first derivative; that is, we take the derivative of a function twice in a row. If the first derivative tells us the rate of change of the function, then the second derivative tells us the rate of change of that same rate.
In geometry, the second derivative helps determine the curvature/concavity of a graph. In physics, if a function represents distance as a function of time, the first derivative is velocity, while the second derivative is acceleration.

Tips for remembering derivative formulas
- Learn formulas in groups rather than individually.
- Save the recipe sheet so you can use it immediately if you forget.

- Learn about derivatives through poetry:
A hundred years in the human world
The derivative is something that lazy students who study it might not be very good at.
X with exponent (en) n
We take the derivative to the power of n first.
Then the exponent above
We just subtract 1 from that.
Derivative of root x, my friend.
Remember that love, my friend, don't forget it.
Death is the number 1, which remains unchanged.
For example, write the two square roots x together for speed.
Derivative of the product of two brothers
I'll teach you first, and save you for later.
Then add a plus sign to speed things up.
Keep the first brother as is, and the second brother after the derivative.
If you truly love someone, you'll endure any hardship.
The virtue of the mother remains unchanged.
Don't forget the minus sign!
The source of death, the path of motherhood follows closely behind.
Where does the square of the denominator go?
Let's take it downstairs so we can memorize it faster.
The sine derivative is truly amazing.
It turns out that cosine is never wrong.
Cosine of the derivative is as beautiful as a dream.
Except for sine, which leaves you bewildered all alone.
Hard work compensates for a lack of intelligence.
One divided by cosine squared is the derivative of tangent.
Only through diligent study can one achieve glory.
Even though the funeral is difficult, it still carries a sense of duty.
Subtract one from the number and remember to do it.
Be a good person, don't be too frivolous.
The hat X is really strange.
Its derivative, we keep it unchanged for now.
We leave the exponential function as is.
The base Nepe number follows immediately.
Nepe x derivative quickly
It's just 1 divided by x, it's not difficult at all.
What is the difference between Logarithm x and Logarithm?
Let us not forget the base number of our country.
(Collect)
Source: https://vietnamnet.vn/dao-ham-la-gi-cac-cong-thuc-dao-ham-chi-tiet-2452539.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds a phone call with the CEO of Russia's Rosatom Corporation.](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765464552365_dsc-5295-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Photo] Closing Ceremony of the 10th Session of the 15th National Assembly](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F11%2F1765448959967_image-1437-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)















































![[OFFICIAL] MISA GROUP ANNOUNCES ITS PIONEERING BRAND POSITIONING IN BUILDING AGENTIC AI FOR BUSINESSES, HOUSEHOLDS, AND THE GOVERNMENT](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/11/1765444754256_agentic-ai_postfb-scaled.png)


















































Comment (0)