In recent days, in the southern provinces, there have been continuous cases of poisoning due to eating mushrooms and cicada pupae. The latest case is that a family of 3 people were poisoned after eating mushrooms picked from the forest and stir-fried with squash, which happened in Tay Ninh, leading to the husband's death, the wife's critical condition, and the child's liver failure and blood clotting disorder.
Poisoned repeatedly
Three days before, the couple, both 44 years old, went into the forest to pick mushrooms to stir-fry with squash. The husband ate the most, half of the stir-fry. After eating for 8-12 hours, the whole family had stomach aches, vomited, and had loose stools. The digestive disorder became more and more severe, so all three were taken to the local hospital for emergency treatment before being transferred to Cho Ray Hospital (HCMC).
On the way to the hospital, the husband's condition worsened, he was in critical condition, had respiratory failure, and was given a resuscitation bag but died shortly after arriving at the hospital. The wife and 17-year-old daughter suffered from acute liver failure and blood clotting disorder.
Dr. Nguyen Thi Thuy Ngan, Deputy Head of the Department of Tropical Diseases at Cho Ray Hospital, said that after 2 days of treatment, the wife's health is still getting worse, her liver failure has not improved, and it is unlikely that she will survive. The son's health has improved a little, and he is being monitored and treated for liver function and blood clotting disorders. "This family has a habit of going to the forest to pick mushrooms to eat during the rainy season. The previous times they ate mushrooms were fine, but this time they were poisoned," said Dr. Ngan.
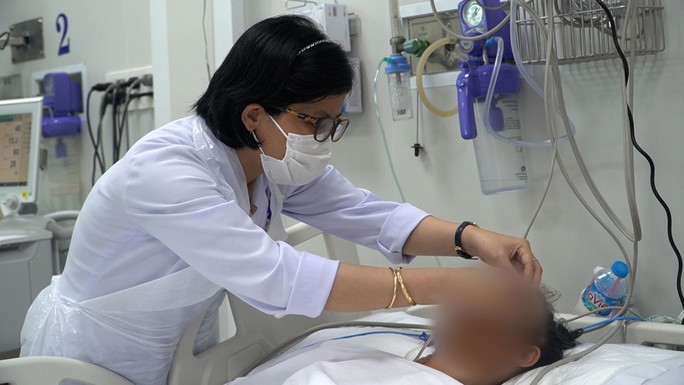
The victim of a family poisoning by mushrooms in Tay Ninh is being actively treated at Cho Ray Hospital (HCMC).
Not long before, Cho Ray Hospital also treated a 34-year-old man from Duc Linh district, Binh Thuan province, who mistakenly ate poisonous mushrooms. While gardening, this man saw cicada pupae with mushroom-like shapes, thought they were "cordyceps" and brought about 12 to 14 of them home to eat. The consequences were vomiting, stomachache, and impaired perception... "Every year, the hospital receives many similar poisoning cases" - Dr. Ngan informed.
Never before has poisoning by natural organisms occurred so frequently everywhere as in recent days, with the number of people infected reaching several dozen.
On June 8, a mother and her child in Xuan Loc district, Dong Nai province, were poisoned by eating mushrooms growing on cicada pupae. The patient PHT (12 years old) was taken to Dong Nai Children's Hospital for emergency treatment, while the mother, NTTN, was also given emergency detoxification by doctors at Thong Nhat General Hospital (Dong Nai) to save her life.
At the same time, Ba Ria Hospital (Ba Ria - Vung Tau province) also treated a 39-year-old victim in Xuyen Moc district who was poisoned after eating mushrooms grown from cicada carcasses picked from a neighbor's garden. A few days earlier, this hospital treated 4 cases in Long Dien district who were poisoned by eating strange mushrooms, of which 2 serious cases were transferred to Ho Chi Minh City.
Meanwhile, the Central Highlands General Hospital received 2 clusters of poisoning cases with 6 patients. The cause of poisoning was also due to eating mushrooms grown from cicada corpses and mistakenly thinking it was "Cordyceps".
According to the Food Safety Department - Ministry of Health, poisoning surveillance data and epidemiological factors show that every year in spring and early summer, in the Northern mountainous provinces and the Central Highlands, poisoning cases often occur due to people using foods containing natural toxins (poisonous mushrooms, wild fruits, wild plants, etc.). The number of poisoning cases reaches hundreds, in which many cases are fatal or leave serious sequelae despite timely treatment.
There is no specific antidote.
Experts warn that there are currently more than 100 species of poisonous mushrooms, and it is difficult to distinguish between edible mushrooms and deadly poisonous mushrooms in terms of appearance. There are many types of poisonous mushrooms that are harmless to animals but are poisonous to humans. Each type of poisonous mushroom has different toxins, affecting different organ systems. Victims may experience hallucinations, perceptual disorders; effects on the digestive system, liver function, kidney failure, etc.
Doctor Nguyen Thi Thuy Ngan said that poisoning after eating mushrooms can start very quickly, within a few hours, but there are also cases after 8 - 12 hours. Symptoms of poisoning are often just digestive symptoms, so people can be subjective. Determining the toxins of many poisonous mushrooms is also not easy.
When cicadas lay eggs in the soil, then develop into larvae (also known as cicada pupae), cicada pupae lie in the soil, possibly next to fungal spores. These fungi attack and parasitize the host and will replace the host's tissues and grow long stems. These fungi will absorb nutrients from the host, causing the host to die and grow outside the host's body. Therefore, they are called "Cordyceps". Depending on the type of fungus parasitizing the host, it is a fungus that is beneficial to human health or a poisonous mushroom. "Cordyceps" can be a nutritious food (traditional medicine) or poisonous to humans. From the above cases, we can see that the danger of eating poisonous mushrooms is greater.
According to doctors, there is currently no specific antidote for mushroom poisoning, only symptomatic treatment. To avoid unfortunate incidents related to poisonous mushrooms, people should not arbitrarily eat wild mushrooms; they should only eat cultivated mushrooms, with a certain species and origin. Absolutely should not and cannot rely on the shape and color of mushrooms to distinguish between healthy and poisonous mushrooms. Poisonous mushrooms, even after cooking, the toxins remain stable and are not destroyed.
"People need to be extremely vigilant when eating wild mushrooms because it is difficult to distinguish between poisonous and non-poisonous mushrooms, especially eating mushrooms following the trend of nutritious mushrooms such as chicken egg mushrooms and goose egg mushrooms that are spread on social networks. In case of mushroom poisoning, relatives need to bring a sample of the mushroom or a picture of the mushroom the victim used when going to the emergency room. That will help the doctor identify the type of mushroom, identify the toxin and have the optimal treatment solution" - Dr. Ngan recommended.
Two brothers with botulinum poisoning receive hospital support
Cho Ray Hospital said on June 9 that two brothers with botulinum poisoning after eating bread with pork sausage were discharged and sent back to their hometown.
Although the critical stage has passed, the two patients still need prolonged mechanical ventilation, which can last for 2 months or more. To prevent the risk of infection as well as facilitate family care, the two patients have been transferred to Hau Giang General Hospital (which has the capacity to treat the remaining stage) for continued treatment.
According to MSc. Le Minh Hien, Head of the Social Work Department of Cho Ray Hospital, due to the difficult circumstances of the two patients, the Social Work Department mobilized benefactors to support 130 million VND. With a total treatment cost of more than 300 million VND, after deducting the amount paid by insurance, the amount of 130 million VND was used to pay for expenses not covered by insurance.
Source


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the VinFuture 2025 Award Ceremony](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764951162416_2628509768338816493-6995-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)


![[Photo] 60th Anniversary of the Founding of the Vietnam Association of Photographic Artists](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F05%2F1764935864512_a1-bnd-0841-9740-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)




![[Infographic] Air pollution and recommendations from the Ministry of Health](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/05/1764950568593_screen-shot-2025-12-05-at-222015-png.webp)


























































































Comment (0)