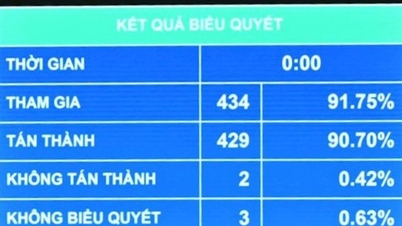
With a high approval rate, the National Assembly affirmed its strong consensus on the necessity of enacting the AI Law, a landmark law that will create a pioneering legal framework to help Vietnam catch up with global AI development trends and enhance national competitiveness in the digital age.
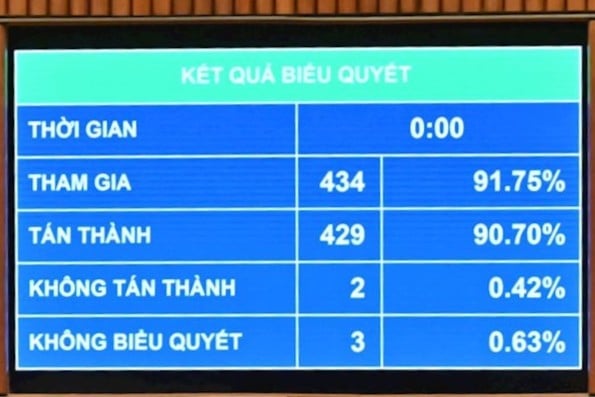
The National Assembly voted to pass the AI Law.
This is the first time Vietnam has drafted and enacted a separate law on AI. The law, comprising 35 articles, is designed with a "management-for-development" approach, ensuring a balance between risk control and innovation promotion, in line with international practices and supporting Vietnam's proactive integration with new technological standards.
AI law identifies humans as the central focus, stipulating that AI should serve humans, not replace them, and that human oversight is required in important decisions.
The AI Law lays the foundation for AI autonomy, from computing infrastructure to data and research capabilities, helping Vietnam build a strong AI workforce capable of competing internationally; it allows the State to invest in a national AI computing center and build a controlled open data system. These directions are expected to reduce computing costs, remove barriers to market entry, and promote a more competitive and transparent AI ecosystem.
The law also creates regulations to promote AI development, such as: establishing a National AI Development Fund, implementing an AI Voucher mechanism to support businesses in applying AI, and establishing a controlled testing sandbox for sensitive AI solutions. These are important tools to reduce risks, lower testing costs, and enable technology companies, especially high-tech startups, to test sensitive AI applications in an environment exempt from certain legal liabilities.
The AI law simultaneously addresses emerging issues such as AI-generated content, algorithmic ethics, and the responsibility of cross-border AI service providers, thereby paving the way for Vietnam to integrate more deeply with international standards while maintaining its digital sovereignty .
A key aspect of the Law is its risk-based management approach. Accordingly, AI systems are classified according to their impact and risk levels, thus linking them to corresponding legal obligations. Applications posing a high risk to the legitimate rights and interests of organizations and individuals (in the fields of finance, healthcare, justice, labor, education , etc.) will have to meet stricter standards regarding data, verification, monitoring, and human intervention mechanisms. This approach allows for a balance between two objectives: encouraging innovation in AI and controlling potential social consequences.
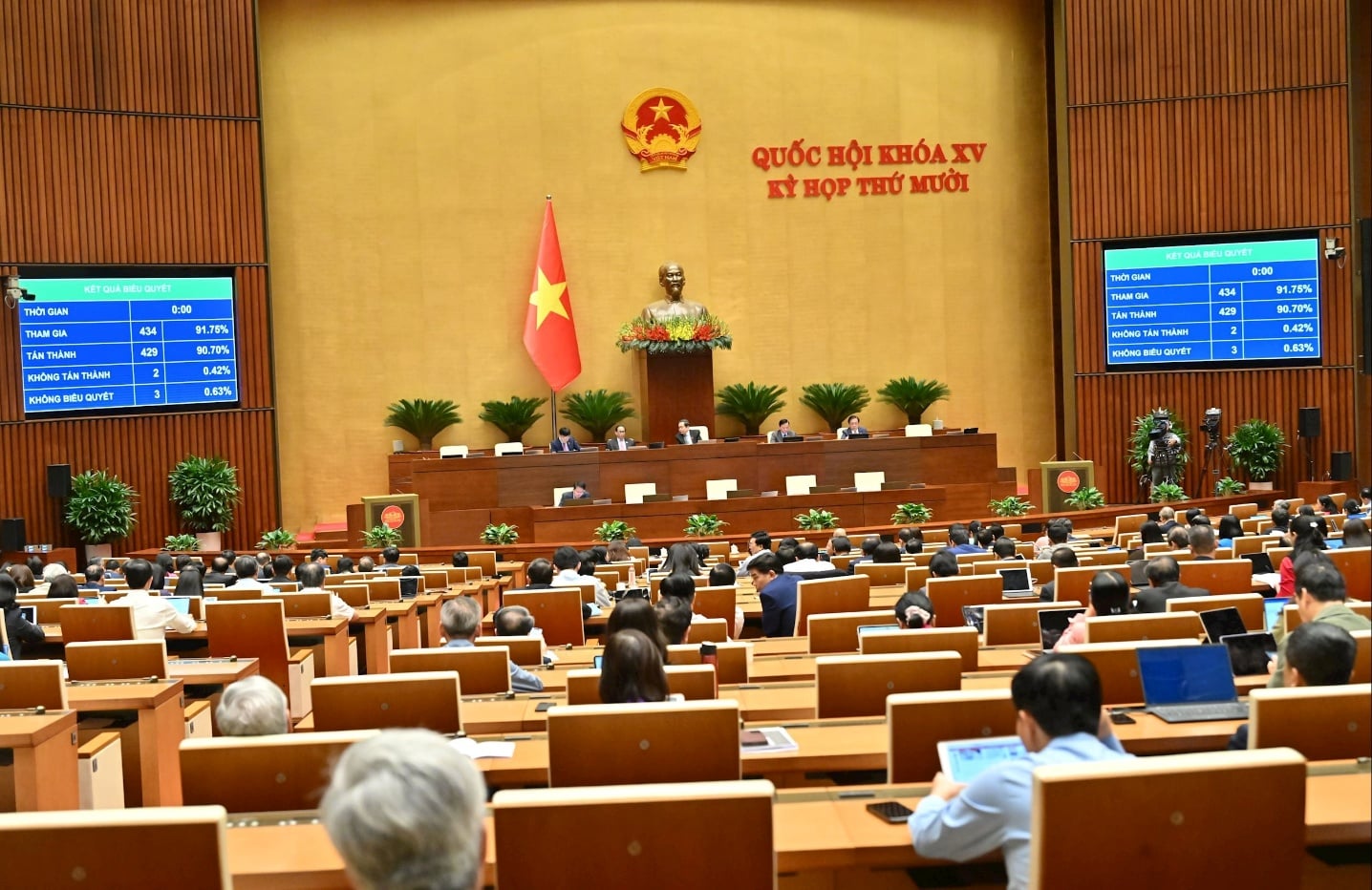

The 10th session of the 15th National Assembly passed the Law on AI.
Alongside regulations on technology and management, the AI Law places a significant emphasis on human resource development. The law requires the development of a long-term national AI human resource strategy; the integration of basic AI knowledge into general education; and encourages universities to open new majors, expand academic autonomy, and attract international experts. The national AI human resource development program will contribute to the formation of a high-quality workforce of AI experts and engineers in the future.
The National Assembly's approval of the AI Law is considered a necessary and timely step as AI is deeply penetrating all aspects of life. A comprehensive and clear legal framework will help Vietnam avoid the risk of falling behind, ensure data security, privacy, and the sustainable development of the AI ecosystem. From here, Vietnam officially enters a new phase, a phase of proactive, responsible, safe, and innovative AI development, creating a foundation for AI to become one of the most important growth drivers of the digital economy.
Source: https://mst.gov.vn/quoc-hoi-thong-qua-luat-tri-tue-nhan-tao-hoan-thien-hanh-lang-phap-ly-cho-ky-nguyen-so-197251210165544671.htm



![[Photo] The captivating scenery of the fragrant maple forest in Quang Tri](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765353233198_lan09046-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)
![[Photo] Explore the US Navy's USS Robert Smalls warship](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fvphoto.vietnam.vn%2Fthumb%2F1200x675%2Fvietnam%2Fresource%2FIMAGE%2F2025%2F12%2F10%2F1765341533272_11212121-8303-jpg.webp&w=3840&q=75)



































![[Video] The craft of making Dong Ho folk paintings has been inscribed by UNESCO on the List of Crafts in Need of Urgent Safeguarding.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/12/10/1765350246533_tranh-dong-ho-734-jpg.webp)





































































Comment (0)