Micronutrient deficiencies are one of the three major nutritional burdens facing Vietnam. These deficiencies negatively impact health and overall development. Knowing how to supplement these nutrients is crucial for preventing disease, promoting growth, and maintaining good health.
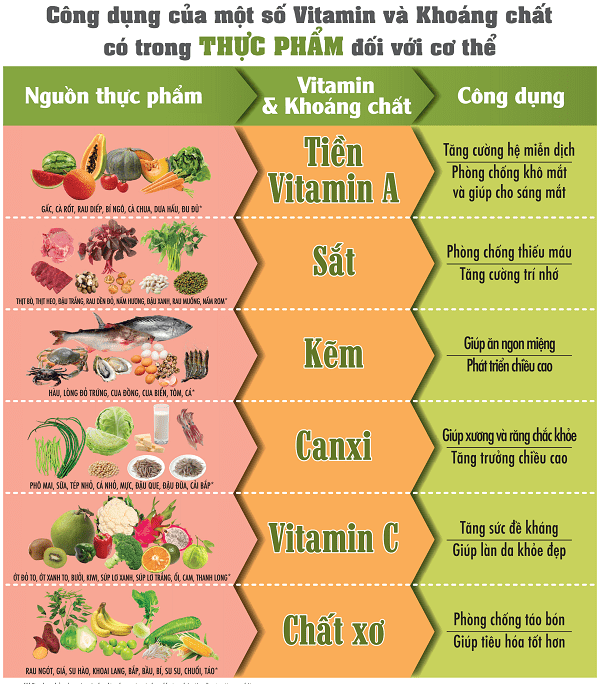
Table illustrating foods rich in micronutrients and their effects.
According to Dr. Nguyen Van Tien from the National Institute of Nutrition, Vietnam faces three nutritional burdens: malnutrition coexisting with micronutrient deficiencies, and overweight and obesity, along with an increasing trend of non-communicable diseases.
The reasons are due to the unbalanced diet of the population (consumption of too much meat, too few fruits and vegetables, etc.) and lack of physical activity.
Micronutrient deficiencies are major causes of stunted growth, negatively impacting health, physical development, stature, and intelligence. They hinder overall growth and development, reproductive capacity, and labor productivity.
Dr. Nguyen Xuan Tuan, a lecturer at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Vietnam National University, Hanoi , said there are many warning signs that the body is lacking nutrients, from simple symptoms like fatigue and cold hands and feet... to constipation, joint pain, and irregular heartbeat...
Calcium deficiency can cause numbness and tingling in the fingers.
According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), calcium helps strengthen bones and controls muscle and nerve function. A deficiency in calcium and vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis. Signs of severe calcium deficiency include numbness and tingling in the fingers, and an irregular heartbeat.
Adults need to consume 1,000mg of calcium daily, while women over 50 and men over 70 need 1,200mg. Milk, yogurt, cheese, fortified cereals, and dark leafy greens such as kale and broccoli are rich in this micronutrient.
Fatigue and bone pain due to vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D is crucial for bone health and helps prevent certain cancers. Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency are sometimes subtle, such as fatigue, bone pain, mood swings, muscle aches or weakness.
Prolonged vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteomalacia (softening of the bones), and more dangerously, cancer and other autoimmune diseases. The U.S. National Institutes of Health recommends that adults consume 15 mcg of vitamin D daily, and those over 70 years old consume 20 mcg.
This vitamin is abundant in fortified milk or yogurt, and fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel. Sunbathing for 10-30 minutes each day, a few times a week, also helps boost vitamin D levels in the body.
Potassium deficiency can cause muscle weakness and constipation.
Potassium helps maintain the function of the heart, nerves, and muscles, providing nutrients to cells while removing waste from the body. Along with sodium, potassium also plays a role in balancing blood pressure.
Short-term potassium deficiency can be caused by diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, antibiotic use, laxatives, or diuretics. People with potassium deficiency may experience muscle weakness, seizures or cramps; constipation; tingling and numbness in the extremities; irregular heartbeat or palpitations.
Some natural sources of potassium include bananas, sweet potatoes, avocados, milk, pumpkin, and beans. Adult men need 3,400mg, while women need 2,600mg of potassium per day.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause fatigue and a swollen tongue.
Vitamin B12 supports red blood cell and DNA production, and improves nerve transmission function. Vegetarians and vegans are at higher risk of deficiency because this vitamin is scarce in plants. Symptoms of deficiency include numbness in the legs, arms, or feet; difficulty maintaining balance; anemia; fatigue; weakness; swollen or inflamed tongue; memory loss, etc.
Adults need about 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 daily from fish, chicken, milk, and yogurt. Vegetarians should choose foods rich in this vitamin such as milk, breakfast cereals, and multivitamins.

Eat a variety of foods to ensure you get your daily micronutrients - Illustration
Iron deficiency causes rapid heartbeat and cold hands and feet.
Iron is essential for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Those at risk of iron deficiency include women during menstruation, growing children, pregnant women, and people following a vegan diet.
Iron deficiency in the body can easily lead to weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, pale skin, headaches, cold hands and feet, sore or swollen tongue, brittle nails, etc. Initial symptoms are often mild and difficult to notice, but they become more pronounced as iron reserves are depleted.
Eating fortified cereals, beef, oysters, beans, and spinach helps supplement iron levels in the body. Men and women over 50 need 8mg of iron per day, while adult women under 50 need 18mg per day.
Folate deficiency can cause diarrhea and a soft tongue.
Folate, or folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, is essential for women of reproductive age. Folate supports healthy fetal development and reduces the risk of birth defects related to the neural tube, brain, and spinal cord. People deficient in folate often experience fatigue, irritability, diarrhea, delayed development, and a soft tongue.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that women of reproductive age supplement their diet with approximately 400 mcg of folic acid daily. Foods that provide this nutrient include fortified cereals, beans, peanuts, sunflower seeds, eggs, and dark leafy greens.
Magnesium deficiency can cause loss of appetite and nausea.
Magnesium helps support bone health and energy production. Adults need 310-420mg of magnesium per day, depending on gender and age. Magnesium deficiency can cause loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and weakness. In more severe cases, it can also cause numbness, tingling, cramps, muscle spasms, irregular heartbeat, or coronary artery spasms.
Certain medications (antibiotics, diuretics) or health conditions (type 2 diabetes, Crohn's disease) can limit magnesium absorption. To increase magnesium intake, eat more almonds, cashews, peanuts, spinach, black beans, and soybeans.
Vitamin B1 deficiency can cause indigestion and diarrhea.
Your body may be deficient in vitamin B1, with symptoms such as indigestion, diarrhea, poor circulation, and anxiety. Foods rich in vitamin B1 include: grains, wheat, oats, meat, liver, and heart.
Vitamin A deficiency causes acne.
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to acne breakouts, pimples on the cheeks, arms, and thighs, dry hair, fatigue, insomnia, blurred vision at night, reduced sense of smell and taste, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Vitamin A is abundant in liver, egg yolks, butter, and cheese. In plants, vitamin A is found in dark green or yellow vegetables and yellow-red fruits. It is recommended to eat water spinach, mustard greens, amaranth, sweet potato leaves, pumpkin, mango, gac fruit, carrots, etc.
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteoporosis and tooth decay.
Excessive night sweats and hair loss in young children. Vitamin D deficiency disrupts calcium and phosphorus absorption, potentially causing acute or long-term disorders in the skeletal and dental systems of children, as well as rickets, delayed fontanel closure, enamel erosion, and osteoporosis in adults.
In particular, a deficiency in calcium and vitamin D can cause excessive sweating, hair loss around the temples, and restless sleep in young children.
Foods rich in vitamin D include milk, cod liver oil, egg yolks, avocados, etc.
Vitamin B deficiency affects the nervous system.
Vitamin B deficiency (B6, B9, and B12) can affect nerve endings under the skin, causing burning, itching, and numbness in the extremities. Additionally, depression, fatigue, exhaustion, anemia, and hormonal imbalances can also cause similar symptoms. Vitamin B2 deficiency can lead to mouth ulcers, lip sores, fatigue, and dry hair.
Foods rich in vitamins include dark green leafy vegetables, milk, meat, fish, and the bran layer of grains.
A simple way to prevent nutrient deficiencies is to maintain a balanced diet. Daily meals should be varied, combining many types of food; prioritize the selection and use of foods rich in micronutrients and foods fortified with micronutrients; exercise regularly and get proper sun exposure every day...
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/dau-hieu-canh-bao-co-the-dang-thieu-vi-chat-can-bo-sung-dinh-duong-kip-thoi-20241030062656785.htm















































































































Comment (0)